Fixed PartitioningThe earliest and one of the simplest technique which can be used to load more than one processes into the main memory is Fixed partitioning or Contiguous memory allocation. In this technique, the main memory is divided into partitions of equal or different sizes. The operating system always resides in the first partition while the other partitions can be used to store user processes. The memory is assigned to the processes in contiguous way. In fixed partitioning,
There are various cons of using this technique. 1. Internal Fragmentation If the size of the process is lesser then the total size of the partition then some size of the partition get wasted and remain unused. This is wastage of the memory and called internal fragmentation. As shown in the image below, the 4 MB partition is used to load only 3 MB process and the remaining 1 MB got wasted. 2. External Fragmentation The total unused space of various partitions cannot be used to load the processes even though there is space available but not in the contiguous form. As shown in the image below, the remaining 1 MB space of each partition cannot be used as a unit to store a 4 MB process. Despite of the fact that the sufficient space is available to load the process, process will not be loaded. 3. Limitation on the size of the process If the process size is larger than the size of maximum sized partition then that process cannot be loaded into the memory. Therefore, a limitation can be imposed on the process size that is it cannot be larger than the size of the largest partition. 4. Degree of multiprogramming is less By Degree of multi programming, we simply mean the maximum number of processes that can be loaded into the memory at the same time. In fixed partitioning, the degree of multiprogramming is fixed and very less due to the fact that the size of the partition cannot be varied according to the size of processes. 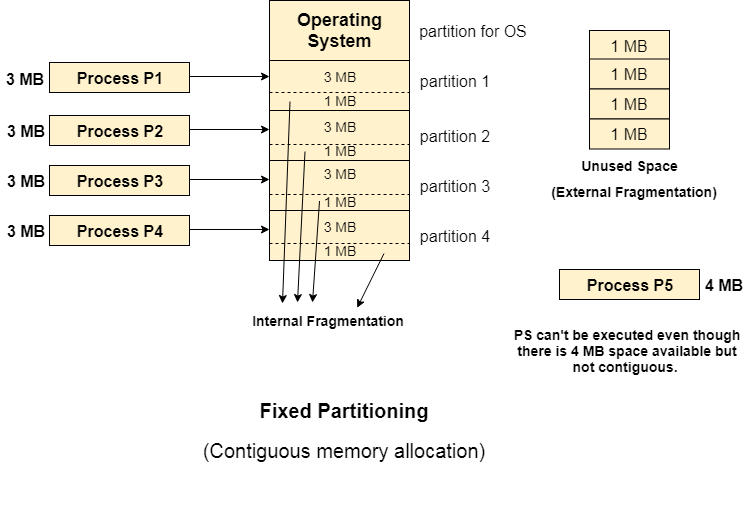
Next TopicDynamic Partitioning
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










