XOR and XNOR operators in JavaOne of the Bitwise operators offered by Java is XOR. Two boolean operands are given to the XOR (also known as exclusive OR), which returns true if they are different. When neither of the two boolean conditions supplied can be true simultaneously, the XOR operator is most useful. XOR Operator in Java (Exclusive OR)The carrot ( ) symbol denotes the XOR operator. If two values are provided, it returns true when they differ; else, it returns false. True gets represented by 1 in binary, whereas false gets represented by 0. The XOR operator's truth table is shown below: 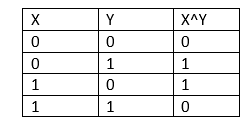
As we can see from the above table, it only returns true if the values of both operands differ. Otherwise, false is returned. Let's use an illustration to clarify it: A good XOR operator example Consider the illustration below: XorExpl1.java Output: 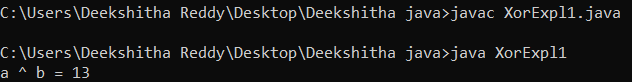
XNOR operatorThe opposite of the binary equivalent of XOR is given by XNOR. Truth table: 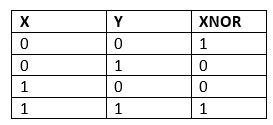
If the bits are the same, it returns 1, else it returns 0. Examples: Input: 10 20 Output : 1 A Binary of 20 is 10100 A Binary of 10 is 1010 So the XNOR is 00001 So the output is 1 Input : 10 10 Output : 15 A Binary of 10 is 1010 A Binary of 10 is 1010 So the XNOR is 1111 So the output is 15 Method 1:- (O(logn))In this solution, each bit is checked separately. If two bits match, we output 1; otherwise, we output 0. Let's explain it using the following code. XNORExpl1.java Output: 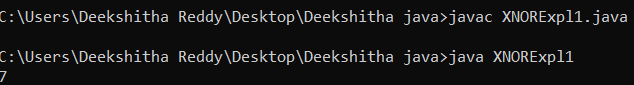
Second Method:- O(1)
XNORExpl2.java Output: 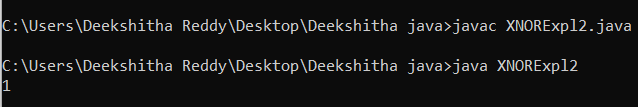
Third Method: Using XORSimply said, A XOR B is the opposite of XNOR of A and B. A bit mask must be created in order to only retrieve the real bits from an inverted binary number because directly inverting any binary number also flips the leading zeroes. Below is an example of this implementation: XNORExpl3.java Output: 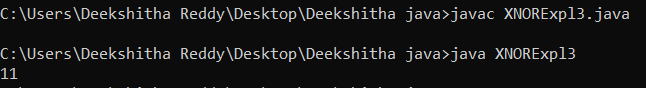
Time Complexity: O(1) Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Next TopicAWS Lambda in Java
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










