Multiprocessing Operating systemIn operating systems, to improve the performance of more than one CPU can be used within one computer system called Multiprocessor operating system. Multiple CPUs are interconnected so that a job can be divided among them for faster execution. When a job finishes, results from all CPUs are collected and compiled to give the final output. Jobs needed to share main memory and they may also share other system resources among themselves. Multiple CPUs can also be used to run multiple jobs simultaneously. For Example: UNIX Operating system is one of the most widely used multiprocessing systems. The basic organization of a typical multiprocessing system is shown in the given figure. 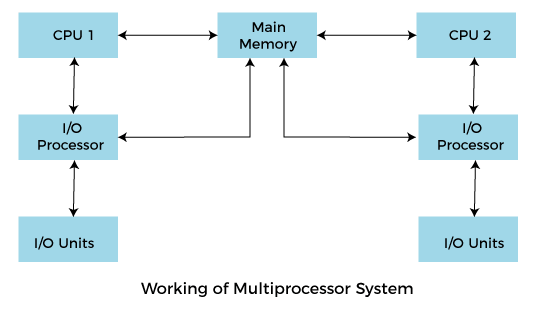
To employ a multiprocessing operating system effectively, the computer system must have the following things:
Advantages of multiprocessing operating system are:
Disadvantages of Multiprocessing operating System
Types of multiprocessing systems
Symmetrical multiprocessing operating system:In a Symmetrical multiprocessing system, each processor executes the same copy of the operating system, takes its own decisions, and cooperates with other processes to smooth the entire functioning of the system. The CPU scheduling policies are very simple. Any new job submitted by a user can be assigned to any processor that is least burdened. It also results in a system in which all processors are equally burdened at any time. The symmetric multiprocessing operating system is also known as a "shared every-thing" system, because the processors share memory and the Input output bus or data path. In this system processors do not usually exceed more than 16. 
Characteristics of Symmetrical multiprocessing operating system:
Advantages of Symmetrical multiprocessing operating system:
Disadvantages of Symmetrical multiprocessing operating system:
Asymmetric multiprocessing operating systemIn an asymmetric multiprocessing system, there is a master slave relationship between the processors. Further, one processor may act as a master processor or supervisor processor while others are treated as shown below. 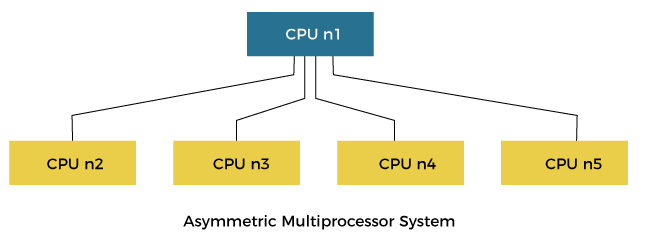
In the above figure, the asymmetric processing system shows that CPU n1 acts as a supervisor whose function controls other following processors. In this type of system, each processor is assigned a specific task, and there is a designated master processor that controls the activities of other processors. For example, we have a math co-processor that can handle mathematical jobs better than the main CPU. Similarly, we have an MMX processor that is built to handle multimedia-related jobs. Similarly, we have a graphics processor to handle the graphics-related job better than the main processor. When a user submits a new job, the OS has to decide which processor can perform it better, and then that processor is assigned that newly arrived job. This processor acts as the master and controls the system. All other processors look for masters for instructions or have predefined tasks. It is the responsibility of the master to allocate work to other processors. Advantages of Asymmetric multiprocessing operating system:
Disadvantages of Asymmetric multiprocessing operating system:
Next TopicMultiprogramming vs Multitasking
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









