What is 5G? Definition, Benefits and Use Cases
5G (fifth-generation wireless technology) is the latest generation of cellular technology that promises to revolutionize how we use wireless networks. It has been engineered to provide faster speeds and lower latency than previous iterations, which is ideal for applications that require real-time feedback. With potential peak speeds of up to 20 Gbps, 5G exceeds the speed of wireline networks and offers a latency of less than 5 ms. Using additional bandwidth and cutting-edge antenna technology allows for a boost in speed and responsiveness.
Throughout the following years, 5G networks and services will be installed to accommodate the rising demand for mobile and internet-enabled devices. When 5G technology is adopted, a vast range of new applications, uses and business cases are planned. This includes transmitting a sharp increase in data over wireless systems, making it possible to develop and utilize new and innovative technologies. In short, 5G has the potential to transform the way we live, work and communicate.

History of 5G development
The development of 5G wireless technology began in the early 2010s, with the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) forming a group to define the requirements for a new standard for wireless communication. The group, known as the International Mobile Telecommunications-2020 (IMT-2020) or 5G Vision, established the goals of 5G technology to include faster speeds, lower latency, increased capacity, and improved connectivity.
In 2015, the ITU set the official requirements for 5G technology, which included the ability to deliver peak data rates of 20 gigabits per second (Gbps) and latency of less than one millisecond (ms). Around the same time, major telecommunications companies and technology firms began investing in research and development to create the technology to meet these requirements.
The Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), a partnership between several telecoms' standards organizations, published the first 5G standards in 2017. This paved the way for the global development and adoption of 5G technology. The first commercial 5G networks were launched in 2019 in the United States, South Korea, and China, with other countries quickly following suit. Since then, major telecommunications companies have continued to expand their 5G networks, with some planning to offer nationwide coverage in the coming years.
The necessity to support emerging technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), driverless vehicles, virtual and augmented reality, and an increase in the need for faster and more dependable wireless communication have all contributed to the creation of 5G. 5G technology promises to provide the infrastructure necessary to support these emerging technologies and enable new use cases and applications that were impossible with previous wireless technology.
How does 5G work?
5G combines different technologies to enable faster and more reliable wireless communication. Here's a brief overview of how 5G works:
- Higher frequency bands: 5G operates at higher frequency bands than previous generations of wireless technology. This allows for faster data transfer speeds as bandwidth is available. These higher frequency bands, however, have a smaller range and are more difficult to pass through objects like trees and buildings. Multiple-input, multiple-output (MIMO) technology, which transmits and receives data via multiple antennas, is used in 5G to get around this.
- Small cell networks: Besides MIMO technology, 5G relies on small cell networks to provide coverage. Small cell networks consist of small, low-powered base stations deployed throughout an area to provide coverage. These base stations are typically mounted on streetlights or other existing infrastructure and can be placed close together to provide continuous coverage.
- Network slicing: 5G also incorporates the concept of network slicing, which involves dividing the network into virtual slices that can be customized to meet the needs of different applications. For example, a slice that is optimized for low latency could be created, which would be ideal for applications that require real-time feedback. Another slice could be optimized for high bandwidth, useful for streaming video or downloading large files.
- Edge computing: Another important technology used in 5G is edge computing, which involves processing data at the network's edge instead of sending it to a centralized data centre. This reduces latency and enables real-time processing, which is essential for applications such as autonomous vehicles and remote surgery.
- Beamforming: Finally, 5G incorporates beamforming technology, which directly directs signals from the base station to the user's device. This results in a stronger, more reliable signal and reduces interference from other devices.
How fast is 5G?
5G wireless technology is expected to be substantially quicker as compared to earlier generations of wireless technology, such as 4G LTE. In some circumstances, 5G is anticipated to be up to 100 times faster than 4G. The frequency band being used, the quantity of spectrum that is available, the number of devices connected to the network, and the distance between the device and the base station are all variables that will affect the actual speed of 5G.
In general, 5G speeds are categorized into three different tiers:
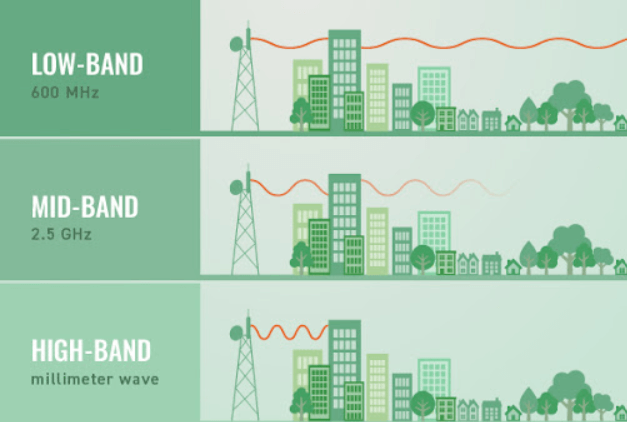

