UPS - Uninterruptible Power Supply
Today, a continuous power supply is the basic necessity of humans. The application of electricity is wide and seen in all industries, domestic appliances, and hospitals. If a power supply is hindered, it causes a delay in production and inconvenience that causes loss to the organization. Hence, it is necessary to have an alternative power supply to avoid such a situation in case of power failure. Therefore, the Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) is invented to be used in a power failure. It saves everyone from the losses that occur if there is a sudden power disruption. What is Uninterruptible Power Supply?UPS, also known as the Uninterruptible Power Supply, is an electrical device used to maintain a continuous power supply to any electrical device in case of a power failure. UPS saves us from the power surges by continuously establishing a connection to the computer and keeping it running even after power failure. It differs from the other power backup devices like batteries and supercapacitors. The UPS can supply power only for a short period sufficient to keep the device safe or facilitate it to shut down properly to avoid damage. The Main Components of a UPS SystemThe four main components of the UPS system are listed below:
How Does a UPS Protect Computer?Certain specifications are necessary for the computer to function continuously, and deviation in these specifications causes the power supply to fail, and the computer stops working. The use of a UPS is to protect the data and any work on the computer while there is a power problem. These power problems are:
Different types of Uninterruptible Power SupplyUPS system accommodates a complete range of applications using its three types which cater to the demands of enterprises and the customers. The three types are;
All three devices operate during power failure; however, they may differ in their operations. 1. Standby UPS: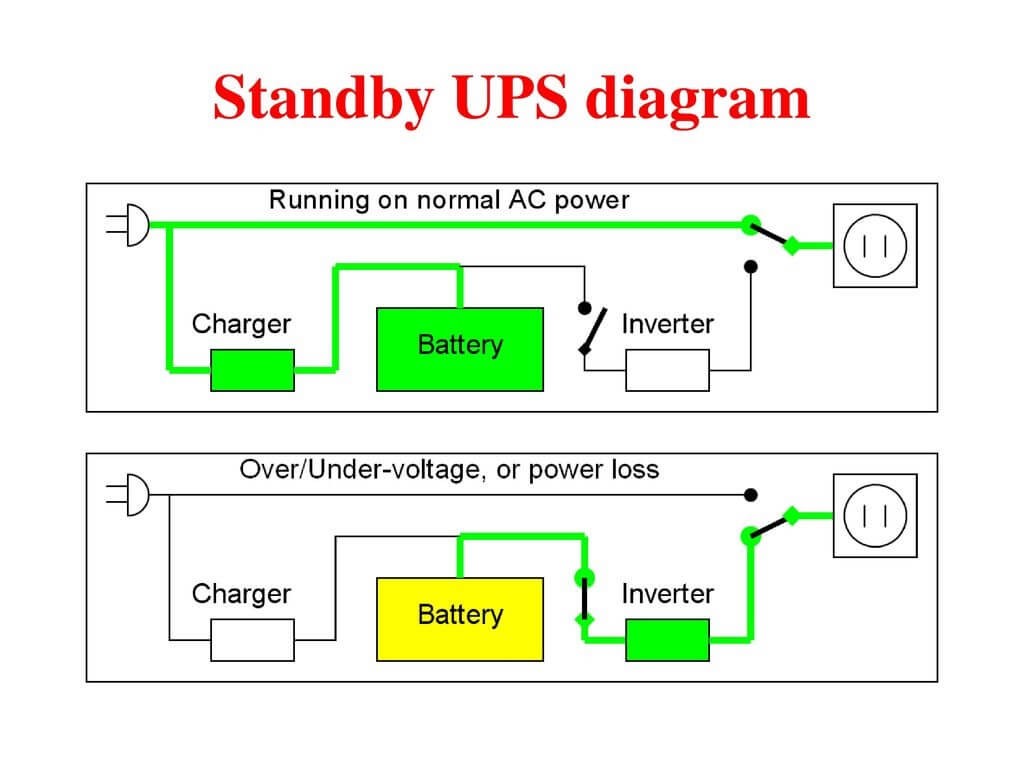
Standby UPS is a type of UPS that is an offline unit. It can detect an electrical failure and automatically switches to the battery-powered mode. Through a direct AC connection, in normal conditions, hardware receives utility power. Common uses of standby UPS include computers, modems, VoIP equipment, etc. Standby UPS is the least expensive among the three UPS types. 2. Line Interactive UPS: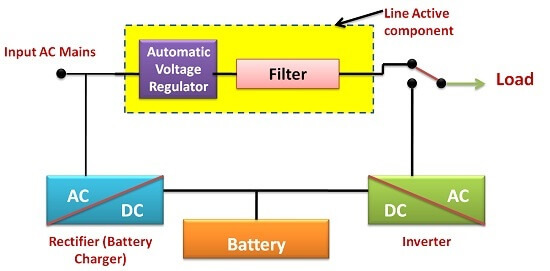
UPS is capable of regulating voltage automatically; it also responds to the conditions of high and low voltage. It supports the system at the time of outages. During outages, it converts the battery power into AC for the continuation of the operations. IT Applications of Line Interactive UPS System: The line interactive system safeguards sensitive equipment during burnouts or blackouts. In this system, units are expensive as compared to the standby system. However, these are cost-effective when compared to the online UPS system. It protects in situations such as short-term power failure or low voltage conditions. Additionally, in cases of a long outage, the battery power of the line interactive UPS system allows the device to shut down safely. 3. Online UPS: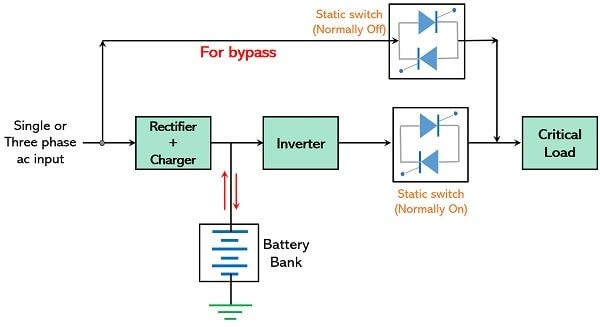
Double or Delta conversion technology is used in the Online UPS system. AC power is carried to the rectifier to become DC power. Hence the network does not receive electricity from the AC outlet directly. It is then carried to the inverter. Afterward, its inversion takes place to AC, and this power is delivered to the equipment. The online UPS system provides continuous clean power to the equipment. Online UPS system costs more as compared to the standby and line interactive UPS systems. Online vs Line Interactive UPSKnowing the difference between the online and line interactive UPS is a must before buying it as an alternative for outages. The line interaction UPS is a version of basic standby UPS with an autotransformer. Comparison of Different Types of Uninterrupted Power Supply
Advantages and Disadvantages of UPSAdvantages:
Disadvantages:
Choosing an Uninterrupted Power SupplyWe may sometimes need to buy a new UPS or replace the existing one. In such conditions, we must know how to choose an appropriate UPS for our devices. Choosing a proper uninterrupted power supply is extremely important, and it depends upon the load required and battery autonomy.
