Operating System ExamplesOverviewAn operating system is typically the initial piece of software we use while utilizing computers, laptops, cellphones, video game consoles, or other similar electronic devices. Every contemporary computing device uses an operating system as its primary piece of software, enabling users to operate the corresponding device invisibly. A number of operating systems are available that are made to support and run on a variety of hardware configurations. In this article, we'll talk about a few of the most well-liked operating system types that can be applied to various devices in order to meet particular needs. But first, let's quickly go over what an operating system is before we talk about some examples of them. What is an Operating System?"An operating system" is defined as "a particularly designed program or software that works as an interface between the computer hardware and the user while executing all the basic operations or functioning of a computer," including managing memory, connecting I/O devices, processes, files, and so on. Computer hardware must have at least one operating system installed in order to execute other programs like browsers or conduct other fundamental tasks. Users have the freedom to install the desired operating system in accordance with their preferences. Therefore, the choice of the operating system on desktop and laptop computers might vary based on the user's interests. However, this isn't necessarily true of other technology, particularly mobile technology. The majority of electronic devices, including smartphones, tablets, game consoles, and other similar gadgets, come pre-installed with an operating system that was created by the device's creator exclusively for that particular gadget. No alternative operating system can be installed on such devices at the request of the user. Only if the manufacturer offers an update to a newer version is it possible. But individuals with in-depth programming and development experience can modify some of these gadgets in this way. What are some operating system examples?Today, a variety of operating systems are available for use on different devices, including mobile phones, laptops, tablets, and so on, and even the newest ones are developing unique characteristics. The following list includes some of the best and most prominent examples of well-known operating systems, despite the fact that there are several operating systems for various devices with various features: MICROSOFT WINDOWSThe Windows operating system has seen numerous minor updates and significant upgrades since its debut in 1985. As a GUI-based upgrade or addition to MS-DOS, Windows 1.0 was originally made available in 1985. MS-DOS was a command-line operating system that was developed in 1981 and was primarily intended for IBM machines. Despite DOS's declining popularity today, users still often use the Windows OS' command shell, also known as Windows Command Line. 
The first Windows operating system to be offered as a standalone OS was Windows 95, which was introduced in 1995. With its intuitive user interface, it helped to drive the quick development of personal computing. Despite the fact that Windows 95 gave the impression to be an operating system unto itself, DOS nevertheless ran in the background because Windows 95 was built on top of it. Microsoft moved away from DOS and toward the contemporary 32-bit Windows NT kernel with the release of Windows XP in 2001. 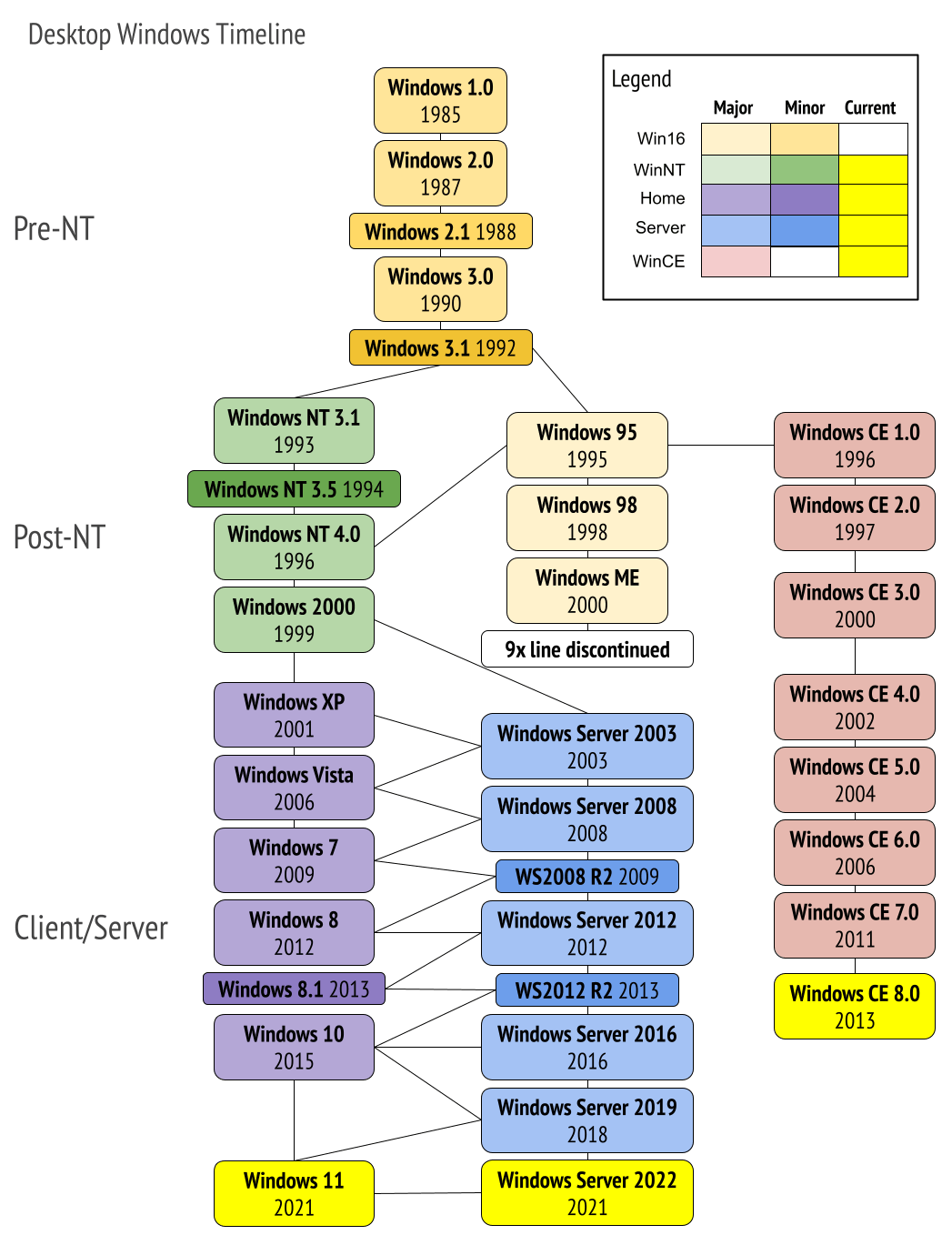
