Mutex vs SemaphoreAs per operating system terminology, mutex and semaphores are kernel resources that provide synchronization services, also called synchronization primitives. Process synchronization plays an important role in maintaining the consistency of shared data. Both the software and hardware solutions are present for handling critical section problems. But hardware solutions for critical section problems are quite difficult to implement. Mutex and semaphore both provide synchronization services, but they are not the same. What is Mutex?Mutex is a mutual exclusion object that synchronizes access to a resource. It is created with a unique name at the start of a program. The mutex locking mechanism ensures only one thread can acquire the mutex and enter the critical section. This thread only releases the mutex when it exits in the critical section. 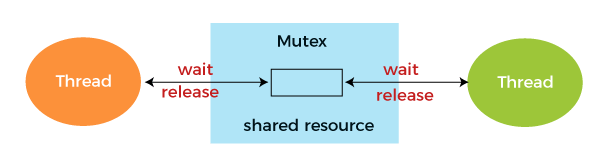
It is a special type of binary semaphore used for controlling access to the shared resource. It includes a priority inheritance mechanism to avoid extended priority inversion problems. It allows current higher priority tasks to be kept in the blocked state for the shortest time possible. However, priority inheritance does not correct priority inversion but only minimizes its effect. Example This is shown with the help of the following example, Use of MutexA mutex provides mutual exclusion, either producer or consumer who can have the key (mutex) and proceed with their work. As long as the producer fills the buffer, the user needs to wait, and vice versa. In Mutex lock, all the time, only a single thread can work with the entire buffer. When a program starts, it requests the system to create a mutex object for a given resource. The system creates the mutex object with a unique name or ID. Whenever the program thread wants to use the resource, it occupies lock on mutex object, utilizes the resource and after use, it releases the lock on mutex object. Then the next process is allowed to acquire the lock on the mutex object. Meanwhile, a process has acquired the lock on the mutex object, and no other thread or process can access that resource. If the mutex object is already locked, the process desiring to acquire the lock on the mutex object has to wait and is queued up by the system till the mutex object is unlocked. Advantages of MutexHere are the following advantages of the mutex, such as:
Disadvantages of MutexMutex also has some disadvantages, such as:
What is Semaphore?Semaphore is simply a variable that is non-negative and shared between threads. A semaphore is a signaling mechanism, and another thread can signal a thread that is waiting on a semaphore. 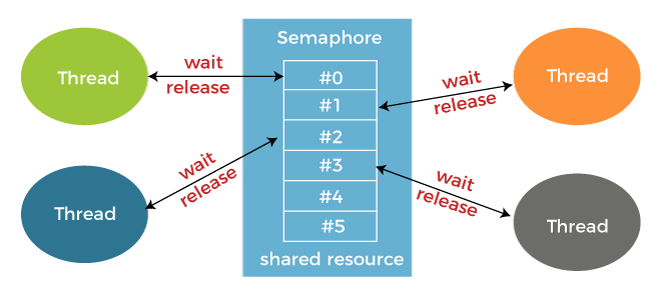
A semaphore uses two atomic operations, 1. Wait: The wait operation decrements the value of its argument S if it is positive. If S is negative or zero, then no operation is performed. 2. Signal for the process synchronization: The signal operation increments the value of its argument S. A semaphore either allows or reject access to the resource, depending on how it is set up. Use of SemaphoreIn the case of a single buffer, we can separate the 4 KB buffer into four buffers of 1 KB. Semaphore can be associated with these four buffers, allowing users and producers to work on different buffers simultaneously. Types of SemaphoreSemaphore is distinguished by the operating system in two categories Counting semaphore and Binary semaphore. 1. Counting Semaphore: The semaphore S value is initialized to the number of resources present in the system. Whenever a process wants to access the resource, it performs the wait()operation on the semaphore and decrements the semaphore value by one. When it releases the resource, it performs the signal() operation on the semaphore and increments the semaphore value by one. When the semaphore count goes to 0, it means the processes occupy all resources. A process needs to use a resource when the semaphore count is 0. It executes the wait() operation and gets blocked until the semaphore value becomes greater than 0. 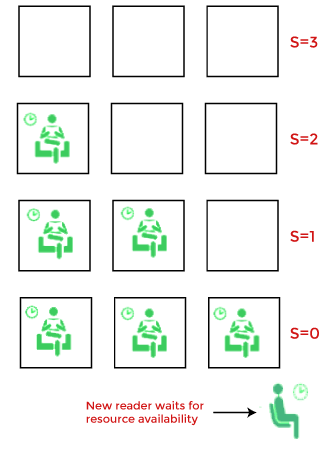
2. Binary semaphore: The value of a semaphore ranges between 0and 1. It is similar to mutex lock, but mutex is a locking mechanism, whereas the semaphore is a signaling mechanism. In binary semaphore, if a process wants to access the resource, it performs the wait() operation on the semaphore and decrements the value of the semaphore from 1 to 0. When it releases the resource, it performs a signal() operation on the semaphore and increments its value to 1. Suppose the value of the semaphore is 0 and a process wants to access the resource. In that case, it performs wait() operation and block itself till the current process utilizing the resources releases the resource. 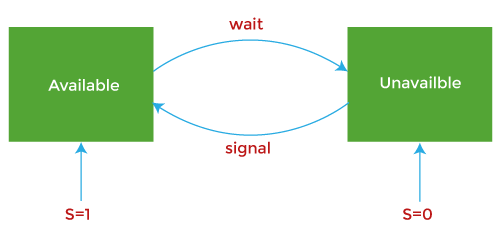
Advantages of SemaphoreHere are the following advantages of semaphore, such as:
Disadvantage of SemaphoresSemaphores also have some disadvantages, such as:
Difference between Mutex and SemaphoreThe basic difference between semaphore and mutex is that semaphore is a signalling mechanism, i.e. processes perform wait() and signal() operation to indicate whether they are acquiring or releasing the resource. In contrast, a mutex is a locking mechanism, and the process has to acquire the lock on a mutex object if it wants to acquire the resource. Here are some more differences between semaphore and mutex, such as: 
Next TopicWhat is Interleaved Memory
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









