Multiprogramming vs. Time Sharing Operating SystemMultiprogramming is the allocation of more than one concurrent program on a computer system and its resources. Multiprogramming allows using the CPU effectively by allowing various users to use the CPU and I/O devices effectively. Multiprogramming makes sure that the CPU always has something to execute, thus increases the CPU utilization. On the other hand, Time sharing is the sharing of computing resources among several users simultaneously. Since this will allow many users to work in a single computer system simultaneously, it would lower the cost of providing computing capabilities. Multiprogramming Operating SystemMultiprogramming is the fast switching of the CPU between several programs. A program is generally made up of several tasks. A task ends with some request to move data which would require some I/O operations to be executed. Multitasking is commonly used to keep the CPU busy while the currently running program is doing I/O operations. Compared to other executing instructions, I/O operations are extremely slow. 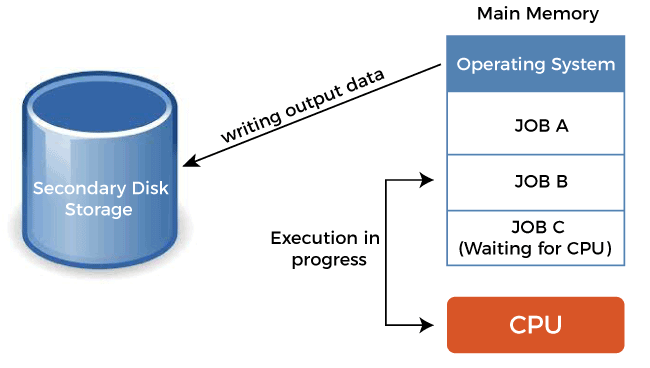
Even if a program contains a very small number of I/O operations, most of the time taken for the program is spent on those I/O operations. Therefore, using this idle time and allowing another program to utilize the CPU will increase the CPU utilization. Multiprogramming was initially developed in the late 1950s as a feature of operating systems and was first used in mainframe computing. With the introduction of virtual memory and virtual machine technologies, the use of multiprogramming was enhanced. It has no fixed time slice for processes. Its main purpose is resource utilization. Advantages of Multiprogramming OS Multiprogramming operating system has the following advantages:
Disadvantages of Multiprogramming OS Here are some disadvantages of multiprogramming operating system:
Time-Sharing Operating SystemTime-sharing is a technique that enables many people located at various terminals to use a particular computer system simultaneously. Time-Sharing is the logical extension of multiprogramming. In this time-sharing Operating system, many processes are allocated with computer resources in respective time slots. In this, the processor's time is shared with multiple users. That's why it is called a time-sharing operating system. It has a fixed time slice for the different processes. Its main purpose is interactive response time. 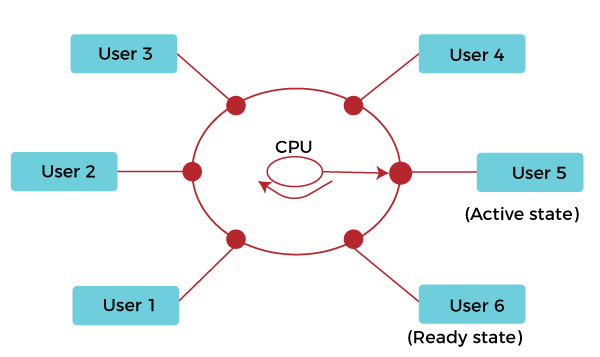
The CPU executes multiple jobs by switching between them, but the switches occur so frequently. Thus, the user can receive an immediate response. The operating system uses CPU scheduling and multiprogramming to provide each user with a small amount of time. Computer systems that were designed primarily as batch systems have been modified to time-sharing systems. The main difference between Multi programmed Batch Systems, and Time-Sharing Systems is that in multiprogrammed batch systems, the objective is to maximize processor use. In contrast, in Time-Sharing Systems, the objective is to minimize response time. Features of Time-Sharing OS Time-sharing OS provides the following features for users:
Advantages of Time-Sharing OS The time-sharing operating system has the following advantages:
Disadvantages of Time-Sharing OS Below are some disadvantages of the time-sharing operating system, such as:
Difference between Multiprogramming and Time-Sharing SystemIn multi-programming, more than one process can reside in the main memory at a time. Thus, when one process goes for I/O operation, the CPU is not waiting and allocated to another process. This keeps the CPU busy at all times. 
The concept of time-sharing overcomes the problem of no user interaction. A Time-sharing system requires that each user be provided with an input device (keyboard or mouse) and an output device (monitor) to interact with the system. In time-sharing, multiple jobs are executed simultaneously, and the CPU switches among them frequently so that each user can interact with each program while it is running. It decreases the system's response time for each user process and gives each user the illusion that the CPU is working slowly. The main difference between multiprogramming and time-sharing is that multiprogramming effectively utilizes CPU time by allowing several programs to use the CPU simultaneously. But time-sharing is sharing a computing facility by several users who want to use the same facility simultaneously. Each user on a time-sharing system gets their own terminal and feels like using the CPU alone. Time-sharing systems use the concept of multiprogramming to share the CPU time between multiple users at the same time. Below are some more differences between multiprogramming system and time-sharing system, such as:
Next TopicDistributed File System
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










