Ubuntu vs. WindowsIntroduction to WindowsCommonly, Microsoft windows are referred to as simply Windows. These windows are a collection of many families of the proprietary graphical operating system, each of which is marketed and developed by Microsoft. All family caters to a particular sector of the computer industry. Many active families of Microsoft Windows include Windows IoT and Windows NT. These might envelopes subfamilies (for example, Windows Embedded Compact or Windows Server). Various different families of Microsoft Windows include Windows Mobile, Windows Phone, and Windows 9x. On 20 November 1985, Microsoft announced an operating platform named Windows as a graphical shell of an operating system for MS-DOS in feedback to the developing interest in GUIs.
Family tree of WindowsThe family trees of Windows are categorized on the basis: By the role of marketingMicrosoft (which is a windows developer) has registered various trademarks, all of which specify a Windows operating system family that targets a particular sector of the computing industry. The below families of windows were being developed actively as of 2014: 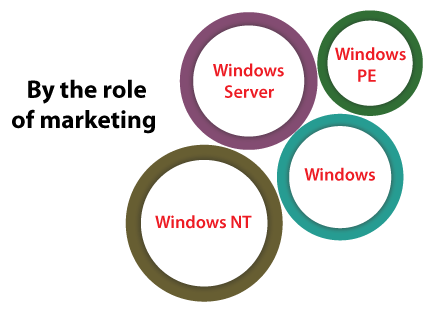
Windows IoT (Windows Embedded previously): Microsoft initially expanded Windows CE as a normal purpose OS for all devices which were extremely resource restricted to be known as a full-fledged computer. However, Windows CE version was eventually known as Windows Embedded Compact and it was developed upon Windows Compact trademark. It also associates Windows Embedded Standard, Windows Embedded Professional, Windows Embedded Automotive, Windows Embedded Handheld,, and Windows Embedded Industry. The below families of Windows are no longer being expanded: 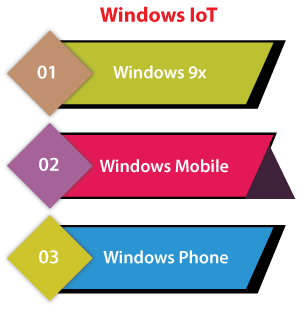
The Version History of WindowsCollectively, the word window specifies any for every of various Microsoft operating system product generation. Generally, these products are divided as follows: Early Versions of WindowsThe windows history dates return to 1981 during Microsoft began to operate on a program known as "Interface Manager".
This version is not a fully operating system; instead, it extends MS-Dos.
Windows 2.0 version was published in December 1987. It was more famous than its predecessor. It provides several developments to the Memory management and user interface. Windows 2.1 version was published in two distinct versions which are windows/386 and windows/286. Besides, Windows/286 executes on both Intel 80286 and Intel 8086 processors. Windows 3.xWindows 3.0 version was published in 1990. This version developed the design mostly due to loadable virtual device drivers and virtual memory that permit windows for sharing arbitrary devices among the applications of Multi tasked DOS. The applications of windows 3.0 can execute inside a protected mode which provides them authorization to various memory megabytes without any obligation for participating in the scheme of software virtual memory. They execute in a similar address space in which the partitioned memory gives a protection degree. Also, Windows 3.0 featured development to do user interface.
