Alternative to Ubuntu
To get a better understanding of the alternatives that Ubuntu has, first, it is required to know what exactly Ubuntu is and its features.

Ubuntu

Ubuntu is a well-known open-source operating system based on the Linux kernel. It was first launched in 2004 by Canonical Ltd., a firm dedicated to promoting an accessible and user-friendly computer environment.
Ubuntu's emphasis on usability and accessibility is one of its most distinguishing aspects. It is designed to be user-friendly, making it a good alternative for both novice and expert users of Linux-based devices.
The operating system is available in numerous flavours, each adapted to a particular purpose. For example, the basic edition, Ubuntu Desktop, is suitable for personal and professional usage, with a user-friendly interface and diverse pre-installed programs.
Ubuntu Server is another variation designed primarily for server environments. It is highly regarded for its dependability, robust security measures, and support for cloud-based applications.
Furthermore, Ubuntu is highly adaptable, allowing users to change and tweak it to meet their requirements. Its open-source nature fosters a large community of developers and users who contribute to its advancement by developing applications, offering support, and constantly improving its capabilities.
Because of its dependability, security, and cost-effectiveness, Ubuntu has received extensive popularity in various fields, ranging from individual users looking for an alternative to Windows or macOS to corporations and organizations deploying it on servers and in cloud environments.
It is well-known for its frequent upgrades, ensuring customers can access the most up-to-date software and security patches. Furthermore, Ubuntu has a large software repository, allowing users to easily install, update, and manage apps.
Ubuntu has greatly affected operating systems by providing a robust, accessible, and open-source alternative that prioritizes user-friendliness, security, and flexibility.
Features Of Ubuntu

As an operating system, Ubuntu provides a diverse set of features that contribute to its popularity and usability. Here are some of its significant characteristics:
- User-Friendly Interface: Ubuntu has an intuitive and user-friendly interface that makes it accessible to novice and advanced users. The graphical user interface is intended to be simple and easy to use.
- Open-Source and Free: Ubuntu is an open-source operating system distributed for free. This means the source code is available to users, allowing them to alter, customize, and contribute to its development.
- Software Center: It contains a Software Centre, which allows users to effortlessly find, install, and update a wide range of software applications. This central repository makes software management easier.
- Variants for Different Purposes: Ubuntu offers various varieties, such as Ubuntu Desktop, Ubuntu Server, and specialized editions, such as Ubuntu for IoT (Internet of Things) and Ubuntu Core, tailored for specific demands and purposes.
- Customization: Users can customize and adjust Ubuntu to meet their interests and needs. The system allows for extensive customization, allowing users to tailor their computer experience.
- Strong Community Support: Ubuntu has a vast, active developer and user community. This community assistance assists in problem resolution, provides guidance, and contributes to the operating system's continued growth and improvement.
These characteristics make Ubuntu a highly functional, dependable, and versatile operating system ideal for various applications, from personal desktop use to enterprise-level server installations.
Alternatives To Ubuntu

Here are five prominent Ubuntu alternatives, each with its own unique set of features and user base:
- Linux Mint
- Debian
- Fedora
- openSUSE
- Manjaro
LinuxMint
Linux Mint is a widespread Linux distribution that is an excellent alternative to Ubuntu, particularly for people who prefer a familiar and user-friendly interface. Based on Ubuntu, Linux Mint prioritizes usability, stability, and a professional desktop experience. Here are a few crucial points:

User Interface and Experience:
- Cinnamon Desktop Environment: The Cinnamon desktop environment, which offers a classic, intuitive, and highly customizable interface, is the primary feature of Linux Mint. Cinnamon is similar to the traditional desktop paradigm, making it suitable for users migrating from Windows.
- Familiarity: Linux Mint's layout and design are intended to deliver a familiar experience, imitating the classic desktop-style with a taskbar, start menu, and system tray. This familiarity may make users accustomed to Windows operating systems appealing.
Software and Package Management:
- Software Manager: Linux Mint features a Software Manager that streamlines program installation and management. A curated repository allows users to explore, install, and update many applications effortlessly.