Other FactorsFollowing are some of the other factors that must be considered before choosing a UPS:
Alternatives of UPSThere are many alternatives to the UPS which will help keep your computer running during power failure. Some of these are discussed below in brief:
Comparison of UPS with AlternativesThere are many alternatives to supply power to devices when power surges, spikes, or power loss occurs. However, UPS has advantages over some of the alternatives. Therefore, it can be used if the requirement of the system matches the features of UPS. UPS VS GeneratorGenerators are useful to keep the device running for a long period of time, whereas UPS keeps the device running for a short period of time. The reason behind this is that the UPS is powered by batteries, whereas the generator is powered by fuel. Another difference between UPS and the generator is that the UPS starts after the power is lost, and however, the generator takes time to start. Therefore, UPS is useful when a continuous power supply is required and generators can be used where power loss is often and for a long time. UPS VS Surge ProtectorsThe use of surge protectors is in conditions such as voltage spikes, power surges, etc. However, Suppressors or power surges cannot be used during power outages and main supply power cuts. UPS, unlike surge protectors, work in the condition of supply cut from the mains. UPS VS InvertersPower inverters are used for the conversion of the direct current to the alternating current. These take input as the DC and produce output as AC. One or more batteries are used to store power for the power inverters to function at the time of power failure. Using power inverters during power failure will cause a delay in the power transfer from one source to another. AVRs, also known as automatic voltage regulators, are used to control fluctuations in the voltage. It is used in power converters and inverters. Single Phase and Three Phase UPS SystemSingle-phase UPS: Single-phase UPS is the one that has single input and output. It requires only conductor and neutral wire to complete the circuit along with one sine waveform. The 1-phase type of uninterruptible power supply is used for installations that are small such as network switches, rack-mounted servers, and telecoms or computer systems. In addition to this application, it can also be used for devices that require a three-pin plug. Three-Phase UPS: This type of UPS system is a 3-phase system. Three-phase UPS utilizes three out of phase sinewaves for providing continuous power to load, and these waveforms are spaced at 120-degree to each other. Hence, a three-phase system requires three conductors and a neutral wire, and it supports single-phase and three-phase output. Applications of three-phase UPS generally include large installations such as industrial applications, data centers, hospitals, and protection of lifts, pumps, and fans. Such equipment needs to be protected as they have motors. Comparison of Single-Phase and Three-Phase UPS
The comparison of the single-phase and a three-phase UPS is presented above. It will help evaluate both and choose the UPS according to the requirement. Working of a Transformer-based and Transformer-free UPSThe use of a transformer in a UPS system is to step up the levels of AC voltage, provide protection during load disruption and galvanic isolation. In the traditional type of UPS. The flow of power to the output is via rectifier, inverter, and transformer. The operation of the transformer-less UPS is similar to that of the transformer-based. However, insulated-gate bipolar transistors (IGBTs) are used in transformer-free UPS. These are advantageous as they eliminate the need for a transformer after the inverter. They are also capable of dealing with high voltages, improving the efficiency of the uninterruptible power supply. Although advancement in technology has increased the energy efficiency of transformer-based UPS, transformer-less UPS systems are extremely beneficial for lower load conditions. Transformer-based UPS are now 95-96% efficient. Advantages of Transformer-based UPSThe transformer-based UPS is advantages as in such a system, the points of failure are fewer. Additionally, it provides separation between input and output, known as galvanic isolation. The galvanic isolation provides protection from spikes, surges, and electrical noise if these are generated. Transformer-based UPS is the choice for 100 KVA and above. It is generally used for large installations. Some of the benefits of the transformer-based UPS are listed below:
Advantages of Transformer-less UPSTransformer-less UPS is beneficial because it doesn't require a bulky and large transformer. Therefore, the heat generated is also less as compared to the UPS with a transformer. Moreover, transformer-less UPS is cost-effective as the transformer costs more. Some of the other benefits of a UPS without a transformer include the following:
Next TopicIIT - Indian Institute of Technology
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