Windows 3.2 version was published in 1994. It was an upgraded version of the 3.1 version of the Windows Chinese version. Windows 9x
Windows 95 version was published in 1995 on August 24. Windows 95 defined support for native preemptive multitasking, plug and play hardware, 32-bit applications, long file names, and given increased stability on its predecessor. Windows NT
A new development team in Microsoft started work over a revamped version of the OS/2 operating system of Microsoft and IBM which is called NT OS/2. Windows XPWindows XP is the major Windows NT version and it was published on October 25, 2001. The windows XP introduction aimed at unifying the consumer-oriented series of Windows 9x along with the architecture defined by Windows NT Windows XP would define a redesigned user interface streamlined Internet Explorer 6, networking and multimedia features, int�gration with .NET Passport services of Microsoft, modes for helping give compatibility with the software developed for previous Windows versions, and functionality of remote assistance. Windows VistaWindows Vista was published on November 30, 2006. It included so many new features through a user interface and redesigned shell to necessary technical changes along with a specific focus on features of security. This version was available in a wide variety of editions and it was subject to a few criticisms like performance drop, criticism of newer UAC, longer boot time, and stricter license agreement. Windows Server 2008 (a server counterpart of vista) was published in 2008. Windows 7
Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7 were published on July 22, 2000, 9 RTM (short for release to manufacturing) during the former was published on October 22, 2009. Windows 8.1 and 8This version of Windows is the successor of Windows 7 and it was published on 26 October 2012. Windows 10Microsoft released Windows 10 on 30 September 2014. This version is the successor of Windows 8.1. It was published on 29 July 2015 and defines shortcomings inside the user interface initially introduced in the 8 versions. Various changes on the personal computer include start menu returns, the ability to execute Windows store apps in windows over the desktop instead of full-screen mode, and a virtual desktop system. Multilingual supportThis type of support has been created into windows since the 3.0 version of windows. The language for the interface and keyboard can be modified by the language and region Control Panel. Elements for each supported input language like input method editors are installed at the time of Windows installation automatically. Platform supportThe version Windows NT contains support for various distinct platforms before the x86-based PC became dominant inside the professional world. The 4.0 version of Windows NT and its predecessor provided support for MIPS R4000, DEC Alpha, and PowerPC. Windows CEOfficially, Windows CE is called Windows Embedded Compact. It is a version of windows that executes on minimalistic computers such as satellite navigation systems and a few mobile phones. Xbox OSIt is an unofficial name provided to the Windows version that executes on the Xbox One. Xbox One is a more particular implementation with the focus on virtualization because it is three OSes executing at once. Microsoft updates this version of OS every month. These updates could be downloaded through the Live Service of Xbox. Also, the system of Xbox One permits backward compatibility along with Xbox 360. The system of Xbox 360 is also backward compatible with the actual Xbox. An alternative implementation of WindowsThese alternatives are: 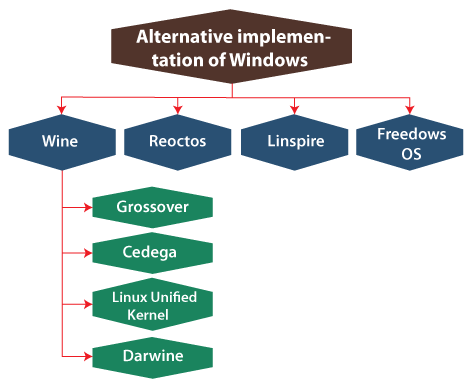
1 Wine: An open-source and free Windows API implementation, permitting one to execute several applications of Windows on x86 based environment including macOS, Linux, and Unix.
2. ReactOS: It is an open-source operating system intended to execute similar software like Windows. It is original developed for simulating the 4.0 version of Windows NT, but now focusing on the compatibility of Windows 7. 3. Linspire: It is a commercial Linux distro that is initially developed with the aim of executing major software of Windows. 4. Freedows OS: It is an open-source experiment at making a clone of Windows for x 86 environments, intended to be published upon the GNU General Public License. In 1996, it was started by Reece K. Sellin, but the project was never successful and complete. It was declined in 2002.Introduction to UbuntuUbuntu is a distribution of Linux which is based on Debian. Mostly, it combines the open source and many free software. Officially, Ubuntu is released in three essential editions which are mentioned as follows:
