Tuberculosis DefinitionTuberculosis (TB) is a potentially deadly infectious disease that primarily affects the lungs but can infect other body parts such as the kidneys, spine, and brain. TB is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which spreads through the air when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or speaks. It is one of the top 10 causes of death worldwide, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). The symptoms of TB can vary depending on which part of the body is infected, but they often include a persistent cough that lasts for more than two weeks, coughing up blood, fever, chills, night sweats, weight loss, and fatigue. TB can be difficult to diagnose because its symptoms are similar to those of other respiratory diseases, and some people with TB may not have any symptoms. 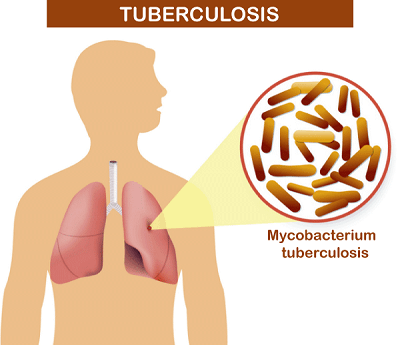
There are two types of TB: latent TB and active TB. 1. Latent TB: Latent TB means that a person has been infected with the TB bacteria but has no symptoms and is not contagious. However, the bacteria can remain dormant in the body and become active later, so people with latent TB need to be monitored and treated with antibiotics to prevent the disease from becoming active. 2. Active TB: Active TB is when the bacteria are actively growing and multiplying in the body, causing symptoms and making the person contagious. Active TB can be categorized further as pulmonary TB (affecting the lungs) or extra pulmonary TB (affecting other body parts). Pulmonary TB is the most common form of active TB, accounting for about 80% of cases. TB is a highly contagious disease that is not easy to catch. The bacteria are spread through the air and can be inhaled by someone in close contact with an infected person. However, it usually takes prolonged exposure to an infected person to become infected with TB. People at higher risk of contracting TB include those who live or work in crowded or poorly ventilated environments, those with weakened immune systems (such as people with HIV/AIDS), and those who have recently been in close contact with someone who has active TB. Ways to Prevent TuberculosisTuberculosis (TB) is a contagious disease that primarily affects the lungs but can also affect other parts of the body. TB is spread through the air when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or speaks, making it easy to contract the disease if you are in close contact with an infected person. Fortunately, there are several steps that you can take to prevent TB. Here are some of the most effective ways to prevent TB:
ConclusionTB has been a significant public health problem for centuries and continues to pose a significant challenge to global health. In the past, TB was commonly referred to as consumption or the white plague because of the emaciation and pallor that characterized its victims. TB was also responsible for many deaths in the past, and it played a significant role in shaping social and cultural attitudes toward illness and death. Efforts to control TB have been ongoing for decades, and progress has been made in reducing the burden of the disease. The WHO has set a goal of ending the TB epidemic by 2030 and significant investments have been made in research and development of new TB diagnosis, treatment, and prevention tools.
Next TopicWeather Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










