Ubuntu Show Hidden FilesIn the Ubuntu system, there are several hidden files which include the user application files and configuration files. Also, we can hide our files in our system if we are sharing them with a few other persons or because of any reason. Although, remember that hiding a file doesn't protect our privacy because anyone can see the hidden files. Hiding files only makes the files hidden for the regular user listing or exploring the files. It also prevents the directory from being messy. In this article, we will explain how to create and view hidden directories and files in the Ubuntu operating system. Important: The GUI and command-line procedure explained here are tested on the 20.04 LTS version of Ubuntu.Create hidden directories and files in UbuntuWe can create hidden directories and files in Ubuntu by using the following methods:
Using the command line methodSimply, we need to add a dot sign (.) at the starting of the file name to hide a directory or file in Ubuntu. For example, we have created a file which is named myfile.txt. We will need to rename this file to .myfile.txt to hide the file. We can run the following command for renaming the file: The file will be hidden after renaming it. Now, if we view this directory with the help of the ls command, we cannot see the file. 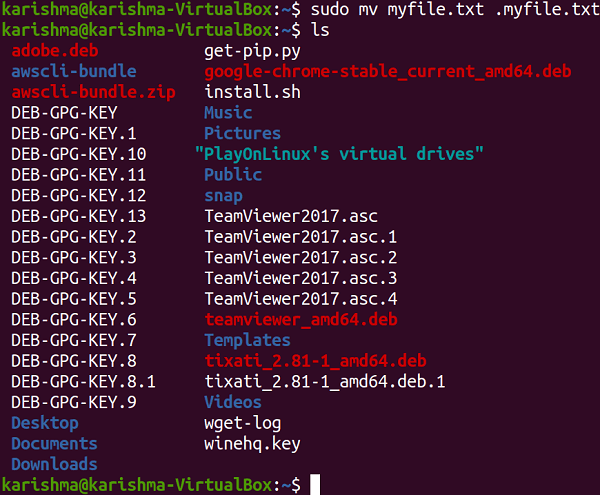
Using the GUI methodWe can hide our files by Linux File Manager if we graphically prefer working. All we need is to only rename a file and add a dot sign at the starting of the file name. For example, to hide a file called myfile.txt, right-click on it, and select the Rename option. Then, we need to add a dot sign before the file name as we can see in the following screenshot, and then we will click on the Rename option. After renaming, it will be hidden. Now, if we view the directory within the File Manager, we cannot see this file. 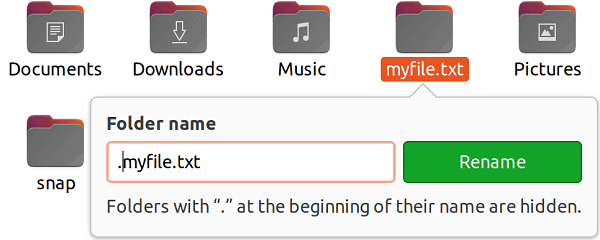
View hidden directories and files in UbuntuWe can view hidden directories and files in Ubuntu by using the following methods:
Using the Command Line MethodWe can use the following command in the terminal window to view hidden directories and files in the Ubuntu system: 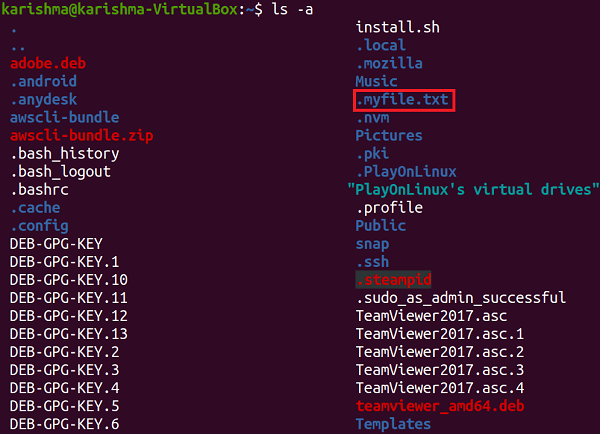
This command will show every hidden file (whose title begin with a dot sign) in our current terminal window. Using the File Manager Toolbar MethodTo view hidden directories and files using the Linux File Manager, we need to press the icon, i.e., three horizontal bars at the upper right side of the file manager. A drop-down menu will display up by doing so. From there, press the check box, i.e., Show Hidden Files. It will display every hidden file (whose title begin with a dot sign) in our opened directory. 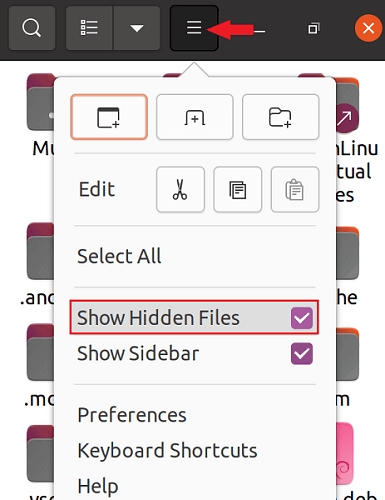
Using the Keyboard Shortcut MethodAlso, we can view hidden files with the help of keyboard shortcuts. We need to open the directory in our File Manager to view any hidden file residing in that directory. Then, use the keyboard shortcut, i.e., Ctrl+H to show the hidden files. We can use similar keyboard shortcuts for hiding them again. Unhiding Directories and Files in Ubuntu SystemWe can unhide the directories and files in the Ubuntu system by using the following methods:
Using the Command Line MethodOnly, we need to delete the leading dot sign from the name of a directory or file to unhide them. For example, we have created a hidden file named .myfile.txt. We can use the following command in the terminal window to make the file unhidden: 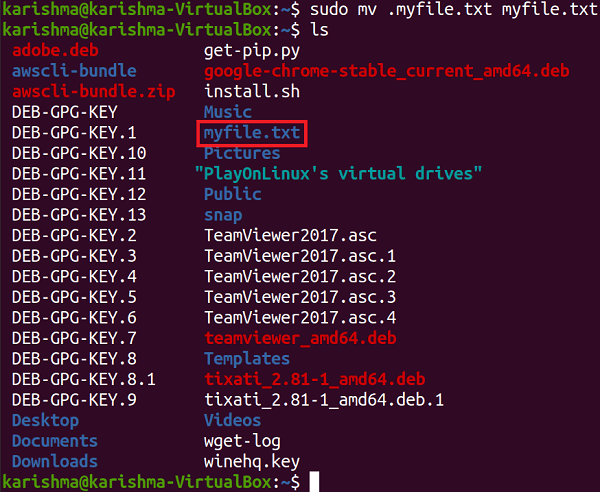
The above command will rename the .myfile.txt file to myfile.txt and now it will be unhidden. Using the GUI MethodTo graphically unhide a file, we need to open the File Manager in our Ubuntu operating system. Click the Ctrl+H shortcut keys or see the Show Hidden Files option for viewing every hidden file. Choose our hidden file and with the help of the right-click menu, delete the leading dot sign from its title. For example, if our hidden file is .myfile.txt, then it should be re-titled to myfile.txt. 
Next TopicUbuntu Super Key
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