All of these editions can execute in any virtual machine or ver the computer alone. Ubuntu is a popular operating system for cloud computing with OpenStack support. The desktop of Ubuntu (default) has been GNOME as of the 17.10 Ubuntu versions. Ubuntu is released every six months with many releases of LTS every two years. The most recent release of LTS is Focal Fossa (20.04) since 2020 22 October. The current standard release is Groovy Gorilla (20.10). It is providing support for nine months. This Linux distribution is proposed by canonical and a team of other developers which is based on a model called meritocratic governance model. Background of UbuntuUbuntu is designed on the infrastructure and structure of Debian. It combines Linux server, desktop, and discontinued tablet and phone operating system system. Predictably, Ubuntu publishes updated versions every six months and each of the publication get no cost support for nine months along with beneficial low-risk bug fixes substantially, high-impact bug conservative and fixes, and security fixes. The first release was announced in 2004 October. The packages of Ubuntu are based on packages through the unstable Debian branch which could be synchronized every six months. These distributions apply the tools of package management (like Ubuntu and APT Software) and deb package pattern of Debian. Essentially, Ubuntu and Debian packages are not binary compatible with each other. However, the packages might require to be recreated via the source to be applied in Ubuntu. Several Ubuntu developers are the managers packages in Debian also. Ubuntu is currently financed via Canonical Ltd. Canonical and Mark Shuttleworth published the creation of Ubuntu foundations on 8 July 2005 and provided starting US$10 million funding. Ubuntu announced the developers support for third-party cloud management platforms on 12 March 2009 like those applied in Amazon EC2. Features of Ubuntu
Security of UbuntuUbuntu by default provides security. User programs run with low privileges and it can't corrupt the operating system or other files of users. The sudo tool is applied for giving privileges to implement various administrative operations, which permit the root account for remaining locked. It also supports inexperienced users through opening security holes or enabling system changes for better security. Polkit is being highly implemented over the desktop. By default, most of the ports of a network can be closed for avoiding hacking. A firewall (built-in) permits all the users who are installing network servers for managing access. Ubuntu also provides support to complete disk encryption and encryption of a private as well as home directories. Installation of UbuntuThe requirements of a system change among Ubuntu products. A PC using a 2 GHz dual-core processor, 25GB of free disk space, and 4GB of RAM is suggested for the Ubuntu 20.0 desktop release of 4 LTS. There are several other distributions of Ubuntu such as Xubuntu and Lubuntu for less strong computers. Ubuntu provides support for the architecture of ARM. It is also available on the Power ISA during the earlier architecture of PowerPC was at an individual point supported unofficially, and now newer CPUs of Power ISA are supported. Officially, AMD64 architecture (x86-64) is supported.
Variants of Ubuntu
The Ubuntu desktop is the version suggested for almost all the users. It is simply named as Ubuntu and formally named as Ubuntu Desktop Edition. Official distributionsMany flavors and versions of Ubuntu simply install a distinct group of default packages as compared to the standard Ubuntu desktop. Because these versions distribute similar package repositories, similar software is present for all of them. Some of the major distributions and their description are discussed below: 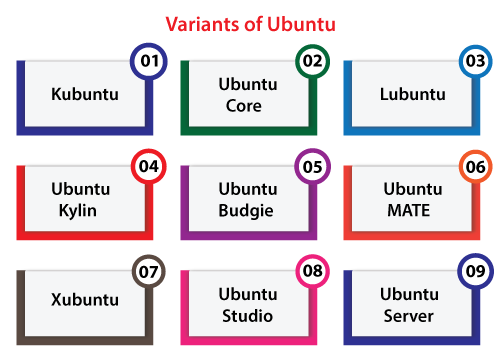
Kubuntu: It is a version of Ubuntu that is applying a KDE interface rather than Unity and GNOME interfaces applied by Ubuntu desktop. Ubuntu Core: It is a version of Ubuntu concentrated over embedded and IoT systems. It doesn't use the package manager of classical apt unlike many other variants but relies over the Snap packages entirely. Lubuntu: This distribution is a version of Ubuntu that is more energy-efficient, lighter, and less resource-hungry. It applies the LXqt desktop platform (applied LXDE before standard 18.10). Ubuntu Kylin: It is a type of Ubuntu focused over the Chinese market. Ubuntu Budgie: It is a standard of Ubuntu using Budgie.
Xubuntu: It is a version of Ubuntu with Xfce. This version is intended for applying on less powerful systems or those who disclose the highly capable desktop platform on the faster systems and applies GTK+ applications mostly as well. Ubuntu Studio: Ubuntu Studio works according to Ubuntu. It is providing many open-source applications for the development of multimedia focused at graphics, audio, and video editors. Ubuntu Server: Ubuntu contains a server edition that uses similar repositories of APT to the Ubuntu Desktop Edition. Main differences among them are the X Window environment's absence inside the default installation of any server edition (but, one could easily be installed including KDE, Unity, GNOME, or Xfce) and a few changes to the process of installation. It provides support hardware virtualization. Also, it could be executed within a virtual machine either inside a hypervisor or host operating system such as Kernel-based Virtual Machine, Oracle, QEMU, Microsoft Hyper-V, VMware ESXi, Citrix XenServer, or other IBM PC compatible emulator or virtualizer. Difference between Ubuntu and WindowsSome of the key differences between Ubuntu and Windows operating system are explained below in a tabular format:
Conclusion
Both Ubuntu and Windows have their features, drawbacks, and user community. The tester and developer community prefers to use Ubuntu software.
Next TopicDifference Between
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










