Operating system servicesIn this article, we understand the basics of an operating system and its services. What do you mean by Operating system?No matter its size and application, every computer needs an operating system to make it functional and useful. The operating system is an integral part of modern computer systems. It is a well-organized collection of programs that manages the hardware. An Operating System provides an interaction between the users and computer hardware. A user is a person sitting at the computer terminal concerned about the application rather than the architecture of the computer. The user never interacts with the hardware directly. To get the services of the hardware, he has to request through the operating system. 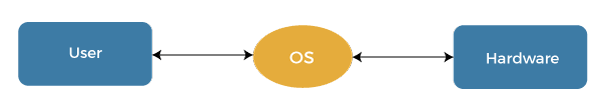
The operating system is a primary resource manager. It manages the hardware, including processors, memory, Input-Output devices, and communication devices. 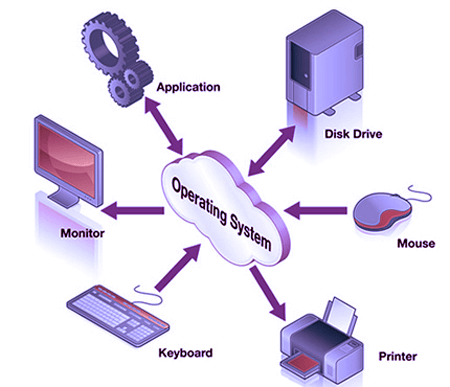
The operating system operates either in kernel mode or user mode. Compilers and editors run in user mode, whereas operating system code runs in kernel mode. 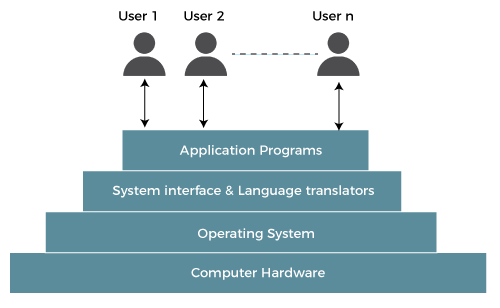
Operating system services: The operating system provides the programming environment in which a programmer works on a computer system. The user program requests various resources through the operating system. The operating system gives several services to utility programmers and users. Applications access these services through application programming interfaces or system calls. By invoking those interfaces, the application can request a service from the operating system, pass parameters, and acquire the operation outcomes. Following are the services provided by an operating system -
Program execution To execute a program, several tasks need to be performed. Both the instructions and data must be loaded into the main memory. In addition, input-output devices and files should be initialized, and other resources must be prepared. The Operating structures handle these kinds of tasks. The user now no longer should fear the reminiscence allocation or multitasking or anything. Control Input/output devices As there are numerous types of I/O devices within the computer system, and each I/O device calls for its own precise set of instructions for the operation. The Operating System hides that info with the aid of presenting a uniform interface. Thus, it is convenient for programmers to access such devices easily. Program Creation The Operating system offers the structures and tools, including editors and debuggers, to help the programmer create, modify, and debugging programs. Error Detection and Response An Error in a device may also cause malfunctioning of the entire device. These include hardware and software errors such as device failure, memory error, division by zero, attempts to access forbidden memory locations, etc. To avoid error, the operating system monitors the system for detecting errors and takes suitable action with at least impact on running applications. While working with computers, errors may occur quite often. Errors may occur in the:
To handle these errors and other types of possible errors, the operating system takes appropriate action and generates messages to ensure correct and consistent computing. Accounting An Operating device collects utilization records for numerous assets and tracks the overall performance parameters and responsive time to enhance overall performance. These personal records are beneficial for additional upgrades and tuning the device to enhance overall performance. Security and Protection Operating device affords safety to the statistics and packages of a person and protects any interference from unauthorized users. The safety feature counters threats, which are published via way of individuals out of doors the manage of the running device. For Example: When a user downloads something from the internet, that program may contain malicious code that may harm the already existing programs. The operating system ensures that proper checks are applied while downloading such programs. If one computer system is shared amongst a couple of users, then the various processes must be protected from another intrusion. For this, the operating system provides various mechanisms that allow only those processes to use resources that have gained proper authorization from the operating system. The mechanism may include providing unique users ids and passwords to each user. File management Computers keep data and information on secondary storage devices like magnetic tape, magnetic disk, optical disk, etc. Each storage media has its capabilities like speed, capacity, data transfer rate, and data access methods. For file management, the operating system must know the types of different files and the characteristics of different storage devices. It has to offer the proportion and safety mechanism of documents additionally. Communication The operating system manages the exchange of data and programs among different computers connected over a network. This communication is accomplished using message passing and shared memory.
Next TopicBatch Operating System
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









