What is a Memory Slot?Memory is an essential computer component, allowing the system to store and access data quickly. Without memory, a computer would not be able to perform tasks efficiently or even function at all. 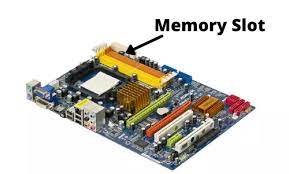
A memory slot is a physical connector on a computer's motherboard designed to hold a memory module. Memory modules come in various shapes and sizes, such as DIMM or SO-DIMM, and they contain a series of memory chips that allow a computer to store and access data temporarily in its RAM. Memory slots are critical to a computer's performance, as they determine the maximum amount of RAM installed on the system. Most motherboards have two to four memory slots, while high-end models may have more. The type, speed, and capacity of the memory module that can be installed in each slot depend on the specific specifications of the slot. Memory slots play a vital role in a computer's ability to store and access data quickly, and they allow users to increase a computer's performance by adding more RAM. Function of a memory slotA memory slot is responsible for temporarily storing data in a computer's RAM (Random Access Memory), a type of volatile memory that allows the system to access data quickly. The computer uses the RAM to store data currently used by the system and applications. The memory slot provides fast access to the computer's current data, allowing the system to retrieve and process data as needed quickly. This is important for tasks such as running applications, playing games, or browsing the internet, which requires the system to access and process large amounts of data quickly. A memory slot can significantly increase a computer's performance by providing more RAM. This is because a computer with more RAM can store more data in memory, reducing the system's need to access data from a slower hard drive or SSD. This results in faster performance and improved overall system responsiveness. The function of a memory slot is to store data temporarily in a computer's RAM, provide fast access to data that is currently in use, and increase a computer's performance by providing more RAM. Types of memory slots:There are several types of memory slots, each with specific specifications. The most common types of memory slots are:
In addition to the type of memory slot, each type has specific specifications. These specifications include the number of pins, the voltage required for the memory module, and the maximum capacity of the memory module that can be installed. For example, DDR3 memory slots typically have 240 pins, require 1.5 volts of power, and can support memory modules with a maximum capacity of 8GB. DDR4 memory slots typically have 288 pins, require 1.2 volts of power, and can support memory modules with a maximum capacity of 16GB. Number of memory slotsThe number of memory slots on a motherboard determines the maximum amount of RAM that can be installed on a computer. Most motherboards have two to four memory slots, although some high-end motherboards may have more. The number of memory slots on a motherboard also affects the type of memory configuration used. For example, a motherboard with four memory slots can support a dual-channel memory configuration, providing faster data transfer rates than a single-channel configuration. It's important to note that the number of memory slots on a motherboard is not the only factor determining the maximum amount of RAM that can be installed on a computer. The maximum amount of RAM is also limited by the type and capacity of the memory modules that can be installed in each slot, and the overall memory capacity supported by the motherboard. ConclusionIn conclusion, memory slots are an essential component of computer hardware, and their proper selection and configuration can significantly impact a system's performance and speed. By understanding the different types and specifications of memory slots, users can make decisions about upgrading or optimizing their computer's memory configuration for maximum performance.
Next TopicWhat is a Tablet
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










