Dynamic PartitioningDynamic partitioning tries to overcome the problems caused by fixed partitioning. In this technique, the partition size is not declared initially. It is declared at the time of process loading. The first partition is reserved for the operating system. The remaining space is divided into parts. The size of each partition will be equal to the size of the process. The partition size varies according to the need of the process so that the internal fragmentation can be avoided. 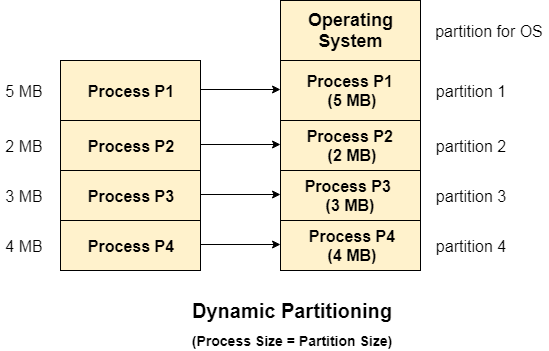
Advantages of Dynamic Partitioning over fixed partitioning1. No Internal FragmentationGiven the fact that the partitions in dynamic partitioning are created according to the need of the process, It is clear that there will not be any internal fragmentation because there will not be any unused remaining space in the partition. 2. No Limitation on the size of the processIn Fixed partitioning, the process with the size greater than the size of the largest partition could not be executed due to the lack of sufficient contiguous memory. Here, In Dynamic partitioning, the process size can't be restricted since the partition size is decided according to the process size. 3. Degree of multiprogramming is dynamicDue to the absence of internal fragmentation, there will not be any unused space in the partition hence more processes can be loaded in the memory at the same time. Disadvantages of dynamic partitioningExternal FragmentationAbsence of internal fragmentation doesn't mean that there will not be external fragmentation. Let's consider three processes P1 (1 MB) and P2 (3 MB) and P3 (1 MB) are being loaded in the respective partitions of the main memory. After some time P1 and P3 got completed and their assigned space is freed. Now there are two unused partitions (1 MB and 1 MB) available in the main memory but they cannot be used to load a 2 MB process in the memory since they are not contiguously located. The rule says that the process must be contiguously present in the main memory to get executed. We need to change this rule to avoid external fragmentation. 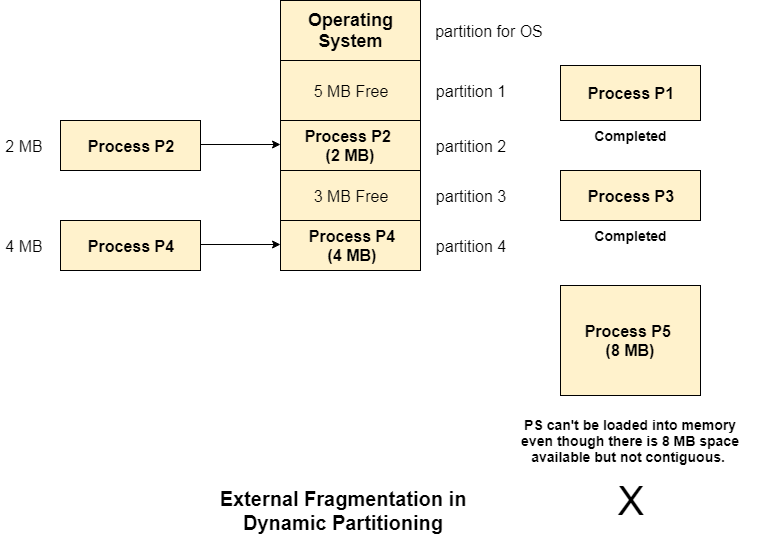
Complex Memory AllocationIn Fixed partitioning, the list of partitions is made once and will never change but in dynamic partitioning, the allocation and deallocation is very complex since the partition size will be varied every time when it is assigned to a new process. OS has to keep track of all the partitions. Due to the fact that the allocation and deallocation are done very frequently in dynamic memory allocation and the partition size will be changed at each time, it is going to be very difficult for OS to manage everything.
Next TopicCompaction
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










