Xamarin Interview Questions
A list of frequently asked Xamarin Interview Questions and Answers are given below. 1) What is Xamarin?Xamarin is a company that builds the software. The main operation of Xamarin is to build mobile apps that work on cross-platforms. It is used to build the UI for Android, iOS, and Windows operating system. Xamarin application shares the codebase. Xamarin's feature is similar to the native application. A developer can download the Xamarin tools in Visual Studio. 2) What is the advantage of Xamarin Development?Benefits of Xamarin Development are:
3) What are the disadvantages of Xamarin Development?Disadvantages of Xamarin app Development are:
4) What are the development approaches in Xamarin?Xamarin has two approaches for app development. These are
5) What are the differences between the Xamarin and Xamarin.Forms?The differences between the Xamarin and Xamarin.Forms are:
6) What is Xamarin Profiler?Xamarin Profiler is a tool which is used by the developers to keep an eye on the information about the particular App inside the Visual Studio. With the help of Xamarin Profiler, developers can easily analyze the App's behavior. We can use the profiler to track the application's memory information and can sample its statistics. 7) What is Xamarin Insights?Xamarin insight is a tool that allowed the developers to identify and track the issue with the apps in real-time. We can also use this for the monitoring system to report the problems. Xamarin introduced Xamarin Insight in October 2014. However, it was closed on March 31, 2016. In today's time, developers can believe in Visual Studio App Center for the same functionality that is provided by the Xamarin Insights. 8) What is Xamarin.Forms?Xamarin.Forms is a framework which is used to build the user interface in the mobile application. In the same codebase, developers have to write the UI separately for each platform. This is time consuming and difficult process. Xamarin.Forms allows the developer to create just one UI which can be used across all platforms like Android, iOS, and Windows. 9) Which programming language supports the Xamarin?Xamarin supports three languages in the development of mobile applications: 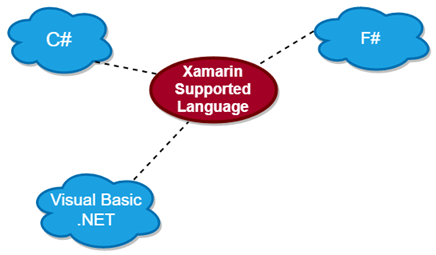
10) What is the role of XAML in Xamarin?XAML or Extensible Markup Language is a special tool that allows the developer to define the user interface in Xamarin app development. XAML has a vital role in Xamarin, but it is not necessary for app development in Xamarin.Forms. Xaml works with ModelView-ViewModel or MVVM architecture of an application. 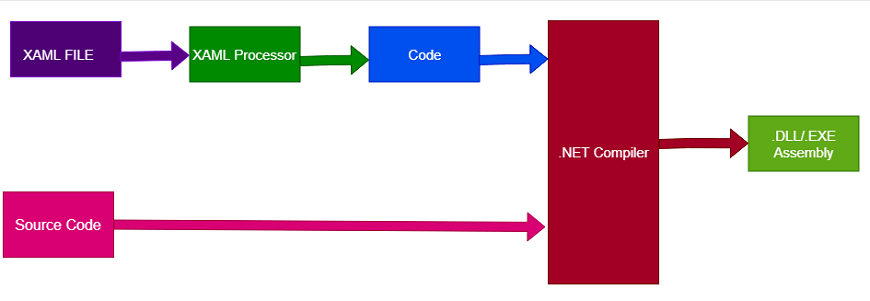
11) What is Xamarin Studio?Xamarin Studio is a standalone IDE for developing the cross-platform mobile application, which is based on the open-source project Monodevelop. 12) What are the differences between the Xamarin Studio and Visual Studio?Both Xamarin Studio and Visual Studio are IDEs used to develop the Android, iOS, Class Library, Console, PCL, and Windows Phone application. Both Xamarin Studio and Visual Studio support F#.
13) What is the lifecycle of Xamarin.Forms apps?Xamarin.Forms is a platform to develop the cross-platform mobile applications by using the XAML for Front-End and C# for the backend of the application. In Xamarin.Forms application, we can share all code. Xamarin.Forms also give the 100% API coverage of Android and iOS native APIs. So that, we can develop native Android, iOS, and Windows apps. For more information about the LifeCycle of the Xamarin.Forms, click on this link: Xamarin LifeCycle When we create Xamarin.Forms application we will see four projects:
14) What are the types of data binding modes in Xamarin?The different types of data binding modes are:
15) What is the difference between the Xamarin and Mono?
