VBA ArraysThe array is a memory location which is capable of storing more than one value. All the values must be of the same data type. If you want to store a list of the same data type in a single variable, you can use an array to store. By using an array, you can mention the related values by the same name. You can use the subscript or an index to tell them apart. The individual values are referred to as the elements of the array. They are contiguous from index 0 to the highest index value. Types of ArrayThere are two types of an array in VBA, such as: 1. Static: static displays have a fixed, pre-determined number of elements that can be stored. You cannot change the size of the data type of a static array. These are very useful when you work with known entities such as gender, number of days in a week, etc. For example: To create a static array, execute the following code, such as: Step 1: First insert a Command button on your worksheet. Step 2: Then, you will get a code window and add the following code. 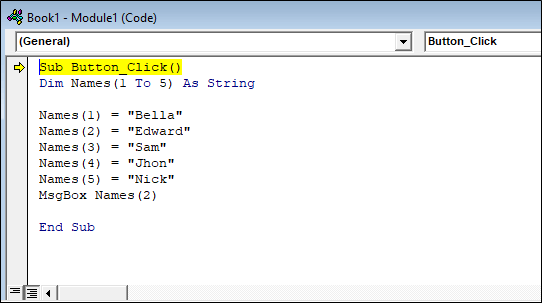
Step 3: Click on the Command button, and you will get your output as shown in the below screenshot. 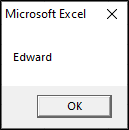
2. Dynamic: The dynamic array does not have a fixed, pre-determined number of elements that can be stored. These are very useful when working with entities that you cannot pre-determine the number. For example, To create a dynamic array, execute the following steps, such as: Step 1: This time, we are going to read the names from the sheet, such as:>
Step 2: Click on the placed Command button on your worksheet and add the following code lines. 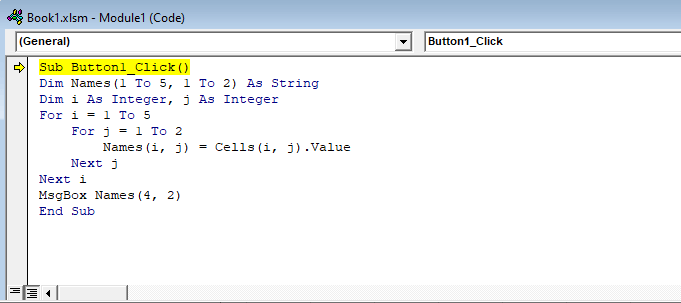
Step 3: Click on the Command button, and you will get your output as shown in the below screenshot. 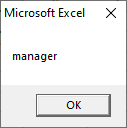
ReDim StatementReDim statements are used to declare the dynamic array variables and are also used to allocate or reallocate the storage space. Syntax of ReDim ReDim statement syntax has the following parts, such as:
The ReDim statement is used to size or resize a dynamic array which is already declared by using a private, public or Dim comment with empty parentheses. You can use the ReDim statement frequently to change the number of an element and the dimensions in an array. You cannot declare an array of one data type. If the array is contained in a variant, then the type of elements can be changed by using an As type. If you are using the preserve keyword, there is no permission to change the data type. Array Dimensions1. One Dimension: the array is used only one index in the one dimension. For example, many people of each age. The only requirement to specify an element is an age. That element holds the count. Dim agecount (100) As UInteger Above example declares a one-dimensional array of age counts form 0 to 100. 2. Two Dimension: the array uses two indexes in the two-dimension. For example, several students in each class. It requires both the number of classes and number of students in each class. Dim studentscounts (50, 5) As Byte Above example declares a two-dimensional array, student counts 1 to 50 and class 1 to 5. 3. Multi dimension: the array is used more than two indexes in the multi-array. For example, the temperature during day time (29, 30, 32). Dim temperature (29, 30, 32) As single Advantages of ArrayThere are some advantages of the array, such as:
VBA Array ExampleLet's start from a simple application. This application occupies an excel sheet with data from an array variable. We have required the following things in this example,
Let's execute the following steps, such as: Step 1: Create a new workbook.
Step 2: Add a Command button into the sheet. 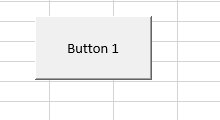

Step 3: Save the excel file.
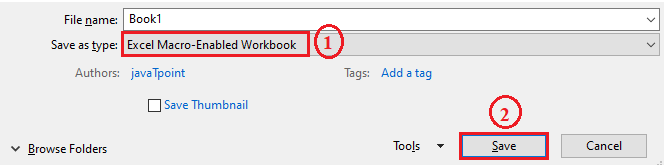
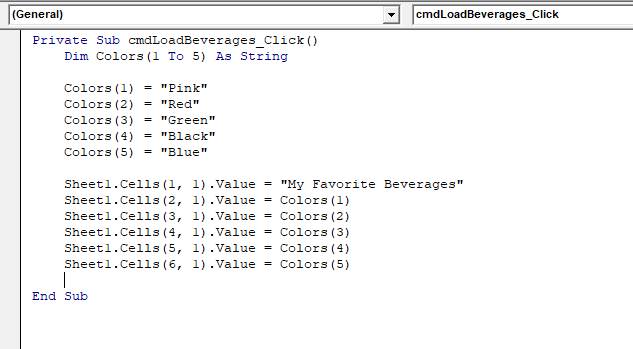
Step 4: Write the code on the code window.
Testing the ApplicationStep 1: Select the Developer tab. Step 2: And turn off the Design Mode button. 
Step 3: The indicator is, it will change into a white background from the greenish coloured background, as shown in the below screenshot. 
Step 4: Click on the Load Beverages button. Step 5: It displays the output of the code, as shown in the following screenshot. 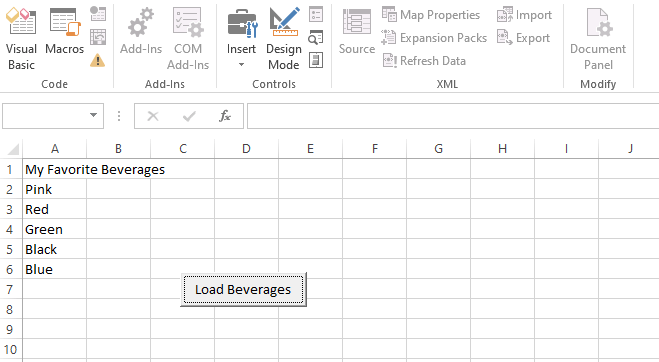
Next TopicVBA Arithmetic Operators
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share