- Low-band 5G: This uses lower frequency bands, typically below 1 GHz, which provide good coverage over a wide area. However, the data transfer speeds are similar to 4G. Low-band 5G is expected to provide average speeds of around 100-400 Mbps (megabits per second), which is still significantly faster than most wired broadband connections.
- Mid-band 5G: This uses higher frequency bands, typically between 1 GHz and 6 GHz, which offer faster data transfer speeds than low-band 5G. Mid-band 5G is expected to provide average speeds of around 1-2 Gbps (gigabits per second), comparable to many wired broadband connections.
- High-band 5G: This employs the fastest data transfer rates, often above 24 GHz, but has a constrained coverage area and is readily hindered by objects like buildings and trees. High-band 5G, also known as mmWave, is expected to provide peak speeds of up to 20 Gbps, although actual speeds will likely be lower due to signal attenuation and other factors.
Note: The abovementioned speeds are theoretical maximums and may not be achievable in real-world conditions. Factors such as network congestion, signal strength, and the number of devices connected to the network can all impact actual speeds. Additionally, the speed of 5G will also depend on the specific implementation by each carrier and the available infrastructure in a particular location.
Benefits of 5G:
In comparison to earlier wireless technology generations, 5G has various advantages, including quicker data transmission rates, reduced latency, and expanded capacity. With the help of these advantages, a number of novel use cases and applications that were not possible with earlier generations of wireless technology are anticipated to be made possible. Here, we'll go over a few of the main advantages of 5G.
- Faster Data Transmission Speeds: 5G is intended to transfer data far more quickly than earlier wireless technology generations. Wider bandwidths, more effective use of the existing spectrum, and better antenna technology work together to achieve this. With 5G, users can expect download speeds of up to 10 Gbps, which is over 100 times faster than 4G LTE. This will enable a range of new use cases, such as streaming high-quality video and downloading large files quickly.
- Lower Latency: Latency refers to the time data travels between the user's device and the network. 5G is expected to have significantly lower latency than 4G, with latency as low as 1 ms in some cases. This will enable real-time applications such as virtual and augmented reality, autonomous vehicles, and remote surgery.
- Increased Capacity: 5G networks are intended to support far more devices and data traffic than previous generations of wireless technology. Wider frequency bands, more effective use of the existing spectrum, and improved network infrastructure work together to achieve this. A variety of new use cases, including smart cities, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and industrial automation, will be made possible by this enhanced capacity.
- Improved Reliability: 5G networks are intended to be more dependable than previous wireless generations. Advanced antenna technology, network slicing, and edge computing are used to accomplish this. These innovations will make it possible for 5G networks to offer more coverage, particularly where there is a lot of network activity or signal interference.
- New Use Cases: The combination of faster data transfer speeds, lower latency, and increased capacity will enable a range of new use cases and applications. Some examples include remote surgery, autonomous vehicles, smart cities, virtual and augmented reality, and industrial automation. These applications will transform many industries and enable new levels of innovation and productivity.
- Energy Efficiency: 5G networks are designed to be more energy-efficient than previous generations of wireless technology. This is achieved through advanced antenna technology, network slicing, and edge computing. These technologies will enable 5G networks to use less power, reducing the carbon footprint of wireless networks.
Use Cases:
The potential use cases for 5G wireless services are numerous, offering benefits across multiple industries and sectors. Here are some of the most promising use cases for 5G:
- Smart Cities and Infrastructure: 5G technology can help build smart cities with connected infrastructure, enabling more efficient and sustainable use of resources. For example, 5G networks can support connected traffic lights and parking systems, helping to reduce congestion and emissions in urban areas. Additionally, 5G can enable sensors and devices that monitor and control everything from water and electricity usage to waste management and air quality.

- Autonomous Vehicles: 5G can enable low-latency communication and high-speed data transfer, making it a key technology for autonomous vehicles. With 5G, cars can communicate with each other and with smart infrastructure, improving road safety and efficiency. For example, 5G networks can support real-time updates on traffic and road conditions, helping autonomous vehicles adjust their routes and speeds accordingly.

- Virtual and Augmented Reality: 5G's fast speeds and low latency make it well-suited for virtual and augmented reality applications. With 5G, users can experience high-quality VR and AR experiences without lag or delays. This has implications for everything from gaming and entertainment to remote collaboration and training.

- Healthcare and Telemedicine: 5G can enable faster and more reliable telemedicine services, allowing healthcare providers to monitor patients remotely and provide real-time consultations. For example, 5G can support high-resolution video conferencing and remote surgeries, enabling doctors to provide specialized care to patients in remote or underserved areas.

