Page Fault Handling in Operating SystemIn this article, you will learn about page fault handling in the operating system and its steps. What is Page Fault in Operating System?Page faults dominate more like an error. A page fault will happen if a program tries to access a piece of memory that does not exist in physical memory (main memory). The fault specifies the operating system to trace all data into virtual memory management and then relocate it from secondary memory to its primary memory, such as a hard disk. 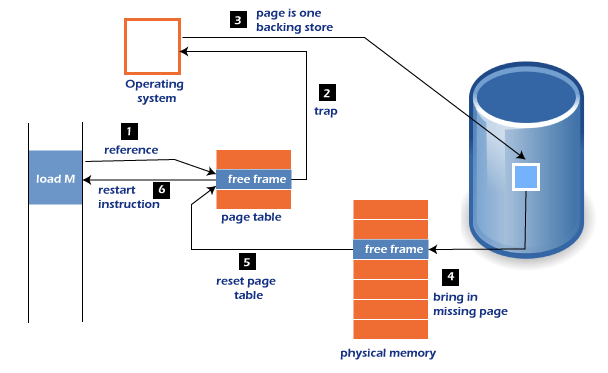
A page fault trap occurs if the requested page is not loaded into memory. The page fault primarily causes an exception, which is used to notify the operating system to retrieve the "pages" from virtual memory to continue operation. Once all of the data has been placed into physical memory, the program resumes normal operation. The Page fault process occurs in the background, and thus the user is unaware of it.
Page Fault HandlingA Page Fault happens when you access a page that has been marked as invalid. The paging hardware would notice that the invalid bit is set while translating the address across the page table, which will cause an operating system trap. The trap is caused primarily by the OS's failure to load the needed page into memory. Now, let's understand the procedure of page fault handling in the OS:
Page Fault TerminologyThere are various page fault terminologies in the operating system. Some terminologies of page fault are as follows: 1. Page Hit When the CPU attempts to obtain a needed page from main memory and the page exists in main memory (RAM), it is referred to as a "PAGE HIT". 2. Page Miss If the needed page has not existed in the main memory (RAM), it is known as "PAGE MISS". 3. Page Fault Time The time it takes to get a page from secondary memory and recover it from the main memory after loading the required page is known as "PAGE FAULT TIME". 4. Page Fault Delay The rate at which threads locate page faults in memory is referred to as the "PAGE FAULT RATE". The page fault rate is measured per second. 5. Hard Page Fault If a required page exists in the hard disk's page file, it is referred to as a "HARD PAGE FAULT". 6. Soft Page Fault If a required page is not located on the hard disk but is found somewhere else in memory, it is referred to as a "SOFT PAGE FAULT". 7. Minor Page Fault If a process needs data and that data exists in memory but is being allotted to another process at the same moment, it is referred to as a "MINOR PAGE FAULT". |
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










