MS-DOS Operating SystemA disk operating system (DOS) is an operating system for x86 based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and some operating systems attempting to be compatible with MS-DOS. Sometimes it is referred to as "DOS", which is also the generic acronym for disk operating system. MS-DOS was the main operating system for IBM PC compatible personal computers during the 1980s. It was gradually superseded by operating systems offering a graphical user interface (GUI) in various graphical Microsoft Windows operating system generations. DOS is also used to describe several similar command-line disk operating systems. Early computers, such as the Commodore 64, Atari 800, and Apple II, all featured a disk operating system, including Commodore Business Machines DOS, Atari DOS, and Apple DOS, respectively. DOS/360 was an OS for IBM mainframes, which first appeared in 1966, but it is unrelated to the 8086-based DOS of the 1980s. 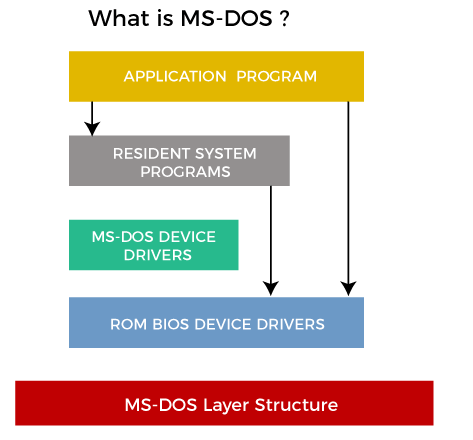
Several competing products were released for the x86 platform during its lifetime, and MS-DOS went through eight versions until development ceased in 2000. Initially, MS-DOS was targeted at Intel 8086 processors running on computer hardware using floppy disks to store and access the operating system, application software, and user data. Progressive version releases delivered support for other mass storage media in ever greater sizes and formats and added feature support for newer processors and rapidly evolving computer architectures. Microsoft's development was the key product from a programming language company to a diverse software development firm, providing essential revenue and marketing resources. It was also the underlying basic operating system on which early versions of Windows ran as a GUI. How DOS works?When a computer is powered on, it goes through various steps called the boot process. For a computer running a disk operating system in the following six steps, such as:
A disk operating system doesn't have a graphical user interface (GUI). Its interface is character-based, so users must type commands in the command line to indicate what actions they want. Features of DOSHere are some of the distinguishing features of a disk operating system, such as:
Limitations of MS-DOSHere are the following limitations of the disk operating system, such as:
Types of MS-DOS CommandsAn instruction given to a computer to perform a specific task is known as a command. The MS-DOS has many commands to perform each task, and these commands are stored in the DOS directory of the disk. The MS-DOS commands are of two types, internal command, and external command.
MS-DOS is not case-sensitive so that commands can type in either uppercase or lowercase. However, other disk operating systems have case-sensitive CLIs. DOS commands include the following.
MS-DOS Files and FilenamesOne of the primary functions of the OS is to handle disk files. A file can contain only data, or it can contain a set of instructions, called a program, telling the computer how to perform a particular task. Every file has associated with it a unique filename which is used to identify it on the disk. A filename in MS-DOS has two parts; the name and an extension. The name can contain up to eight characters. Each filename can have a three-character extension. The extension is separated from the name by a period. The period serves as a delimiter, indicating where one portion of the filename ends, and the next begins. An extension is usually used to identify files that are related in some way. MS-DOS allows the following characters to be used in a filename and extension:
Any other character used in a filename, including spaces, will cause the name to be terminated at that character. It is generally good practice not to use special characters in filenames because some programs may use them as delimiters or other special purposes. In addition, the extensions BAT, COM, EXE, and SYS have special meanings in MS-DOS and should therefore normally not be used with your data files. Shown below are examples of both valid and unacceptable filenames. Valid MS-DOS Filenames:
Invalid MS-DOS Filenames:
Next TopicSpooling in Operating System
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









