What is the full form of CPUCPU: Central Processing UnitCPU stands for Central Processing Unit. It is also known as the brain of the computer. It carries out instructions and computer programs and performs all the basic arithmetical and logical operations. CPU is installed in the motherboard on a specific area known as the CPU socket. Traditionally the term CPU refers to a processor, which includes a control unit and an arithmetical logical unit. Central Processing Unit (CPU) = Arithmetical Logical Unit (ALU) + Control Unit (CU)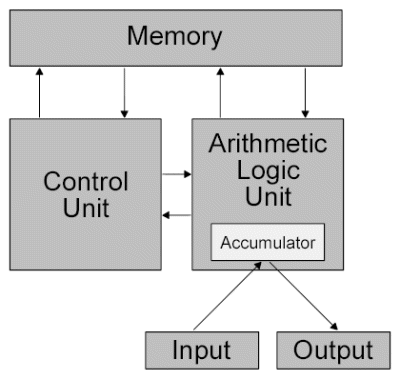
Components of CPUsArithmetical Logic Unit: This is a key part of the CPU. This is responsible for performing all the logical and arithmetical operations. The responsibility for performing arithmetic and logical operations falls to the ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit). It has two subsections, which are as follows:
Let us learn more about these subsections now: Arithmetic Section: Addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division are examples of arithmetic operations, and the ALU is responsible for carrying out all of these tasks. Additionally, the ALU uses the aforementioned procedures repeatedly to complete all complex computations. Logic Section: The ALU is responsible for performing all logical processes, which include choosing, comparing, matching, and merging data. Note: The CPU may have multiple ALUs, and ALUs can be utilised to keep timers that aid in the operation of the computer system.Control Unit: It is the most important part of the CPU. It instructs the complete computer system to carry out a particular task. A control unit does not handle any data; rather, it controls how each component of the computer operates, as the name suggests. It gives the computer instructions to carry out previously saved data by using electrical impulses to communicate with the computer system. It pulls instructions from the memory unit, decodes them, and then carries out the commands. As a result, it manages how the computer operates. Its primary responsibility is to keep information moving freely throughout the CPU. Here is a list of several of the main responsibilities that the control unit has:
Registers: Registers are a special type of memory device. They store the data that have to be processed and are already processed by the processor. Types of CPUsCPUs can be divided into three major categories:
HistoryThe term CPU was first used in the computer industry in the early 1960s. Initially, the term CPU was used to define a device for software execution, and it came with the advent of the stored program computer. Some of the important events related to the history of CPU are as follows:
Next TopicFull Form
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









