Difference between Voltage and CurrentThis is a very basic question we face in school or college days, but if you are new to electronics and electrical, sometimes it becomes difficult to understand the concepts of voltage and current. Read on the given tutorial to know the difference between Voltage and Current. What is Voltage?Voltage refers to the potential difference between two points per unit electric charge (Excess of lack of electron on the given body is called charge at the body). The voltage between two points is equal to the work done per unit electric charge against an electric field to move the charge from one place to another. In other words, Voltage is also known as Electromotive force (EMF) OR Electric Pressure or Potential difference or electric tension. Voltage may be caused by electric fields when a current-carrying conductor is passing through a magnetic field. A voltage can be represented as a source of energy (EMF) or stored energy (Potential drop between two points). The S.I unit of voltage is Joule per Coulomb or volts. The voltage is measuring through a device called a voltmeter. There are various formulas for voltage calculation, But Ohm's law is the best choice to calculate the voltage. As per Ohm's law, a flow of electric current in the circuit is directly proportional to the applied voltage and inversely proportional to resistance.
V α I = V = IR or E = IR
Where, I = Electric current (in Amperes) R = Electric resistance (In ohms) V = Applied voltage in volts. Let's understand the concept of voltage with the help of problem Example: If a 5amp of current flowing through 4ohm resistance, what is the voltage drop across the resistor? Solution: As per Ohm's law, V = IR Given I = 5amp, R = 4 ohm Therefore, V = 5 * 4 = 20 volt What is Current?An electric current refers to the rate of flow of charge or electron in a region or a point. An electric current is said to exist in a region or a point when there is a net flow of charge through a region. In an electric circuit, the charge is usually carried by a free electron. On moving through the wire of the circuit. The S.I unit of electric current is the ampere, which is the flow of electric charge over the surface at the rate of coulomb per second. The device used to measure the electric current is called an Ammeter. One ampere means one coulomb of electrons. One coulomb of electrons = 6.24 × 10 18 electrons. In other words, the rate of change of charge is called current i.e., 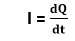
Where, dQ = Rate of change in charge Q = ne Where n is the number and e are the charge on an electron (1.6 × 10 -19C) There is various formula for voltage calculation, But Ohm's law is the best choice to calculate the voltage. As per Ohm's law, a flow of electric current in the circuit is directly proportional to the applied voltage and inversely proportional to resistance.
V α I = V = IR or I = V/R
Example: Find the value of current, If the 5ohm resistor is connected through the circuit and the voltage drop across the resistor is 10V? Solution: As per Ohm's law, V = IR Given, I = ?, R = 5 ohm and V = 10V 10 /5= I I = 2 ampere. Relationship between Voltage and Current The voltage and current have a various relationship with different components
V = IR or E = IR Where, I = Electric current (in Amperes) R = Electric resistance (In ohms) V = Applied voltage in volts.
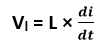
Where, Vl = Voltage applied across the Inductor L = Inductance of the coil
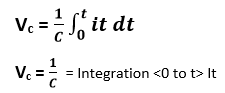
Where, Vc = Voltage applied across the capacitor I = current flowing through the capacitor. Difference between Voltage and Current
Next TopicDifference between
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share





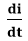 = Rate of change of current with respect to time.
= Rate of change of current with respect to time.