16) What are the different scenarios used in Xamarin.Forms?The following are the different types of scenarios that are used in Xamarin.Forms:
17) What is data binding in Xamarin?Data Binding is a technique that is used to synchronize the source of the data with the user interface. When the data binding is done and the data or our business model changes, then it shows the changes automatically to the UI elements and vice versa. 18) What is the Xamarin test cloud?The Xamarin test cloud allows us to test the mobile application on various devices. The Test cloud is also used for automated testing in many real devices simultaneously. 19) How to set up the Xamarin?For Xamarin set up, there are four steps:
For more information click here: Installation of Xamarin 20) What are the types of layout control in the Xamarin.Forms?Different types of layout control in Xamarin.Forms are:
For more information about layout click on this link: XamarinLayout 21) What are the different kinds of Pages present in the Xamarin.Forms?The different types of pages present in the Xamarin.Forms are:
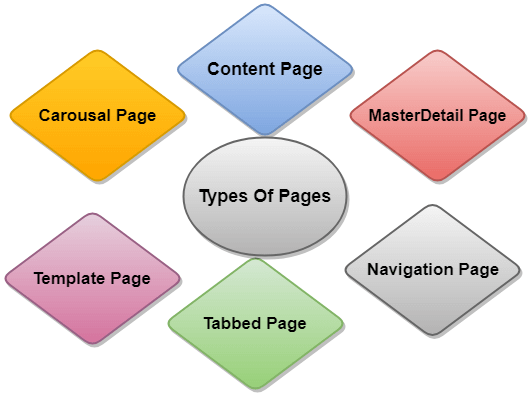
For more information about the Xamarin Page, click on this link: Xamarin.Forms 22) What are the advantages of Xamarin?Benefits of Xamarin are:
23) What are the code-sharing techniques in Xamarin.Forms?There are two methods of sharing the code between the cross-platform applications:
The goal of the code-sharing strategy is to support the architecture where multiple platforms can utilize a single code base. 24) What is the difference between the portable class library and shared projects?Portable Class Library 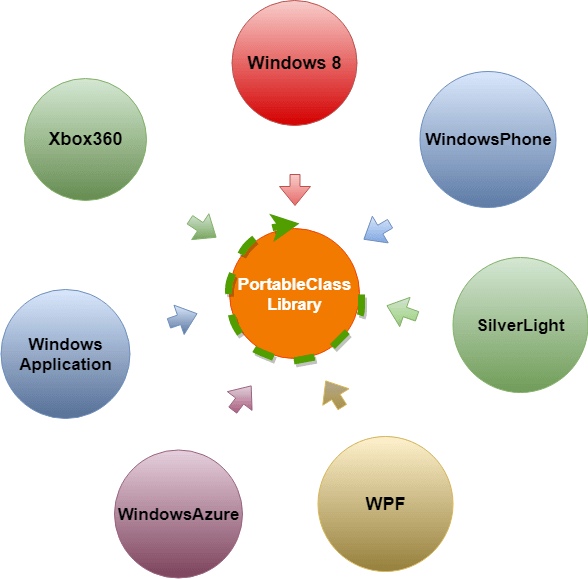
We create Class Library in .Net to reuse our code or to make our code reusable with the same type of application only, but that might not work for some conditions. Here we assume, we have created the class library for WPF or any other kind of application. And if we want to access the same type of class library for Windows 8 or Windows phone application, then in this scenario, we can't refer this as a class library. We want the same application for all the platforms to make our life easy. We want the same application used on multiple platforms. Microsoft technology is growing day by day, and it covers every device. All types of applications we can build and validate within one framework on all types of platform Windows, Web, Mobile, or Tab. PCL solves this problem. .Net 4.5 introduced the Portable Class Library (PCL) for developing the business logic in one location, and we can use this library end to end in all types of applications or all platforms (Windows, web, or Mobile) on .Net Framework. The figure shows the flow of the Portable Class Library (PCL). All these applications run on the .Net Framework. All these applications have different environments and platforms, but they all can easily use the Portable Class Library. In other words, we can say that we only need to prepare the UI and do the DataBinding of our application for all the windows, web and mobile, because the same business logic can then use the entire platform. Shared Project A shared project is a project that contains standard code and linked to each specific platform library or App. It is compiled as a part of the platform-specific code. To develop a nice solution that is based on a shared project, there is a need to architect it to have the core features in the shared project. Here possibly, we may use partial classes, abstract classes, and interfaces to manage the objects which are specific for each platform in the platform-specific project. These kinds of projects are good when we are in a prototype phase because it is fast to implement the shareable project for the common code. We can use all the advantages of the platform-specific Framework. 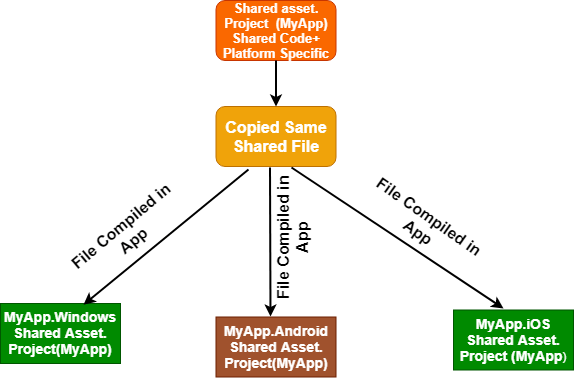
Shared Code can be branched base on the platform using compiler directive (e.g. #if_Android_,#if_iOS_,#if_Windows_Phone_App.etc.)