Since then, Windows OS has grown in popularity as one of the top desktop and laptop operating systems worldwide. Nowadays, Microsoft Windows OS is preinstalled on the majority of contemporary devices. Additionally, certain mobile devices include Windows Mobile OS. However, customers did not like Windows' compatibility and usefulness on mobile devices as much as was anticipated. Up to this point, Microsoft has created, promoted, and sold a variety of Windows operating systems, including Windows 95, Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7/8/10/11, etc. ANDROIDRegarding the number of installed devices, Android is now the most widely used operating system worldwide. Android has grown to be one of the key operating systems that compete with Windows and Apple's while being primarily built for mobile (smartphones and tablets). A customized Linux kernel, along with certain open-source software, is used to create this mobile operating system. Google financially supports the Open Handset Alliance, a group of programmers who create the Android operating system. With the first commercial Android smartphone, the HTC Dream, Android (version 1.0) was initially made available in 2008. Since then, it has grown significantly in popularity and keeps expanding thanks to wonderful new features. Android OS, in contrast to iOS, is available to numerous handset makers, not only Google. Additionally, the makers have the ability to alter various OS components to add particular features that best suit their requirements or to make the OS simpler for users to use. Users can also install unique variations of operating systems that they or other developers have changed. However, the majority of customers like using the official OS offered by the relevant manufacturer because of its consistent performance, increased security, and warranty requirements. The Google Play Store offers a huge selection of mobile applications that Android users may choose from and download. iOSEven though it was created particularly for Apple mobile devices like the iPhone, iPad (which now has its own iPadOS), and iPod Touch, iOS, originally known as iPhone OS, is the second most commonly used and installed mobile operating system behind Android. Apple is the only company that develops and maintains iOS; it is not made available to other manufacturers. In 2010, Apple changed the name "iPhone OS" to "iOS." In the beginning, iOS (version 1) did not accept third-party native applications when it was initially released in 2007 alongside the first iPhone (sometimes referred to as the iPhone 2G, iPhone 1, and iPhone Original). Later in 2008, Apple unveiled the iOS App Store, which supported third-party apps that benefited from the iPhone SDK. These days, iOS users can choose from a huge selection of applications. The operating system's distinctive user interface and powerful encryption capabilities are its most well-known characteristics. With frequent updates and improvements, iOS has established itself as a dependable mobile operating system for Apple iPhone hardware, boasting a variety of distinctive features, including iMessage, iCloud, Apple Pay, Siri etc. MacOSMacOS, originally known as "Mac OS X," is a family of graphical operating systems similar to Windows. Originally known as "Mac OS X," it was abbreviated to "OS X" in 2012 and then changed its name to "macOS" in 2016. The Apple firm is responsible for creating, disseminating, and selling its proprietary operating system. Only Apple's Mac laptops and workstations include this operating system as standard equipment. After Windows, macOS has the second-highest global desktop usage rate. In 2001, the Mac OS X 10.0 desktop version of the operating system was introduced. The OS shares several fundamental characteristics with the early Unix operating systems on which it is based. Despite having different graphical user interfaces, Linux and macOS both share a lot of the same CMD features and underlying program interfaces. iOS is a version of macOS that runs on mobile devices. The security, encryption, user-friendliness, performance, and