Top 30+ Most Asked Verilog Interview QuestionsFollowing is the list of most frequently asked Verilog interview questions and their best possible answers. 1) What is Verilog?Verilog is a Hardware Description Language (HDL) used for describing a digital system such as a network switch, a microprocessor, a memory, or a flip-flop. Verilog is mainly used to verify analog circuits, mixed-signal circuits, and the design of genetic circuits. It is also used in the design and verification of digital circuits at the register-transfer level of abstraction. Verilog supports a design mainly at the following three levels of abstraction:
2) Who is the founder of the Verilog programming language?Verilog was introduced by Prabhu Goel, Phil Moorby, Chi-Lai Huang, and Douglas Warmke between late 1983 and early 1984. 3) What is VHDL? / What is the full form of VHDL in VLSI?VHDL is an acronym that stands for Very high-speed integrated circuit Hardware Description Language. It is a programming language used to describe circuits in digital systems and model the digital system by using dataflow, behavioral and structural style of modeling. 4) What are the different variants of the VHDL?VHDL is defined by IEEE standards and has mainly two common variants:
5) What are the main usages of VHDL?Following are the main usages of VHDL:
6) Are Verilog and VHDL the same?Verilog and VHDL are not identical. They are different, and the main difference between Verilog and VHDL is that Verilog is based on C language while VHDL is based on Ada and Pascal languages. 7) What is the difference between Verilog and VHDL?Difference between Verilog and VHDL: Although both Verilog and VHDL are Hardware Description Languages (HDL) used to describe digital system hardware such as microprocessors and flip-flops. These languages are different from common programming languages. Let's compare them to see the main differences between them:
8) What are HDL simulators?HDL simulators are software packages that are used to simulate expressions written in one of the Hardware Description Languages, such as Verilog, VHDL, SystemVerilog. 9) What is the difference between blocking and non-blocking in Verilog?There are two types of procedural assignment statements in Verilog known as blocking and non-blocking. You can identify them as they use different assignment operators represented by the symbols = and <=.
10) What do you understand by Verilog full case statements and Verilog parallel case statements?There are two types of case statements in Verilog.
Verilog full case statements The Verilog full case statements are statements in which binary patterns of every potential case expression can match either a case item or default. If your considered case statement does not involve a case default and is likely to discover a binary case expression that does not match any of the defined case items, the case statement would not be considered full. Verilog parallel case statements A parallel case statement is a statement where it matches a case expression, just one case item. If you can find a case expression that would fit more than one case item, the matching case items are called 'overlapping case items,' and the case statement would be not parallel." 11) What are the main differences between Task and Function in Verilog?Following is a list of main differences between a Task and a Function in Verilog:
12) What is the full form of PLI? Why is it used?PLI is an acronym that stands for Programming Language Interface. It is a mechanism that facilitates interfacing between Verilog programs and programs written in C language. It also provides a mechanism used to access the internal databases of the simulator within the C program. Using Verilog syntax, the users can utilize PLI to implement difficult system calls. It also provides the advantage of both the parallel and hardware-related features of Verilog and the sequential progress of a C program. 13) What do you understand by Sensitivity list?The sensitivity list is used to specify that when you make changes in any one of the elements in the list change, begin end statement inside that always will get executed. 14) What is the difference between == and === in Verilog?Following is a list of main differences between == and === in Verilog:
15) What do you understand by $monitor, $display, and $strobe?The $monitor, $display, and $strobe are commands with similar syntax and show text on the screen while running a simulation. These commands are typically less convenient to use than waveform tools, such as cwaves. The $display and $strobe command appear once each time you execute them, but the $monitor command is used to display each time you change one of the parameters. The main difference between the $display and the $strobe command is that the $strobe command is used to display the parameters after the current simulation time unit. On the other hand, the $display command displays the parameters when you execute it. In these commands, the format sequence is similar to C/C++ and sometimes contains format characters. The most commonly-used format characters are "%d" for decimal, "%h" for hexadecimal, "%b" for binary, "%c" for character, "%s" for string, "%t" for time, and "%m" for hierarchy level. 16) What is the difference between $monitor and $display?The $monitor and $display are system functions or command and are used to see the test bench results. Following is a list of some key differences between $monitor and $display.