25) What are the advantages of XAML?The advantages of XAML are:
26) What are the Views?Views are known as control of widgets. They can be visual objects such as Label, Button, Entry, BoxView, ListView, TableView, etc. All the UI elements are the sub-classes of view. 27) What is the difference between ListView And TableView?ListView and TableView controls are similar. We can take them as a single control. The major difference between them is how they layout the items. ListView: ListView control displays the stacks of data vertically. It is just like a standard Listbox. We use this control to display the order of data in the list, especially the long list, that requires scrolling, like a list of email messages, a list of contacts, or search results. TableView: TableView displays the stacks of data horizontally in rows. We use this control when we need more space for rich visualization of the item to be displayed. 28) What are the types of the App which use Xamarin?The different types of apps which use the Xamarin are:
29) What are the different types of scenario used in Xamarin.Forms?The scenario used by the Xamarin.Forms are:
30) What are the apps designed by Xamarin for Android?The apps designed by Xamarin for Android are:
31) Name the apps that were designed by Xamarin for iOS?The apps that were designed by Xamarin for iOS are:
32) How Xamarin.Android applications work?Xamarin.Android applications depend on Microsoft's Mono Virtual Machine. Mono is Microsoft's open-source implementation of the .Net Framework, which is based on open source standards of C# and CLR. Mono was launched in the year 2001. It was created to allow the .Net applications to work on the Linux platform, but was later modified to support the development on various devices, including embedded systems. In Xamarin, Mono works in parallel with Android's ART. On Android, most of the system facilities like Audio, Graphics, OpenGL, and Telephony are not available directly to the native applications. They can be added through the Android Runtime Java APIs, which is available in one of the Java.*namespaces or the Android.*namespaces. The native applications then interact with the exposed .NET APIs. These APIs then, through the Android Binding, call the Android runtime Java APIs. The architecture looks like this: 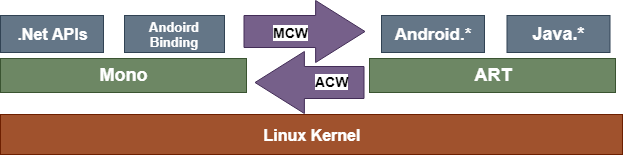
33) What is Fresh MVVM?Fresh MVVM is a super light MVVM framework which is designed specifically for Xamarin.Forms only. Its design is easy, simple, and flexible. It is easy to learn and uses the convention over configuration. Fresh MVVM is a little different from MVVM. FreshMvvm uses the concept of Page and PageModel instead of View and ViewModel. 34) What is the difference between the MVVM Cross and MVVM Light?MVVM Cross: MVVM Cross is a .NET cross-platform MVVM framework. It allows us to make a cross-platform solution for platforms such as Xamarin. Forms, Xamarin.Android, Xamarin.iOS, Xamarin.Mac and WPF. It is an inactive state of development. MVVM Cross requires the application to be divided into two parts: Core and the UI. The Core part contains the View Models, Service, Models, and the Business logic, whereas the UI part consists of the different views and platform-specific code that interact with the core. The views are the View Screens, which contain the graphical content. In addition to Core and UI, the application may contain additional libraries for various functionalities. Features that are provided by MVVM Cross are:
Consequences of MVVM Cross are: It has an excessive learning curve and lacks a Wiki for how to get started developing the apps. MVVM Light: MVVM Light is another Framework that allows the creation of Enterprise-Grade apps using the MVVM Architectural pattern on Xamarin. MVVM Light enables the developer to create and develop MVVM applications on a variety of platforms like Xamarin. Forms, Xamarin.Android, Xamarin.iOS, UWP, and WPF. It allows us to separate the View from Model and hence write the testable and extensible applications. It does not support async. MVVM Light application is divided into the following parts:
35) What is the need of the Model-View-ViewModel (MVVM ) pattern in Xamarin?The Model-View-ViewModel can be used on all platforms. It intends to provide a clean separation between the user interface controls and their logic. 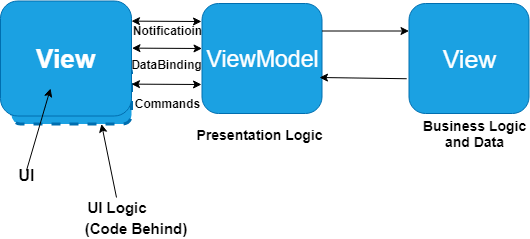
Benefits:
36) What is NuGet and how this can be useful in App development?NuGet is the most popular package manager for the development in .Net. It is present in Xamarin Studio 5 and Visual Studio. We can easily search and add package/third party libraries to the Xamarin.Forms using IDE. 37) What is the HTTP client?HTTPClient helps the developers to connect with the external world through the internet using the REST-based services. HTTPClient class is used for sending the HTTP requests and receiving HTTP response from a resource, which is identified by URI. HTTPClient class present in System.Net.HTTP namespace. 38) What is ResourceDictionary?ResourceDictionary is used to define the XAML Resources, which can be reused more than once throughout the Xamarin.Forms application.
