What is Dielectric Heating?Dielectric heating is the method of heating in which the dielectric materials are heated using a high-frequency alternating electric field, radio waves, or microwave electromagnetic radiation.
Principle of Dielectric HeatingThe capacitor's operating concept underlies the dielectric heating technique (i.e. electrostatic). As far as we are aware, dielectric heating is only effective when used to heat non-conducting materials. The dielectric material to be heated is sandwiched between two conducting electrodes in this heating technique, which uses alternating voltage at a high frequency. The diagram below depicts the analogous circuit and schematic layout of the dielectric heating process. 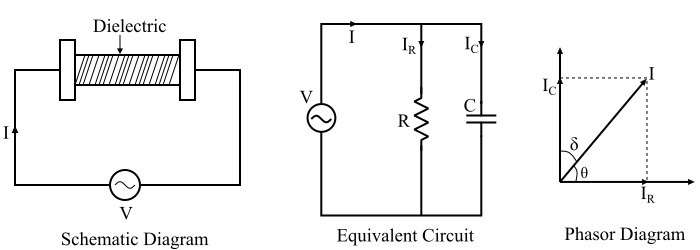
A high frequency potential difference is delivered across two electrodes that are separated from one another by a dielectric medium (the substance to be heated). This configuration creates a capacitor. The accompanying graphic also displays the corresponding circuit's phasor diagram. Due to the possibility that the capacitor created during the configuration for the dielectric heating is not pure, a resistor "R" is also presented in parallel in the circuit. However, the resistance, or "R," is quite high, resulting in a very little amount of current passing through it. Therefore, it may be said that the capacitor current Ic is equal to the entire current. Applications of Dielectric Heating:Dielectric heating is only utilized when other heating techniques are impractical since it is a costly heating technology. The following list includes some examples of dielectric heating applications: Industry of PlasticNumerous gadgets are made from plastic. Plastic molding will be quicker and error-free if the plastic is uniformly pre-heated. Before sending the plastic compounds into the molding area, the plastic is pre-heated using dielectric heating, which takes relatively little time to achieve the necessary heat in the plastic compounds. Binding of booksThe premium books are moved back and forth between tubular electrodes in alternating electrostatic fields. Through the use of dielectric heating, this dries the adhesive on the cover binding in a matter of seconds (about 5 to 10). Because of this, the book may be shipped and packaged without having to wait for the covers to dry. As a result, book binding uses dielectric heating. Baking of sand coresBefore being employed in molding operations, the sand cores composed of dry sand, water, and some resin must be supported. These sand cores are dried by passing them through an alternate electrostatic field while being transported on a conveyor belt. Industry of PlywoodThe glue lines are dried using dielectric heating in the plywood industry. It is employed since, in normal circumstances, the glue lines may take a day or more to cure and fix the joint. However, it takes a few minutes for the joints to dry and solidify when they are heated using high frequency dielectric heating. Dielectric heating is essential for consistent heating in the plywood sector since the process of creating multilayer plywood requires quicker bonding. BakeriesFor the backing of biscuits, cakes, and other bakery goods, the automatic bakeries' machines employ dielectric heating. Digital sewingDielectric heating is also used while creating plastic apparel, including raincoats. If the raincoats were sewed on a standard sewing machine, rainwater may seep through the stitching gaps. In order to heat these materials more rapidly and evenly, cold rollers fed with high frequency supply (i.e., dielectric heating) are used. Cigarette industryDielectric heating is being used in the tobacco industry to dry tobacco after it has been mixed with glycerin, etc. Drying off oil emulsionsThe moisture content of the oil emulsions is also taken out using dielectric heating. Because some chemical processes call for the blending of water and oil. The water content must then be eliminated in order to give the product the desired life. Because the dielectric constants of oil and water are so different, the dielectric heating method is used for this purpose. As a result, when heating is accomplished through dielectric heating, water will boil off while temperature of oil will continue to stay significantly lower than the boiling point of water. The emulsion is securely, swiftly, and efficiently dried in this manner. Food DehydrationIn order to dehydrate food so that it may be kept for a long time, the dielectric heating method is also used. Examples of food that has been dried through dielectric heating include dehydrated peas, packaged candies, etc. Through the use of an alternating electrostatic field, the food is put through a process that causes dielectric heating and, ultimately, dehydration. Applications of ElectromedicineDielectric heating is also employed in medicine to cure a variety of illnesses. Consider the procedure known as "diathermy," which involves heating the interior of the affected area using dielectric heating to treat a section of the body that is experiencing a particular form of discomfort. The body portion is clamped by two electrodes during this procedure, and the electrodes are kept apart from the body. The body's tissues and bones between the electrodes produce dielectric heat as the electrodes are subsequently activated by a high frequency, high voltage power source.
Next Topic#
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