several special features of Apple operating systems are their most well-known strengths. MacOS is known for its distinctive keyboard shortcuts, including the Command key, stoplight-colored resizing buttons, and the Dock for finding programs or files. CHROME OSA well-known operating system created or created by the Google Corporation on top of the Linux kernel is known as Chrome OS (or ChromeOS). Chrome OS's foundation was originally built on Ubuntu, but was eventually switched to Google's own Linux. Additionally, it is based on open-source software called Chromium OS and uses the Chrome browser as its default user interface. In 2011, Chromebooks (Computers made specially to run Chrome OS solely) made by Samsung were released alongside the first Chrome OS version for the general market. Later, other producers adopted Chrome OS as well and produced Chromebooks under their own brands. Google introduced its own built-and-manufactured Chromebook Pixel in 2013. Only Chromebook users were intended for the initial development of Chrome OS. It was made available, though, as a bootable OS for additional Macs and PCs that could be used or installed through USB. The most recent iteration of Chrome OS is compatible with a wide variety of progressive web applications, Chrome applications, and Play Store-available Android apps. To make Chrome OS more functional, safe, and loaded with necessary features while maintaining performance stability even with limited hardware resources, Google has worked on a variety of sections and modifications. According to studies and market information from a number of research firms, Chrome OS has surpassed macOS based on installed devices in a number of different quarters, often claiming the title of the second most popular desktop OS behind Windows. UNIXA multitasking, multiuser, and sophisticated computer operating system called UNIX was created in 1969 by AT&T Laboratories employees Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and a few others. Its main application was at the Bell's Labs Research Center. It was later licensed to a number of more outside businesses, though, which helped to keep the work going. Since then, UNIX has served as the foundation for other contemporary operating systems, including Linux, Sun Solaris, and even Mac OS X. The packaged version of Linux, known as the GNU/Linux distribution, became quite well-known. Additionally, there are a large number of Linux distributions, both free and paid, available for a wide range of equipment. In many contemporary PCs, workstations, servers, and even mobile devices, UNIX-based operating systems continue to be widely utilized as the foundation. UNIX comes in many distinct forms, but they all have a lot in common. UNIX-based operating systems have a graphical user interface, just like other operating systems, to make them simpler for users to use. The kernel, the shell, and the programs are the three primary components of the UNIX operating system, which is regarded as the brains of many other operating systems. The availability of a hierarchical file system, the ability to multitask and support multiple users, portability (can run on different systems), simplicity, and a sizeable software library are only a few of UNIX's key features. LINUXOne of the most well-known examples of a free and open-source operating system is Linux (technically, the Linux kernel). The Linux kernel, which serves as the foundation of the Linux operating system, was created by Linus Torvalds in 1991, and it is usually referred to as a Unix-like OS. Linux has been developed by programmers from all over the world, despite being the work of Linus Torvalds. They work together by changing its source code, which they subsequently submit for review to the connected applications and the kernel software. 