39) What is the difference between Xamarin. Forms and Xamarin Native?Xamarin.Forms : Xamarin.Forms are used when:
Xamarin Native: Xamarin Native is used when:
40) What is the App.cs class?App.cs is the main class of the App which offers features like: MainPage: It helps us to set the initial page of the App. Properties Dictionary: It helps us to store the values across the state of the lifecycle. Static Current Property: It gives the instance of the current application object 41) What is the lifecycle method of the Xamarin.Forms App?Lifecycle methods are the set of techniques which are executed when the application enters into a specific state. The ways are:
42) What is the purpose of XAML compiler (XALC)?Using the XAML compiler, we can directly compile XAMLs into intermediate (IL) language. Benefits:
43) What is XAML namespace declaration?XAML namespace is the declaration of the namespaces on top of the XAML file. There are two declarations available within the root element when we create any new XAML UI. Here is the default declaration of the xmlns without any prefix: The second declaration uses the x prefix: All declaration of the namespace which uses the prefix is a non-default declaration. Suppose we want to bind the ViewModel with XAML and that ViewModel is declared inside the namespace, "XamSample.ViewModels". Then we can access the element from inside this namespace using VM prefix. 44) What is the way of navigation from one page to another?After clicking on the button of the first page, we call the following method through which we can navigate from one page to another page. We have to use the "Navigation" page property which is available under the ContentPage class. This code is written in the coding page of the MainPage.XAML file. 45) What is ViewCell?A ViewCell is a small individual element which represents a single item of the ListView or Table. A ViewCell is not a visual element, but it is a description of the template which creates the visual aspect. 46) What are the types of Built-in cells?The types of built-in cells are:
47) What is the difference between ControlTemplate and DataTemplate?ControlTemplate: This template decides how the control should look. It defines the representation style for control. For example, A Button can contain Image and Text. 48) What are the triggers? How many types of triggers are available?Triggers allow us to declare actions in XAML, which changes the appearance of the control when specific condition met for a particular property of the control. We can add triggers at control-level, page-level, or application-level in the resource dictionary. Here are the four types of triggers available. These are:
49) What is hockey app?Hockeyapp offers the testing service for iOS, Android, and Windows phone. 50) What is TestFlight?Apple is the owner of the TestFlight. This is the primary way of the beta test of our Xamarin.iOS apps. 51) What are the types to create the Xamarin applications?Here, are the three ways to build the apps in Xmarin. |
You may also like:
- Java Interview Questions
- SQL Interview Questions
- Python Interview Questions
- JavaScript Interview Questions
- Angular Interview Questions
- Selenium Interview Questions
- Spring Boot Interview Questions
- HR Interview Questions
- C Programming Interview Questions
- C++ Interview Questions
- Data Structure Interview Questions
- DBMS Interview Questions
- HTML Interview Questions
- IAS Interview Questions
- Manual Testing Interview Questions
- OOPs Interview Questions
- .Net Interview Questions
- C# Interview Questions
- ReactJS Interview Questions
- Networking Interview Questions
- PHP Interview Questions
- CSS Interview Questions
- Node.js Interview Questions
- Spring Interview Questions
- Hibernate Interview Questions
- AWS Interview Questions
- Accounting Interview Questions







