What is Access Token in Operating SystemAn access token is an object that describes the security context of a process or thread. A token is used to make security decisions and store tamper-proof information about some system entity. While a token is generally used to represent only security information, it can hold additional free-form data attached while the token is created. Tokens can be duplicated without special privilege, for example, creating a new token with lower access rights to restrict the access of a launched application. An access token is used by Windows when a process or thread tries to interact with objects that have security descriptors. In Windows, an access token is represented by the system object of the type of the token. In a token, the information includes the identity and privileges of the user account associated with the process or thread. An access token is generated by the logon service when a user logs on to the system, and the credentials provided by the user are authenticated against the authentication database. The authentication database contains credential information required to construct the initial token for the logon session, including its user id, primary group id, and other information. The token is attached to the initial process created in the user session and inherited by subsequent processes created by the initial process. Whenever a process opens a handle to any resource which has access control enabled, Windows reconciles the data in the target object's security descriptor with the contents of the current effective access token. The result of this access check evaluation indicates whether any access is allowed and, if so, what operations (read, write/modify, etc.) the calling application is allowed to perform. Uses of Access TokenThe system uses an access token to identify the user when a thread interacts with a securable object or tries to perform a system task that requires privileges. Access tokens are the thing that applications use to make API requests on behalf of a user. The access token represents the authorization of a specific application to access specific parts of a user's data. Access tokens contain the following information:
Example of Access TokenThis example shows the contents of an access token. The token only contains authorization information about the application's actions at the API, and such permissions are referred to as scopes.
{
"iss": "https://my-domain.auth0.com/",
"sub": "auth0|123456",
"aud":
[
"https://example.com/health-api",
"https://my-domain.auth0.com/userinfo"
],
"azp": "my_client_id",
"exp": 1311281970,
"iat": 1311280970,
"scope": "openid profile read:patients read:admin"
}
Elements of Access TokenA typical access token holds three distinct parts, all working together to verify a user's right to access a resource. Following three key elements are included in most access tokens. 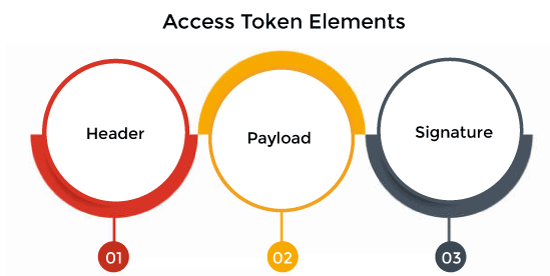
Types of Access TokenThere are two types of access tokens available in the operating system, primary token and impersonation token. Every process has a primary token that describes the security context of the user account associated with the process. By default, the system uses the primary token when a process thread interacts with a securable object. Moreover, a thread can impersonate a client account, and impersonation allows the thread to interact with securable objects using the client's security context. A thread that impersonates a client has both a primary token and an impersonation token. 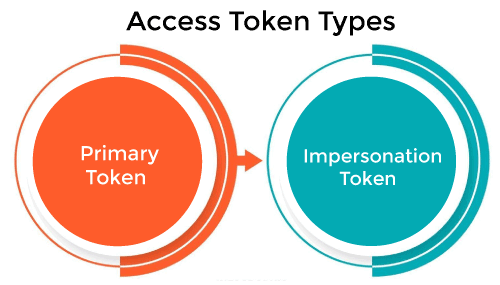
1. Primary Token Primary tokens can only be associated with processes, and they represent a process's security subject. The creation of primary tokens and their association to processes are both privileged operations, requiring two different privileges in the name of privilege separation. The typical scenario sees the authentication service creating the token and a logon service associating it to its operating system shell. Processes initially inherit a copy of the parent process's primary token. 2. Impersonation Token Impersonation is a security concept implemented in Windows NT that allows a server application to temporarily be the client in terms of access to secure objects. Impersonation has four possible levels:
The client can choose the maximum impersonation level (if any) available to the server as a connection parameter. Delegation and impersonation are privileged operations. Impersonation tokens can only be associated with threads, and they represent a client process's security subject. Impersonation tokens are implicitly created and associated with the current thread by IPC mechanisms such as DCE RPC, DDE, and named pipes. How do Access Tokens work?Users don't write their own access codes. Servers communicate with devices, and all the work completes easily in a few time. You need to follow the following set of steps, such as:
You can also use access tokens for single sign-on (SSO). Your credentials from one site become your key to enter another. Only you need to follow the following steps, such as:
Requests for SSO expire quickly. Most requests expire within about 10 minutes, but some shut down the process after just 60 seconds. Security of Access TokensAccess tokens should be protected as they move through the open space of the internet. Companies that don't use encryption or protected communication channels could allow third parties to grab tokens, meaning unauthorized access to very sensitive data. It pays to be very careful. Most access tokens also expire. That simple step allows websites to ensure users are still online and active, which could help avoid large-scale duplication or deletion. Expiration dates can vary from company to company. |
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