17) What are the main differences between Wire and Reg?Key differences between Wire and Reg
18) What is the process to execute blocking and non-blocking assignments?There is a simple process to execute blocking and non-blocking assignments. To execute blocking assignments, we have to use a simple process of evaluating the right-hand side equation and updating the left-hand side expression without interference from another Verilog statement. A function of a blocking assignment is to block trailing assignments until after the completion of the current assignment. On the other hand, the process of executing non-blocking assignments needs two steps:
19) What do you understand by continuous assignment?In Verilog, the continuous assignment statements are used to model combinational logic. By combinational logic, we mean the digital logic implemented by Boolean circuits. In combinational logic, the output is a pure function only of present inputs. The combinational logic is completely different from sequential logic, where the present input depends on the present input and the past inputs. The continuous assignment statements are implemented with an assigned statement or with a wire declaration. A continuous assignment is used to drive values to the net. The left-hand side can be scalar, vector net, or concatenation of both, while the right-hand side can be scalar or vector net or register or concatenation of both. 20) What are the full case and parallel case statements?Full case statement: The full case is a case statement in which all possible case expressions can be matched with case items or case default. Parallel case statement: A parallel case statement is a case statement in which it is possible to match a case expression with one and only one case item. If you find a case expression that would match more than one case item, the matching case is called an overlapping or non-parallel statement. 21) What do you understand by transport delay and inertial delay?Transport delay: Transport delay is a type of delay caused by the wires that connect to the gates. Due to the wire's resistance and inductance, it delays the signal. Inertial delay: The inertial delay is the time it takes for a gate to change its output. 22) How can you write an FSM code in Verilog?There are mainly four ways to write FSM code in Verilog:
23) In a pure combinational circuit, is it necessary to mention all the inputs in the sensitivity disk? If yes, then why?Yes. In a pure combinational circuit, it is necessary to mention all the inputs in the sensitivity disk; otherwise, you will get a pre and post-synthesis mismatch in the result. 24) Which will be updated first between variable and signal?Signals are updated first between variable and signal. 25) What do you understand by the freeze, deposit, drive, and force command in Verilog?The freeze, deposit, drive, and force are commands used in Verilog that can be defined in the following way:
26) Write a Verilog code to swap contents of two registers with and without a temporary register?A Verilog code to swap contents of two registers with a temporary register: A Verilog code to swap contents of two registers without a temporary register: 27) What does the timescale 1 Ns/ 1 Ps signify in a Verilog code?The timescale directive is a compiler directive used to measure simulation time or delay time. The timescale / reference_time_unit specifies the unit of measurement for times and delays. The time_precision specifies the precision to which the delays are rounded off. 28) What is the difference between $setup and $hold?In Verilog, the $setup and $hold are used to monitor the setup and hold time constraints for sequential logic. The setup time is the minimum time in which the data must arrive before the active edge of a clock signal. The hold time is the minimum time in which the data cannot change after the active edge of a clock signal. These two constraints are defined in the following image: 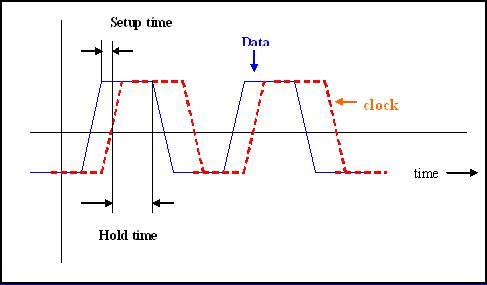
29) How can you generate a sine wave using the Verilog coding style?In Verilog, the easiest and efficient way to generate sine waves is using CORDIC Algorithm. 30) What do you understand by casex and casez statements in Verilog?The casex and casez are the types of case statements in Verilog. Here, casez treats all z values in the case alternatives or the case expression as don't cares. All bit positions with z can also be represented by ? in that position. casex treats all x and z values in the case item or the case expression as don't cares. Don't cares are not allowed in the case statement so, we have to use casex and casez. 31) What is a repeat loop in Verilog?The repeat loop is used to execute loop fixed for several times. It is not used to loop expression such as we see in the while loop statement. It contains constant, variable, or signal. For example, repeat(5). |
You may also like:
- Java Interview Questions
- SQL Interview Questions
- Python Interview Questions
- JavaScript Interview Questions
- Angular Interview Questions
- Selenium Interview Questions
- Spring Boot Interview Questions
- HR Interview Questions
- C Programming Interview Questions
- C++ Interview Questions
- Data Structure Interview Questions
- DBMS Interview Questions
- HTML Interview Questions
- IAS Interview Questions
- Manual Testing Interview Questions
- OOPs Interview Questions
- .Net Interview Questions
- C# Interview Questions
- ReactJS Interview Questions
- Networking Interview Questions
- PHP Interview Questions
- CSS Interview Questions
- Node.js Interview Questions
- Spring Interview Questions
- Hibernate Interview Questions
- AWS Interview Questions
- Accounting Interview Questions







