What is matter | States of Matter | Classification of MatterMatter is anything that has mass and occupies space such as atoms, protons, compounds, tree, house, table, computer, etc. So, as per the definition of matter, light, heat, and radiations are not matter. So, we can say that everything in the universe that has mass and occupies space and the presence of which can be felt by any of our senses is matter. A matter consists of particles such as atoms or elements. The constituting particles of a particular matter have specific chemical and physical properties, so they cannot be broken down into any other substance. For example, a bar of the gold element is made of gold atoms (particles). There are 118 elements out of which 92 elements are found naturally and the rest of the elements are created in laboratories and they are unstable. Physical classification of matter (Physical Forms)It means based on the physical state or properties under normal conditions of temperature and pressure, we can classify the matter into three states which are solids, liquids and gases. For example, the things that we see around us exist in three different states such as chair is in the solid-state, the water in a glass is in the liquid state and the oxygen that we inhale is present in the gaseous state. So, physically matter exists in three different states in nature. Each state has its own unique physical properties. The three physical states of matter are described below; States of Matter I Physical forms
i) SolidsIn this state of matter, a substance possesses definite volume and a definite shape. We can say that a substance with fixed volume and shape is called a solid. For example, iron, gold, wood, sugar, etc. In this state of matter, the constituting particles of a substance are very close to each other as there are strong intermolecular forces between the particles and space between the particles is also very less or negligible. Characteristic features or physical properties of solids are as follows:
ii) LiquidsIn this state of matter, a substance has a definite volume but its shape is not fixed. We can say that a substance is said to be a liquid if its volume is fixed but the shape is not fixed. For example, water, milk, mercury, alcohol, etc. The constituent particles are less tightly packed as compared to solids. It is the intermediate state between solid and gas. The characteristic feature or physical properties of liquids are given below;
iii) GasesIn this state of matter, a substance neither possesses a definite shape nor a definite volume. We can say that a substance is said to be a gas if it does not a have definite volume and shape. In the gaseous state, the particles are far apart from each other and tend to occupy the whole container in which they are placed. For example, hydrogen gas (H2), Oxygen (O2), Carbon dioxide (CO2), Nitrogen gas (N2), and more. The main properties of gases are as follows;
Chemical classification of matterAs per the chemical classification, the matter is classified into two types; pure substance and mixture. 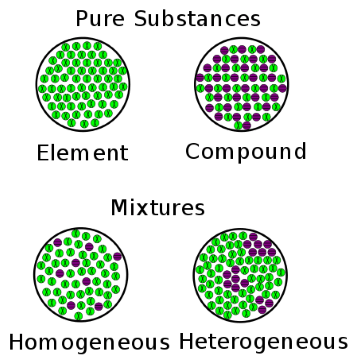
1) Pure SubstanceAs the name suggests, it is made of only one type of particles, which means all the constituting particles are identical in a pure substance. The constituting particles of a pure substance cannot be separated or broken into simple substances by physical method. For example, we cannot separate oxygen and hydrogen from water by physical method. Although, it can be done by using chemical methods. A pure substance can be found only in two forms either in the form of elements or in the form of compounds. So, we can say that a pure substance is further divided into two types that include elements and compounds and are described below; i) ElementIt is the simplest form of a pure substance that is made of the identical or same type of constituting particles or atoms. It has specific physical and chemical properties and it cannot be broken into any other simple substance and cannot be built from any other simple substance. For example, hydrogen element will contain only hydrogen atoms, helium element will contain only helium atoms, and so on. This is the reason that element is considered a pure substance as it is made of the same type of atoms. Element is further divided into three types depending on their physical and chemical properties. Metals, Non-Metal and Metalloids, etc. ii) CompoundA compound is also considered a pure substance although it is made of more than one type of elements or atoms. The reason for this is that in a compound the different atoms or elements are combined in a fixed proportion by weight to form molecules. We can say that compounds are made of identical particles that are called molecules, which contain specific atoms in a specific proportion. For example, water is made of water molecules and each water molecule is made of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. Besides this, the properties of compounds are different from their constituent elements. Compounds can be broken into simpler substances by using appropriate chemical methods. Some common examples of compounds are HCl, H2O, and H2SO4. As the same type of molecules combines to form compounds. So, we call compounds pure substance. On the other hand, if there are different molecules that form a substance, we cannot call it a compound, in that case, it is known as a mixture. Molecules in a compound may be physically attracted towards each other but they do not react chemically just like atoms in elements don't react with each other although they have a physical force of attraction between them. However, the atoms in a molecule definitely react with each other and form chemical bonds. For example, the chemical bond between oxygen and hydrogen in a water molecule. 2) MixtureA material that contains or made of two or more substances, which are mixed in any ratio by weight and which are not reacting with each other chemically, is called a mixture. It can be a solid, liquid or gas. For example, a metal alloy such as steel that is made of iron and carbon is a mixture of iron and carbon. The air that we inhale is also a mixture of gases such as oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, etc. Similarly, sea water is a mixture of salt and water. Properties of mixtures
Mixtures are further divided into two types, homogenous mixtures and heterogeneous mixtures. i) Homogenous mixtureAs the name suggests, a mixture in which a substance is uniformly mixed or distributed into another substance is called a homogenous mixture. They are also known as solutions. At the macro level, you cannot see any differences in the homogenous mixture as it looks consistent from all angles and there is no boundary of separation between different components as the components are present in a single phase. Such as steel, a mixture of iron and carbon contains both iron and carbon in the solid phase. In steel, you cannot see the iron and carbon separately but at the micro-level, you can see different metals are mixed to form the alloy. So, you can see the only one phase in a homogeneous mixture such as sugar in water will have only a liquid phase after sugar dissolves completely in water to form a homogenous mixture. A homogenous mixture has the same properties and combination of its constituting particles throughout their mass. Some examples of homogenous mixtures are as follows;
Properties of homogenous mixtures:
ii) Heterogeneous MixtureA mixture that has a non-uniform composition or in which the components are not mixed or distributed uniformly is called a heterogeneous mixture. In this mixture, the composition of components vary from one part of the mixture to another part and the components can be seen separately. So, samples taken from different parts have different proportions of components. Examples of heterogeneous mixtures:
Properties of heterogeneous mixtures
Difference between a homogeneous mixture and a heterogeneous mixture
Next TopicWhat is atom
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










