Operating System
Process Management
Synchronization
Deadlocks
Memory Management
File Management
Misc
MCQ
Tree Structured DirectoryIn Tree structured directory system, any directory entry can either be a file or sub directory. Tree structured directory system overcomes the drawbacks of two level directory system. The similar kind of files can now be grouped in one directory. Each user has its own directory and it cannot enter in the other user's directory. However, the user has the permission to read the root's data but he cannot write or modify this. Only administrator of the system has the complete access of root directory. Searching is more efficient in this directory structure. The concept of current working directory is used. A file can be accessed by two types of path, either relative or absolute. Absolute path is the path of the file with respect to the root directory of the system while relative path is the path with respect to the current working directory of the system. In tree structured directory systems, the user is given the privilege to create the files as well as directories. 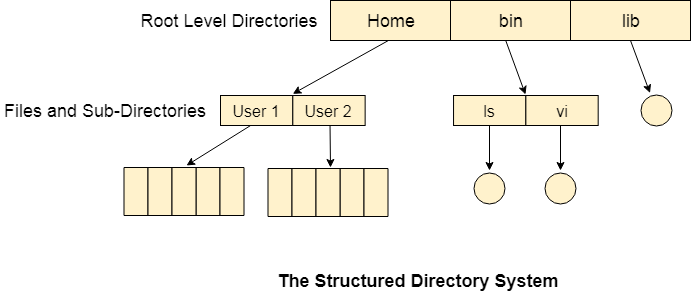
Permissions on the file and directoryA tree structured directory system may consist of various levels therefore there is a set of permissions assigned to each file and directory. The permissions are R W X which are regarding reading, writing and the execution of the files or directory. The permissions are assigned to three types of users: owner, group and others. There is a identification bit which differentiate between directory and file. For a directory, it is d and for a file, it is dot (.) The following snapshot shows the permissions assigned to a file in a Linux based system. Initial bit d represents that it is a directory. 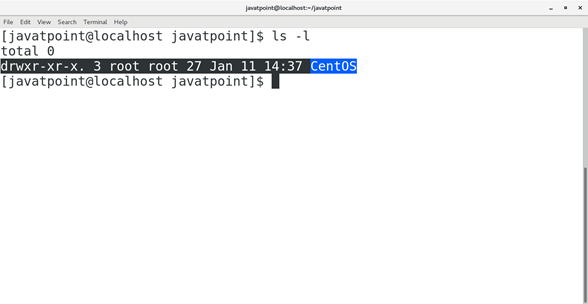
Next TopicAcyclic Graph Directories
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