Linux does not have a graphical user interface or commonly used software, such as browsers, media apps, word editors, etc., unlike other well-known operating systems like Windows and macOS. As an alternative, it has numerous distributions with comparable characteristics. There are countless Linux distributions available. In all of these distributions, Linux serves as the primary operating system, sitting on top of all currently running programs. Being open-source, Linux (technically its kernel) source code is available for use, editing, and distribution by anybody who abides by the conditions of each license. In contrast to Red Hat Enterprise Linux, which is a well-liked commercial distribution, Ubuntu is a well-liked non-commercial distribution. Linux was first intended to be used exclusively on personal computers. However, it was later ported to numerous additional platforms, becoming the fundamental component of numerous operating systems. Along with smartphones and laptops, it also runs a number of embedded products, including routers, gaming consoles, digital video recorders, wearables, televisions, and car controls. UBUNTUUbuntu is a Linux-based operating system that is available for free. It works well with desktops, mobile devices, and network servers. All required applications, including a browser, media player, email client, office suite, etc., are already included in the operating system. Thousands of more third-party programmes are also available for download via the Ubuntu Software Center. Ubuntu OS was first published in 2004 with version 4.10. Numerous further variations have since been produced. Every Ubuntu release has a unique version number that starts with the associated release year, then the accompanying month number. Ubuntu is a free operating system that may be set up independently, booted from a USB drive, or used to run other operating systems, including Windows, with emulator software. The current Ubuntu Desktop edition supports nearly every popular Windows program that is available. Ubuntu is regarded as one of the most secure operating systems because it comes with a built-in firewall and virus protection. Additionally, updates are continuously distributed to Ubuntu users to improve security or provide new features to the operating system. FEDORAThe Linux OS kernel design serves as the foundation for Fedora, another well-known open-source operating system for computing devices. It is a general-purpose operating system that is extremely secure and was created as part of the Fedora Project and supported by Red Hat, an IBM company. 2003 saw the release of the Fedora Core 1 edition of this operating system. Every year, Fedora strives to release two significant improvements. Even though the Fedora official support cycle is brief, users can easily move from one version to another without having to repeatedly reinstall the operating system. Everyone can use Fedora for free, and it has the additional permissions to be modified and distributed in accordance with their needs. Over a thousand distributions, including Red Hat Enterprise Linux and the XO operating system, are built on top of Fedora. Being the second most popular Linux distribution after Ubuntu, Fedora is also well renowned for its usefulness. Despite the fact that Fedora lacks Ubuntu's flash, it is still a viable operating system for consumers, especially those who favor Linux, thanks to its strong foundation, good Flatpak/Snap support, extensive software availability, and quick release of new features such as opposed to regular software updates. BLACKBERRY OSFor its line of smartphones, the Canadian corporation Blackberry created one of the most well-known mobile operating systems, known as Blackberry OS. The OS (version 3.6) for the BlackBerry 5810 smartphone first became available in 2002. People like Blackberry OS because of its novel and distinguishing features, including a QWERTY keyboard, robust multitasking capabilities, a trackball, and push internet email. All of these characteristics, nevertheless, were later adopted by other well-liked operating systems and companies. Despite its great popularity, BlackBerry couldn't compete with Apple and Samsung for the top spot in the smartphone industry. One of BlackBerry's major faults was to prioritize businesses and businessmen over the tastes and preferences of normal customers. Additionally, Blackberry kept its smartphone's physical design unchanged while not updating its operating system to keep up with new products from its rivals, which significantly decreased customer interest. BlackBerry OS had a limited selection of apps that could be installed because there weren't many apps to choose from. Despite being among the first smartphones, Blackberry was unable to innovate or respond appropriately because it was unable to grasp the shifting market conditions. When the revamped BlackBerry 10 was released in 2013, BlackBerry OS was no longer supported. But up to the end of 2013, the business offered assistance for gadgets running the outdated BlackBerry OS. Beginning in early 2022, BlackBerry discontinued providing full support for all of its operating systems, effectively rendering their renowned devices almost outdated. SUMMARYAn operating system is a component of the system software that controls the various crucial apps, services, and programs required for computers and other mobile devices to run and function. It is in charge of controlling both the device's hardware and software operations. The operating system is a necessary component for computing devices to function. According to online usage, Android, an operating system based on the Linux kernel, is the most popular operating system worldwide as of December 2022. It commands 44.6% of the global market, trailing only Windows (28.41%), Apple iOS (17.29%), macOS (5.53%), Linux (desktop) (1.11%), which also uses the Linux kernel, and Unknown (1.88%). These figures do not account for game consoles or embedded devices.
Next TopicWhat is Starvation in Operating System
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