- Industry 4.0 and Manufacturing: 5G can help enable the next generation of smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0 applications. With 5G, factories can become more connected and efficient, with sensors and devices communicating in real-time to optimize production and reduce downtime. Additionally, 5G can support remote maintenance and equipment monitoring, helping prevent breakdowns and improve overall productivity.
- Gaming and Entertainment: With 5G, gamers can experience high-quality, low-latency gameplay on mobile devices. Additionally, 5G can enable new forms of entertainment, such as immersive VR experiences and interactive live events.

- Streaming High-Quality Video: With 5G, users can stream high-quality video content on their mobile devices without buffering or delays. This has implications for everything from video conferencing and live streaming to entertainment and education.
- Communication Among Devices in an IoT Environment: 5G can support the growing number of devices in an Internet of Things (IoT) environment, enabling seamless communication and data transfer between devices. For example, 5G can support connected homes with smart appliances, security, and energy management systems.
- More Accurate Location Tracking: With 5G, devices can more accurately track their location, enabling new location-based services and applications. For example, 5G can support real-time mapping, navigation systems, personalized advertising, and marketing.
- Fixed Wireless Services: 5G can provide an alternative to traditional wired broadband services, enabling faster and more reliable internet access in areas with limited or no access to wired connections. With 5G fixed wireless services, users can access high-speed internet without needing a physical connection to their home or office.
Challenges
- Infrastructure and deployment challenges: 5G requires a significant amount of new infrastructure, including more cell towers, small cells, and fibre optic cable to support the higher frequency and increased data transfer rates. Deploying this infrastructure can be time-consuming and expensive, particularly in rural areas and developing countries where existing infrastructure may be lacking.
- Interference with other wireless signals: 5G uses higher frequency radio waves than previous cellular networks, which can interfere with other wireless signals and impact their performance. This can lead to increased competition for radio frequencies and potential conflicts with other wireless technologies, such as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth.
- Technical challenges: The implementation of 5G technology involves complex technical challenges, including the design and production of new chips, antennas, and other hardware, as well as the development of new software to support the increased data speeds and connectivity.
Limitations of 5G
Security concerns: As with any wireless network, security is a major concern for 5G. The increased connectivity and data transfer rates of 5G create new opportunities for cyberattacks and data breaches, which could seriously affect individuals and organizations. There is also concern that 5G infrastructure built by foreign companies could pose a national security risk.
Limited coverage: While 5G is expected to provide nationwide coverage eventually, initial deployments will likely be limited to urban areas and major cities. This means that rural and remote areas may need more access to 5G services for the foreseeable future.
Cost: The deployment of 5G infrastructure is expected to be expensive, and upgrading devices to be compatible with 5G technology could also be a barrier to adoption for many consumers and businesses. This could result in a digital divide, with some groups having access to the benefits of 5G while others are left behind.
Leading Companies in 5G Development
The race to develop 5G technology is in full swing, with telecommunications companies, tech giants and other players investing billions of dollars in research, development and deployment of 5G networks. These companies are developing hardware, software and infrastructure to enable the next generation of wireless communication technology. Here are some of the leading companies in 5G development:
1) Verizon Communications Inc.

Verizon is one of the leading companies in 5G development and has invested heavily in the technology for several years. The company is currently focusing on implementing mmWave 5G, which offers the fastest speeds and lowest latency, but with limited coverage. Verizon has launched 5G in several cities and plans to continue expanding its 5G network.
Verizon has established Verizon Ventures, an investment fund in addition to rolling out 5G networks. Verizon Ventures seeks to invest in sectors including augmented reality, IoT, and artificial intelligence that will profit from 5G.
2) AT&T Inc.

AT&T is another significant player in the 5G sector, though it lags behind several of its competitors. Although AT&T has begun investing in 5G, it has yet to introduce a nationwide 5G network. The business has also launched 5G Evolution (5GE), which is an improved version of 4G LTE rather than 5G.
3) T-Mobile US Inc.

T-Mobile has emerged as a leader in the 5G market, focusing on a multi-tier 5G strategy that uses low-band, mid-band and mmWave frequencies. The company has launched 5G in half a dozen markets.
T-Mobile is also a company that has invested in developing 5G hardware, such as routers and smartphones. The company is partnering with Nokia and Qualcomm to build its 5G network.
4) Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd.

Huawei is a Chinese tech giant investing heavily in 5G development. The company has developed a range of 5G hardware and software, including 5G base stations, routers, and modems.
Despite being one of the leading companies in 5G development, Huawei has faced controversy due to concerns over its ties to the Chinese government. Several countries have banned using Huawei's 5G technology, citing security concerns.
5) Nokia Corporation

Nokia is a Finnish telecommunications company involved in 5G development for several years. The company has developed a range of 5G hardware and software, including 5G base stations and routers.
Nokia is also partnering with several companies to build out 5G networks. In 2020, the company announced a partnership with AT&T to deploy a 5G network for the US military.
6) Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd.

