Operating System Tutorial
Operating System Tutorial provides the basic and advanced concepts of operating system . Our Operating system tutorial is designed for beginners, professionals and GATE aspirants. We have designed this tutorial after the completion of a deep research about every concept. The content is described in detailed manner and has the ability to answer most of your queries. The tutorial also contains the numerical examples based on previous year GATE questions which will help you to address the problems in a practical manner. Operating System can be defined as an interface between user and the hardware. It provides an environment to the user so that, the user can perform its task in convenient and efficient way. The Operating System Tutorial is divided into various parts based on its functions such as Process Management, Process Synchronization, Deadlocks and File Management. Operating System Definition and FunctionIn the Computer System (comprises of Hardware and software), Hardware can only understand machine code (in the form of 0 and 1) which doesn't make any sense to a naive user. We need a system which can act as an intermediary and manage all the processes and resources present in the system. 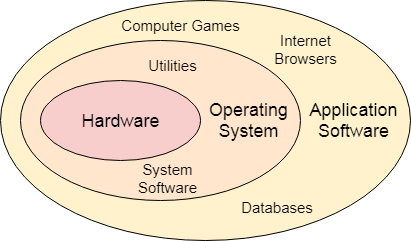
An Operating System can be defined as an interface between user and hardware. It is responsible for the execution of all the processes, Resource Allocation, CPU management, File Management and many other tasks. The purpose of an operating system is to provide an environment in which a user can execute programs in convenient and efficient manner. Structure of a Computer SystemA Computer System consists of:
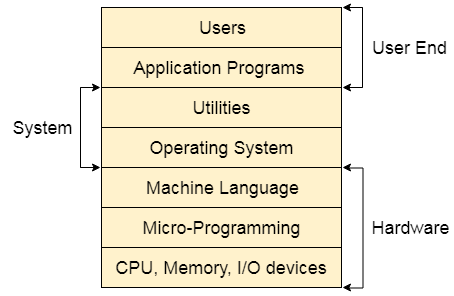
What does an Operating system do?
Operating System IndexOperating System Tutorial Process Management
Synchronization
Deadlocks
Memory Management
File Management
PrerequisitesBefore learning the operating system tutorial, you must have the basic knowledge about the way in which a computer system operates. AudienceOur operating system tutorial is designed to help beginners, professionals and GATE aspirants. ProblemWe can assure you that you will not find any problem in this operating system tutorial. However, if you find any, you can post the problem in the contact form.
Next TopicTypes Of Operating Systems
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









