Thermal runawayThermal runaway refers to the rise in temperature that can cause the destructive result. The energy emitted or released during the process is accelerated by the increasing temperature. It is not a topic of any particular subject. Thermal runaway can occur in almost every field and subject related to the temperature. For example, ChemistryChemical or chemical engineering deals with the study of chemicals and their chemical reactions. It is further divided into organic chemistry and inorganic chemistry. Inorganic chemistry is a branch of the study of organic compounds. The term thermal runaway is known as runaway reaction. Otherwise, it is known as thermal explosions. The reaction rate increases rapidly with the rise in temperature resulting in thermal explosions, which it cannot control. It also leads to industrial explosions or leakage of chemical gases. 
The chemical reactions are of various types. Some reactions are endothermic, and some are exothermic. The endothermic reactions occur at lower energy, while an exothermic reaction occurs at high energy. The high energy reactions are more prone to thermal explosions and require safety measures and care, such as hydro-cracking and oxidation. Thermal explosions can also occur due to system or machine failure. ElectricalSometimes in high current applications, the low capacity electronic circuits are connected in parallel. It causes a problem of current hogging, which can damage the transistors and the devices. The current drawing power of each device varies due to difference in the device's resistance. Thus, it brings instability in the circuit leading to thermal runaway. It can be improved by balancing the load and matching the characteristics of the connected devices. Civil engineeringCivil engineering is a branch of study and design of construction related work, such as roads, bridges, buildings, etc. The thermal runaway can occur due to the heat dissipation in concrete materials used for construction buildings. It is an exothermic reaction, which occurs when the water and the concrete (particularly cement) are mixed. A chemical reaction occurs between the two substances, and the heat is released. It is also known as the heat of hydration. In low temperatures, the hydration is low, while in high temperatures, the hydration of cement is high. It directly impacts the strength of the material. Thermal runaway can be prevented by controlling the temperature of the surroundings, using chilled water at high temperatures, mixing liquid nitrogen, etc AstrophysicsIt is a branch of the space science or the study of space. The common phenomenon of explosion in stars is known as nuclear fusion, which occurs due to thermonuclear reactions and the gravitational force of the layers in space. 
For example,
ClimateThe rise in the number of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere increases the surface temperature of the Earth. These harmful gases not only lead to global warming but also pollute the air we breathe. The increase in global warming beyond human control is known as thermal runaway, also known as abrupt global warming. Microwave heatingMicrowaves are used for cooking and industrial processes. The rate of heating depends on the type of material and its dielectric constant. Every material has different dielectric constant, which is dependent on the temperature. Microwave heating is dangerous for thermal insulators due to the low heat exchange between the two materials (insulator and the material). SemiconductorsSemiconductors are materials with conductivity lying between conductors and insulators. It is widely used in the manufacturing of chips, electronic devices, etc. The leakage current in such devices increases with the increase in temperature. It is because the temperature increases the flow of electrons in the circuit, which increases the current flow. Thus, the power dissipation causes a further increase in the leakage current. The thermal runaway also occurs when the internal resistance of the semiconductor material decreases. It results in overheating (heating above the threshold) and allows more current to pass through such region. The temperature can further increase depending on the surrounding's temperature. The condition is similar to current hogging called a current filament. It is one of the reasons for the failure of semiconductor devices. Similarly, MOSFETs (Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistors) can have unstable regions due to the rise in temperature at the junction. The on-resistance of the MOSFETs increases with the rise in temperature. It is one of the advantages of MOSFETs that prevent it from current hogging when connected in parallel. BatteriesIn batteries, thermal runaway is often referred to as overheating. It is a rapid heating process due to the change in the chemical reactions inside the battery cells. It can cause a short circuit and affect the performance of the connected components. The temperature can rise due to the battery's exposure to high temperatures, internal resistance, etc. 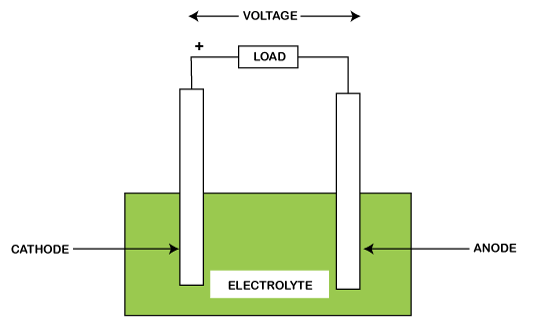
The increasing temperature may not always leads to damage. In certain conditions it occurs, when the heat generation exceeds the heat loss of the battery. Among various batteries, Lithium-ion batteries are more prone to thermal runaways. It releases more thermal energy. But, it can be improved by enhancing the battery's heat dissipation. The runaway in batteries can be prevented by storing them at an ambient temperature, preventing overcharging, and replacing the old stored batteries. Condition for thermal stabilityEffective care is required to prevent thermal runaway in various devices. Let's discuss the condition of thermal stability is BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistors). The circuit of BJT is shown below: 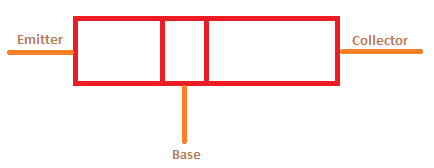
It consists of three regions, emitter, base, and collector. The collector region is doped lightly, while the base region is heavily doped. The rate of dissipation (waste) of the charge carriers should be larger than the generation (making) rate at the collector region. This condition prevents the circuit from any thermal runaway.
Next TopicJava Apple
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