- Compatibility with Ubuntu Repositories: Because Linux Mint is built on Ubuntu, it is compatible with Ubuntu repositories, giving users access to a wide range of software packages accessible in the Ubuntu ecosystem.
Stability and Performance:
- Long-Term Support (LTS): Linux Mint typically provides LTS releases, which ensure stability and long-term support for customers who prefer fewer system upgrades and a more consistent environment.
- Resource Efficiency: It is considered lightweight and efficient, which suits older hardware or systems with lower requirements.
Community and Help:
- Community and Documentation: The Linux Mint community is active and helpful, offering support, forums, and copious documentation. Users may quickly find solutions to problems and instructions for customizing their system.
Personalization and adaptability:
- Options for Customization: While giving a familiar experience, Linux Mint allows for extensive customization. Users can customize their desktops with various themes, applets, and plugins.
- System Stability: Linux Mint is well-known for being a stable and dependable operating system, making it a good choice for novice and seasoned Linux users.
Debian:

Ubuntu is based on Debian and is known for its dedication to free software values and stability. It's a robust and adaptable operating system that's more conservative with upgrades, making it a good choice for servers and users looking for a rock-solid, dependable platform. Debian has a distinct approach and has a different set of characteristics:
Philosophy and Stability:
- Stability and Reliability: Debian is well-known for its dependability. It takes a cautious approach to upgrades, focusing on adequately tested and stable software packages. As a result, it is a popular choice for servers and mission-critical systems.
Community-Driven:
- Open Source Philosophy: Debian's dedication to free software and open-source ideas has helped shape the greater open-source community. It places a premium on democratic decision-making and the use of free software.
Software Packaging and Release Cycle:
- Package Management: Debian uses APT (Advanced Package Tool) to manage packages. APT makes it easier to install, update, and remove software.
- Multiple Releases: Debian provides several release branches, including Stable, Testing, and Unstable. Stable, also known as Debian "stable," is the main release that focuses on dependability and stability. Testing and Unstable are more recent but perhaps less stable.
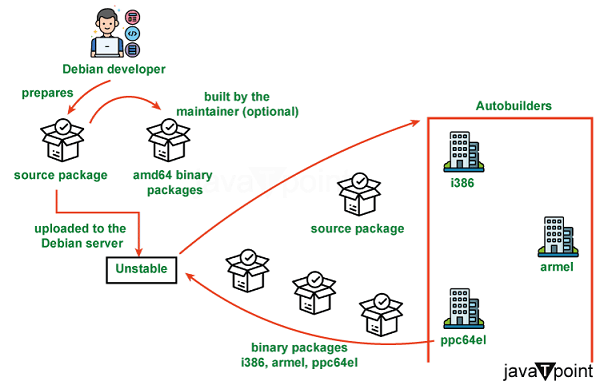
Customization and Flexibility:
- Desktop Environments: Debian does not impose a particular desktop environment but instead gives various options such as GNOME, KDE, Xfce, and others, allowing users to choose best.
- Extensive Software Repositories: It has a massive repository comprising hundreds of pre-compiled software packages, allowing users to install various programs.
Community and Help:
- Large Community: Debian has an active user and developer community contributing to support, documentation, and continuing development.
- Documentation and Stability: Debian's emphasis on stability provides robust documentation and strength, making it suited for experienced users who prefer a more conservative approach to system updates.
Fedora
Fedora is a cutting-edge Linux distribution sponsored by Red Hat. It focuses on combining advanced technologies and provides a rapid development cycle. Fedora suits people looking for the most up-to-date software features and innovations.
Fedora has a unique collection of features and principles:
Cutting-Edge Functions:
- Innovative and Current Software: Fedora prioritizes incorporating cutting-edge software, technologies, and features. It acts as a testing environment for new improvements that may appear in Red Hat Enterprise Linux in the future.
- Fast Development Cycle: Fedora has a reasonably speedy development cycle, allowing users to rapidly obtain new features and enhancements.
GNOME Desktop Environment:
- GNOME Desktop Environment: Fedora Workstation primarily employs the GNOME desktop environment, which provides a modern and user-friendly interface.
- Software Selection: It provides a selected assortment of software, providing a functioning and modern environment without overwhelming customers with many pre-installed programs.

Security and Community:
- Security Features: Fedora prioritizes security, employing a variety of security precautions by default and continuously upgrading its software to safeguard users from potential vulnerabilities.
- Community-Driven Development: It thrives on the contributions of a thriving community, with active participation from both users and developers.
Package Administration and Philosophy:
- Package Management System: Fedora uses the DNF (Dandified Yum) package manager, facilitating programme installation, upgrading, and removal.
- FOSS Philosophy: Fedora is dedicated to free and open-source software ideals, and by default, only open-source apps and tools are provided.
Versatility and customization:
- Modularity: Fedora emphasizes modularity, allowing users to tailor their environment to their unique requirements, from desktop users to developers and system administrators.
openSUSE:

OpenSUSE is well-known for its reliability and user-friendliness, and it offers two primary distributions: openSUSE Leap and openSUSE Tumbleweed. Tumbleweed is a rolling-release version constantly updated with the latest software, whereas Leap is more reliable and provides regular releases. openSUSE, a Linux distribution, stands out as an alternative to Ubuntu by offering a unique approach and a fantastic set of features.
Various Distributions:
- openSUSE Leap: A stable release that adheres to a regular development cycle emphasizing dependability and consistency. It offers a high-quality operating system with extended support periods.
- openSUSE Tumbleweed: A rolling-release version regularly updated to provide the most recent stable software versions. It's perfect for people who wish to always have the latest software updates.
Package Administration:
- Zypper Package Manager: Zypper is used for package management in openSUSE. This program makes software installation, updates, and uninstallation easier.

