Operating System
Process Management
Synchronization
Deadlocks
Memory Management
File Management
Misc
MCQ
CompactionWe got to know that the dynamic partitioning suffers from external fragmentation. However, this can cause some serious problems. To avoid compaction, we need to change the rule which says that the process can't be stored in the different places in the memory. We can also use compaction to minimize the probability of external fragmentation. In compaction, all the free partitions are made contiguous and all the loaded partitions are brought together. By applying this technique, we can store the bigger processes in the memory. The free partitions are merged which can now be allocated according to the needs of new processes. This technique is also called defragmentation. 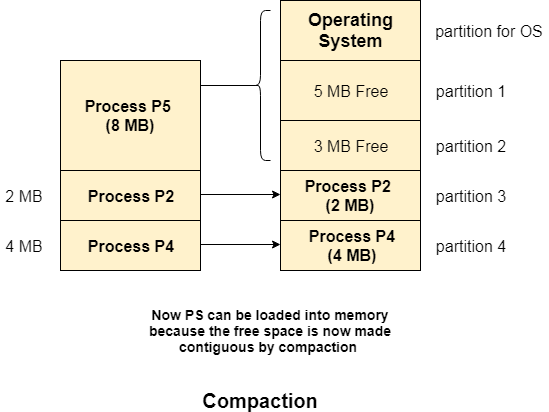
As shown in the image above, the process P5, which could not be loaded into the memory due to the lack of contiguous space, can be loaded now in the memory since the free partitions are made contiguous. Problem with CompactionThe efficiency of the system is decreased in the case of compaction due to the fact that all the free spaces will be transferred from several places to a single place. Huge amount of time is invested for this procedure and the CPU will remain idle for all this time. Despite of the fact that the compaction avoids external fragmentation, it makes system inefficient. Let us consider that OS needs 6 NS to copy 1 byte from one place to another. hence, it is proved to some extent that the larger size memory transfer needs some huge amount of time that is in seconds.
Next TopicBit Map for Dynamic Partitioning
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










