Ubuntu ServerIntroductionUbuntu server can be described as an open-source environment that does more than we might think. This operating system could do it all with its capability for serving as an internal enterprise server or for scaling every way up and out to match enterprise-level requirements. Ubuntu Server is an operating system of the server that is integrated by Canonical. It executes every major architecture such as POWER8, ARM64, ARM v7, x86-64, x86, and IBM System z mainframes by LinuxONE. Ubuntu OS is a server environment that everyone could use for the below and others: 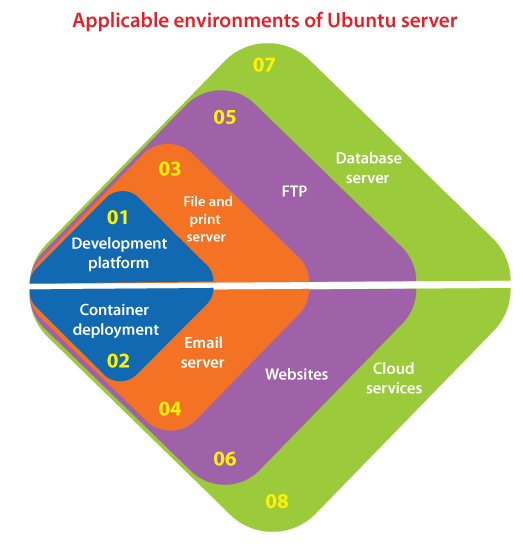
System RequirementsUbuntu server facilitates a minimalist and common base for various types of server applications like print/file services, email hosting, web hosting, etc. This version of the Ubuntu server supports 64-bit architecture:
Ubuntu server includes the following requirements:
One feature that enables the Ubuntu server very appealing is that it is cost-effective. So, anyone can easily download the copy of the current release of the Ubuntu server and expand it on as various machines as essential at zero cost. The current release includes necessary upgraded features to the platform. Now, the Ubuntu server supports ZFS (file system using capabilities of the built-in snapshot) and includes the initial production version of DPDK (Data Plane Development Kit) which is a group of drivers and libraries for faster packet processing. If we run a company and we are looking for a web server or file server to deploy, then the Ubuntu server can manage that. If we are an enterprise-level organization looking for scaling out a massive render farm, a Hadoop Cluster, or an OpenStack Cloud, then Ubuntu has us covered. Also, the Ubuntu server is certified for HPE Cloud, IBM, Joyent, Microsft Azure, and AWS for those who are concerning to operate with Ubuntu as any guest on the virtual platform. Several businesses do not have to worry about insufficient support just because the Ubuntu server is open-source software. Desktop and Server DifferencesThe Ubuntu desktop and the Ubuntu server uses similar apt repositories, enabling it only as easy for installing the server application over a desktop as over a server. One important difference is that a graphical platform applied for a Desktop is not installed for a server. It includes itself a graphical server, the graphical applications and utilities, and several user-supporting services required by all desktop users. Importance of Ubuntu ServerSome key points are mentioned as follows:
Affect of Ubuntu ServerUbuntu server impacts everyone from developers, IT pros, end-users, and CFOs. The conclusion for drawing is that the Ubuntu server is not just ruling the cloud. However, it would continue to be a great force for leading IT. Several users and organizations have become reliant on the cloud. So, the Ubuntu server would become more necessary. The platform creates rolling out clouds and containers incredibly simple fortunately for all IT pros. Release of Ubuntu ServerInitially, the Ubuntu server was published on 1st June 2010 and the version was known as Ubuntu 6.06 (Dapper Drake). Ubuntu images could be downloaded for a server platform or a desktop as with all the releases since. The server version uses the repositories similarly desktop. Hence, there has been stability between the releases since inception. Ubuntu server always has published sans GUI because of the repositories sharing (it's feasible to install a graphical platform). The server has walked a long way from its polite startings. The Ubuntu server was widely examined as an option for web servers, FTP, and mail when it was initially published. Competitors of Ubuntu ServerOn the Ubuntu server platform, the competition is passionate along with proprietary and open-source solutions available. The main competition is as follows for market share: 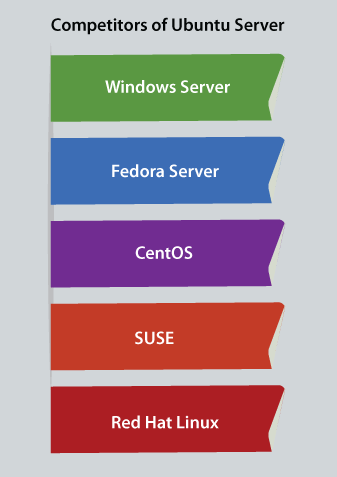
Note: Only Fedora and CentOS Server are free from the above servers.How do we start using Ubuntu Server?If we are going to install and use the Ubuntu server with bare metal (or via virtual hosts like Vmware or VirtualBox), we need to download the ISO image of the Ubuntu server and either burn the image onto DVD/CD or make a bootable flash drive (USB). Put the media inside the desired hardware and restart the system. The operating system's installation is an easy process like other operating systems. We will wish to log into our deployment dashboard (like Amazon EC2 Console) and proceed through the deployment process of the cloud service if the cloud deployment is our chosen route. No matter which way we take, beginning out with Ubuntu server is painless fairly. We will also be working with the command line. Hence, get up to speed using tools like apt-get. Backing UpWe should ensure that each data on our system has been backed up before installing the Ubuntu server. It is possible that we will have to re-partition our disk for making space for Ubuntu if it is not the initial time an OS has been installed on our computer. We should be prepared for losing everything on that disk anytime we partition our disk. It is possible that we will do some mistakes or something will go wrong at the time of partitioning. In the installation, the programs used are quite liable, most have look years of use. However, they implement destructive actions as well.
Next TopicUbuntu Wallpaper
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