For several years, Samsung has been a Korean tech giant involved in 5G development. The company has developed 5G hardware and software, including 5G smartphones and base stations.
Samsung is also partnering with several companies to build out 5G networks. In 2019, the company announced a partnership with AT&T to deploy a 5G network for the manufacturing industry.
The Current State of 5G: Availability and Deployment
5G technology is not just a concept or an idea; it is already available today. Global operators began launching new 5G networks in early 2019, and over 60 countries have deployed the technology. The rollout of 5G has been faster compared to 4G, and consumers are excited about the high speeds and low latency it offers.
To access 5G, users must have a device that supports the technology and be within range of a 5G node. Major phone manufacturers such as Samsung, Huawei, and OnePlus are already commercializing 5G phones, and more are expected to follow. However, the availability of 5G varies depending on the region, carrier, and infrastructure.
Despite the current limitations, 5G provides faster speeds and the capability for mission-critical services, enhanced mobile broadband, and massive IoT. It can potentially revolutionize healthcare, transportation, and manufacturing industries by enabling real-time data transfer and analysis.
The deployment of 5G networks has faced some challenges, such as infrastructure and deployment issues, security concerns, and interference with other wireless signals. However, major carriers such as Verizon, AT&T, and Sprint are working to build up their 5G networks and have started to embrace a multi-tier 5G strategy that includes low-band, mid-band, and mmWave frequencies.
While it is difficult to predict when everyone will have access to 5G, the momentum of 5G launches in its first year is promising, and more countries are expected to launch their 5G networks in 2020 and beyond. The possibilities of 5G technology are vast, and it is just a matter of time before it becomes the new standard for mobile communication and connectivity.
5G-Enabled Smartphones available in market
As 5G networks continue to roll out, the demand for smartphones that can use this new technology is rising. Many major smartphone manufacturers have released 5G-enabled devices, offering consumers faster download speeds, lower latency, and the potential for new applications and experiences. Let's take a closer look at some of the 5G-enabled smartphones currently available in the market:

- Samsung Galaxy S10 5G: The Samsung Galaxy S10 5G was one of the first 5G-enabled smartphones on the market. The device debuted in early 2019 and included a 4,500mAh battery, a Snapdragon 855 CPU, a 6.7-inch AMOLED display, and 8GB of RAM. The device also has two front-facing and four rear cameras, including a 3D time-of-flight sensor.
- Samsung Galaxy Note10+ 5G: The Samsung Galaxy Note10+ 5G was released in late 2019 and offered a 6.8-inch AMOLED display, a Snapdragon 855 chipset, 12GB of RAM, and a 4,300mAh battery. The device includes four rear cameras, including a 3D time-of-flight sensor and a front-facing camera.
- Samsung Galaxy A90 5G: The Samsung Galaxy A90 5G offers a more affordable option for those looking to experience 5G. For those interested in using 5G, the Samsung Galaxy A90 5G offers a more reasonable option. The 2019 smartphone has a 4,500mAh battery, a Snapdragon 855 CPU, a 6.7-inch AMOLED display, and 6 or 8GB of Memory. The gadget has a front-facing camera as well as a triple-camera arrangement on the back.
- OnePlus 7 Pro 5G: The OnePlus 7 Pro 5G was released in mid-2019 and offered a 6.67-inch Fluid AMOLED display, a Snapdragon 855 chipset, 8GB of RAM, and a 4,000mAh battery. The device includes three rear cameras and a front-facing camera.
- Moto Z3: The Moto Z3 was one of the first 5G-enabled devices on the market, released in mid-2019. The device features a 6.01-inch Super AMOLED display, a Snapdragon 835 chipset, 4GB of RAM, and a 3,000mAh battery. The device includes a dual-camera setup on the back and a front-facing camera.
- Xiaomi Mi MIX 3 5G: The Xiaomi Mi MIX 3 5G was released in early 2019 and offered a 6.39-inch AMOLED display, a Snapdragon 855 chipset, 6 or 8GB of RAM, and a 3,800mAh battery. The device includes dual rear cameras and a dual front-facing camera.
- Huawei Mate X: The Huawei Mate X was released in late 2019 and featured a foldable design, offering an 8-inch OLED display when unfolded. The device includes a Kirin 980 chipset, 8GB of RAM, and a 4,500mAh battery. The device includes a quad-camera setup on the back and a front-facing camera.
- Huawei Mate 30 Pro 5G: The Huawei Mate 30 Pro 5G was released in late 2019 and offered a 6.53-inch OLED display, Kirin 990 chipset, 8GB of RAM, and a 4,500mAh battery. The device includes four rear cameras and a front-facing camera.
|









 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
















