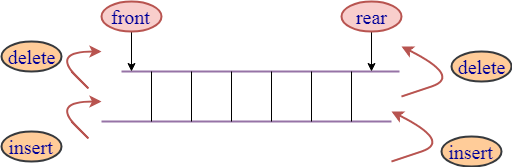
Deque stands for double ended queue. It generalizes the queue data structure i.e insertion and deletion can be performed from both the ends either front or back.
| Method |
Description |
| assign() |
It assigns new content and replacing the old one. |
| emplace() |
It adds a new element at a specified position. |
| emplace_back() |
It adds a new element at the end. |
| emplace_front() |
It adds a new element in the beginning of a deque. |
| insert() |
It adds a new element just before the specified position. |
| push_back() |
It adds a new element at the end of the container. |
| push_front() |
It adds a new element at the beginning of the container. |
| pop_back() |
It deletes the last element from the deque. |
| pop_front() |
It deletes the first element from the deque. |
| swap() |
It exchanges the contents of two deques. |
| clear() |
It removes all the contents of the deque. |
| empty() |
It checks whether the container is empty or not. |
| erase() |
It removes the elements. |
| max_size() |
It determines the maximum size of the deque. |
| resize() |
It changes the size of the deque. |
| shrink_to_fit() |
It reduces the memory to fit the size of the deque. |
| size() |
It returns the number of elements. |
| at() |
It access the element at position pos. |
| operator[]() |
It access the element at position pos. |
| operator=() |
It assigns new contents to the container. |
| back() |
It access the last element. |
| begin() |
It returns an iterator to the beginning of the deque. |
| cbegin() |
It returns a constant iterator to the beginning of the deque. |
| end() |
It returns an iterator to the end. |
| cend() |
It returns a constant iterator to the end. |
| rbegin() |
It returns a reverse iterator to the beginning. |
| crbegin() |
It returns a constant reverse iterator to the beginning. |
| rend() |
It returns a reverse iterator to the end. |
| crend() |
It returns a constant reverse iterator to the end. |
| front() |
It access the last element. |