Multi-User Operating SystemIn this article, you will learn about the multi-user operating system, types, working with its advantages and disadvantages. What is Multi-User Operating System?A multi-user operating system is an operating system that permits several users to access a single system running to a single operating system. These systems are frequently quite complex, and they must manage the tasks that the various users connected to them require. Users will usually sit at terminals or computers connected to the system via a network and other system machines like printers. A multi-user operating system varies from a connected single-user operating system in that each user accesses the same operating system from different machines. 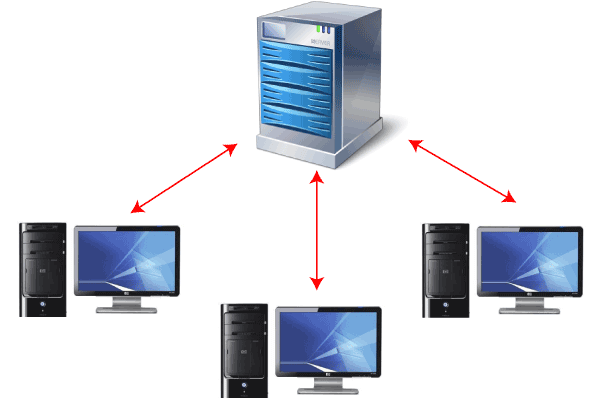
The main goal of developing a multi-user operating system is to use it for time-sharing and batch processing on mainframe systems. This multi-user operating system is now often used in large organizations, the government sector, educational institutions like large universities, and on servers' side such as Ubuntu Server or Windows Server. These servers allow several users to access the operating system, kernel, and hardware at the same time. It is usually responsible for handling memory and processing for other running programs, identifying and using system hardware, and efficiently handling user interaction and data requests. It's especially important for an operating system, a multi-user operating system because several users rely on the system to function properly at the same time. Components of Multi-User Operating SystemThere are various components of a multi-user operating system. Some of them are as follows: MemoryThe physical memory present inside the system is where storage occurs. It is also known as Random Access Memory (RAM). The system may rectify the data that is present in the main memory. So, every executed program should be copied from physical storage like a hard disk. Main memory is determined as an important part of OS because it specifies how many programs may be executed simultaneously. KernelA multi-user operating system makes use of the Kernel component, which is built in a low-level language. This component is embedded in the computer system's main memory and may interact directly with the system's H/W. ProcessorThe CPU (Central Processing Unit) of the computer is sometimes known as the computer's brain. In large machines, the CPU would necessitate more ICS. On smaller computers, the CPU is mapped in a single chip known as a microprocessor. User InterfaceThe user interface is the way of interaction between users and all software and hardware processes. It enables the users to interact with the computer system in a simple manner. Device HandlerEach input and output device needs its device handler. The device handler's primary goal is to provide all requests from the whole device request queue pool. The device handler operates in continuous cycle mode, first discarding the I/O request block from the queue side. SpoolerSpooler stands for 'Simultaneous Peripheral Output on Line'. The Spooler runs all computer processes and outputs the results at the same time. Spooling is used by a variety of output devices, including printers. Types of Multi-User Operating SystemThere are various types of multi-user operating systems. Some of them are as follows: Distributed SystemA distributed system is also known as distributed computing. It is a collection of multiple components distributed over multiple computers that interact, coordinate, and seem like a single coherent system to the end-user. With the aid of the network, the end-user would be able to interact with or operate them. Time-Sliced SystemsIt's a system in which each user's job gets a specific amount of CPU time. In other words, each work is assigned to a specific time period. These time slices look too small to the user's eyes. An internal component known as the 'Scheduler' decides to run the next job. This scheduler determines and executes the job that must perform based on the priority cycle. Multiprocessor SystemMultiple processors are used in this system, which helps to improve overall performance. If one of the processors in this system fails, the other processor is responsible for completing its assigned task. How to work the Multi-User operating system?The single master system is contained within the multi-user system. All network users can access the master system anytime and from any place and open their local version of the system. The local version is also known as a 'working model'. All users can update, delete, and create new files on their local working model, but this model will not be available to other users until it is saved to the master system. Characteristics of Multi-User Operating SystemThere are various characteristics of a multi-user operating system. Some of them are as follows: Resource SharingSeveral devices, like printers, fax machines, plotters, and hard drives, can be shared in a multi-user operating system. Users can share their own documents using this functionality. All users are given a small slice of CPU time under this system. Multi-TaskingMulti-user operating systems may execute several tasks simultaneously, and several programs may also execute at the same time. Background ProcessingBackground processing is a term that refers to when commands are not processed but rather executed "in the background". Usually, other programs interact with the system in real-time. Time-SharingA strategy used by multi-user operating systems to operate on several user requests at the same time by switching between jobs at very short periods of time. SystemThe operating system must handle a computer's combination of hardware and software resources. InvisibilityVarious functions of the multi-user operating system are hidden from users. It is due to factors such as the OS being instinctive or happening at the lower end, such as disk formatting, etc. Examples of Multi-User Operating SystemThere are various examples of multi-user operating systems. Some of them are as follows: UnixA highly dependable open system architecture for small and medium-scale business computing systems. Because it is based on Open System Architecture, tech giants including AIX, Solaris, and even Mac OS have their own version of Unix. For example, the Hospitality industry, Healthcare, etc. Multiple Virtual StorageIBM develops an operating system for use on mainframe systems. It's commonly utilized in enterprise computing, where high-intensity I/O is required. For example, Banking, Insurance, Aviation business, etc. Shared ComputingA multi-user OS is a software that operates the servers that support most webmail apps. A typical webmail application may require the utilization of hundreds of computers. Each one runs a multi-user operating system capable of supporting various users at the same time. Because these systems have millions, if not billions, of users who constantly log on to check their messages, they require operating systems that can handle a high number of users at once. Advantages and Disadvantages of Multi-User Operating SystemThere are various advantages and disadvantages of a multi-user operating system. These are as follows: AdvantagesThere are various advantages of a multi-user operating system. Some of the advantages are as follows:
Disadvantages of Multi-User Operating SystemThere are various disadvantages of a multi-user operating system. Some of the disadvantages are as follows:
Next TopicMemory Management
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