- YaST: (Yet Another Setup Tool) is a robust, all-in-one system administration tool unique to openSUSE, allowing users to easily configure and maintain the system.

Versatile Desktop Environments:
- KDE and GNOME: openSUSE supports, among others, the KDE and GNOME desktop environments, allowing users to select their favourite interface.
Features and tools:
- openQA Testing: It is an automated testing framework used in openSUSE to ensure system reliability.
- Snapper: A robust utility for managing file system snapshots, allowing for simple system rollbacks and ensuring system integrity.
Community and Help:
- Active Community: openSUSE has a thriving user and developer community contributing to documentation, forums, and continuous development.
- Documentation and Support: The distribution includes extensive documentation and support materials to help users navigate the system and troubleshoot problems.
Manjaro:

Based on Arch Linux, Manjaro attempts to create a user-friendly operating system without sacrificing Arch's strength and flexibility. It is well-known for its user-friendly approach and provides stable, rolling-release versions to accommodate various user preferences. Manjaro is a user-friendly, rolling-release Linux distribution that offers multiple distinct features and qualities as an alternative to Ubuntu:
Constant upgrades:
- Constant Updates: Manjaro uses a rolling-release architecture to regularly upgrade the system and applications. This allows customers to always have access to the most recent software versions without the need for substantial upgrades.
- Stability and Freshness: Manjaro's rolling-release strategy balances system stability with the availability of new features, making it appealing to customers who desire up-to-date software and a reliable system.

User Interface and Customization:
- Desktop Environment Support: Manjaro supports a variety of desktop environments, including Xfce, KDE, and GNOME, allowing users to choose the interface that best meets their needs.
- Customization: It provides considerable customization possibilities, allowing users to modify their desktop experience with themes, extensions, and settings.
Pacman Package Manager:
- Pacman Package Manager: Pacman, a fast and efficient package manager for installing, updating, and deleting software, is used by Manjaro for package management.

- Access to AUR: Access to the Arch User Repository (AUR), a massive community-driven repository featuring a wide range of software packages unavailable in official repositories, is one distinguishing characteristic. This increases the number of software options available to users.
Community and Help:
- Active Community: Manjaro has an active community that contributes to forums, wikis, and help channels, making it easier for users to find solutions and guidance.
- Documentation and Support: The distribution includes extensive documentation to assist users in navigating the system and resolving any issues that may arise.
Accessibility and Usability:
- User-Friendly Approach: Manjaro is designed to be accessible and user-friendly, providing a simple experience for new and seasoned Linux users.
- Hardware Compatibility: It has high hardware compatibility, making it appropriate for a wide range of devices and systems.
Conclusion
The Linux ecosystem includes various distributions, each with its traits and techniques. Ubuntu, a user-friendly operating system with significant community support, prioritizes reliability, usability, and a wide range of software options. It is suitable for novice and experienced users and provides a solid foundation for various applications, from personal desktop use to server installations. Debian, the fundamental distribution from which Ubuntu is derived, prioritizes reliability, uses a conservative updating methodology, and strictly adheres to free software ideals. It offers adaptability in desktop environments and is well-liked for its dependability and support.
On the other hand, Fedora appeals to consumers who appreciate cutting-edge technological integration, a fast-paced release cycle, the latest software developments, and a robust, developer-friendly environment. With its Leap and Tumbleweed versions, openSUSE allows users a stable, enterprise-grade system or a regularly updated rolling-release model. It is well-known for its robust management features, support for a wide range of desktop environments, and an active community. Meanwhile, using a rolling-release model, Manjaro seeks a compromise between system stability and up-to-date software. Manjaro provides a new yet trustworthy Linux experience for those wanting the latest software updates in a stable environment, thanks to its user-friendliness, comprehensive customization options, access to the enormous Arch User Repository (AUR), and an active community. Each of these distributions caters to distinct user tastes, ranging from stability to bleeding-edge innovation, and provides solutions for diverse user demands within the Linux ecosystem.
|












 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now














