What is an adjacency matrix?In this article, we are going to discuss the adjacency matrix along with its representation. Adjacency matrix definitionIn graph theory, an adjacency matrix is a dense way of describing the finite graph structure. It is the 2D matrix that is used to map the association between the graph nodes. If a graph has n number of vertices, then the adjacency matrix of that graph is n x n, and each entry of the matrix represents the number of edges from one vertex to another. An adjacency matrix is also called as connection matrix. Sometimes it is also called a Vertex matrix. Adjacency Matrix RepresentationIf an Undirected Graph G consists of n vertices then the adjacency matrix of a graph is n x n matrix A = [aij] and defined by - aij = 1 {if there is a path exists from Vi to Vj} aij = 0 {Otherwise} Let's see some of the important points with respect to the adjacency matrix.
Note: In an adjacency matrix, 0 represents that there is no association is exists between two nodes, whereas 1 represents that there is an association is exists between two nodes.How to create an adjacency matrix?Suppose there is a Graph g with n number of vertices, then the vertex matrix (or adjacency matrix) is given by -
Where the aij equals the number of edges from the vertex i to j. As mentioned above, the Adjacency matrix is symmetric for an undirected graph, so for an undirected graph, aij = aji. When the graphs are simple and there are no weights on the edges or multiple edges, then the entries of the adjacency matrix will be 0 and 1. If there are no self-loops, then the diagonal entries of the adjacency matrix will be 0. Now, let's see the adjacency matrix for an undirected graph and for directed graphs. Adjacency matrix for an undirected graphIn an undirected graph, edges are not associated with the directions with them. In an undirected graph, if there is an edge exists between Vertex A and Vertex B, then the vertices can be transferred from A to B as well as B to A. Let us consider the below-undirected graph and try to construct the adjacency matrix of it. 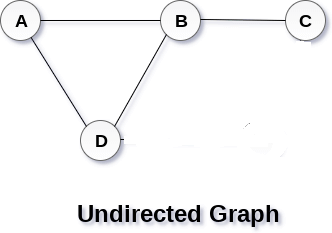
In the graph, we can see there is no self-loop, so the diagonal entries of the adjacent matrix will be 0. The adjacency matrix of the above graph will be - 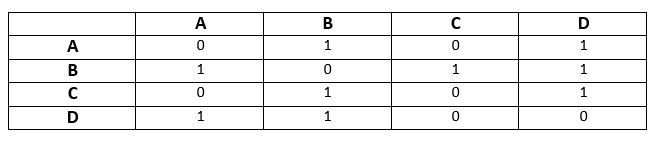
Adjacency matrix for a directed graphIn a directed graph, edges form an ordered pair. Edges represent a specific path from some vertex A to another vertex B. Node A is called the initial node, while node B is called the terminal node. Let us consider the below directed graph and try to construct the adjacency matrix of it. 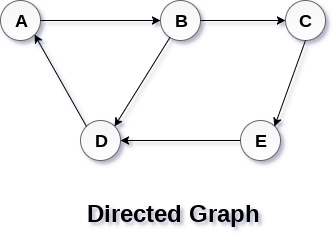
In the above graph, we can see there is no self-loop, so the diagonal entries of the adjacent matrix will be 0. The adjacency matrix of the above graph will be - 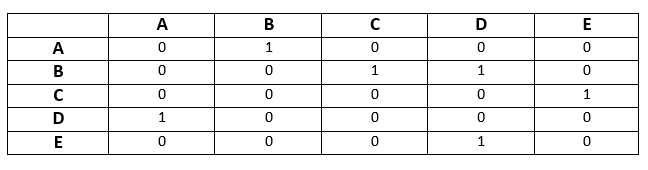
Properties of the adjacency matrixSome of the properties of the adjacency matrix are listed as follows:
Let's see some questions of the adjacency matrix. Below questions are on the weighted undirected, and directed graphs. NOTE: A graph is said to be the weighted graph if each edge is assigned a positive number, which is called the weight of the edge.Question 1 - What will be the adjacency matrix for the below undirected weighted graph? 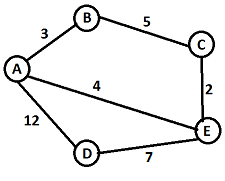
Solution - In the given question, there is no self-loop, so it is clear that the diagonal entries of the adjacent matrix for the above graph will be 0. The above graph is a weighted undirected graph. The weights on the graph edges will be represented as the entries of the adjacency matrix. The adjacency matrix of the above graph will be - 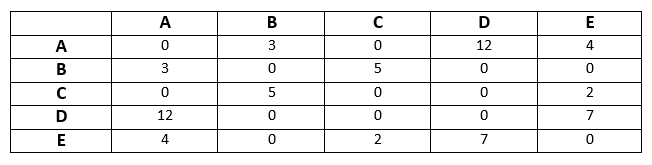
Question 2 - What will be the adjacency matrix for the below directed weighted graph? 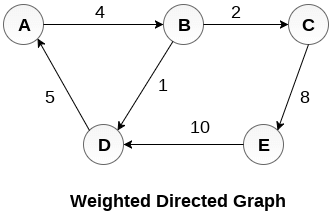
Solution - In the given question, there is no self-loop, so it is clear that the diagonal entries of the adjacent matrix for the above graph will be 0. The above graph is a weighted directed graph. The weights on the graph edges will be represented as the entries of the adjacency matrix. The adjacency matrix of the above graph will be - 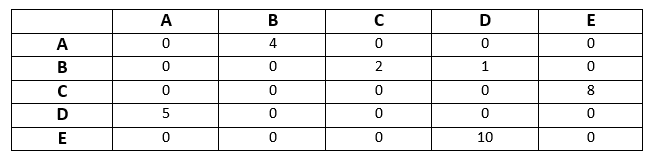
Hope this article is beneficial to you in order to understand about adjacency matrix. Here, we have discussed the adjacency matrix along with its creation and properties. We have also discussed the formation of adjacency matrix on directed or undirected graphs, whether they are weighted or not.
Next TopicBest Photo backup apps for Android
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










