First Come First Serve CPU Process Scheduling in Operating SystemsIn this tutorial, we are going to learn an important concept in CPU Process Scheduling Algorithms. The important concept name is First Come First Serve. This is the basic algorithm which every student must learn to understand all the basics of CPU Process Scheduling Algorithms. First Come First Serve paves the way for understanding of other algorithms. This algorithm may have many disadvantages. But these disadvantages created very new and efficient algorithms. So, it is our responsibility to learn about First Come First Serve CPU Process Scheduling Algorithms. Important Abbreviations
First Come First ServeFirst Come First Serve CPU Scheduling Algorithm shortly known as FCFS is the first algorithm of CPU Process Scheduling Algorithm. In First Come First Serve Algorithm what we do is to allow the process to execute in linear manner. This means that whichever process enters process enters the ready queue first is executed first. This shows that First Come First Serve Algorithm follows First In First Out (FIFO) principle. The First Come First Serve Algorithm can be executed in Pre Emptive and Non Pre Emptive manner. Before, going into examples, let us understand what is Pre Emptive and Non Pre Emptive Approach in CPU Process Scheduling. Pre Emptive ApproachIn this instance of Pre Emptive Process Scheduling, the OS allots the resources to a Process for a predetermined period of time. The process transitions from running state to ready state or from waiting state to ready state during resource allocation. This switching happens because the CPU may assign other processes precedence and substitute the currently active process for the higher priority process. Non Pre Emptive ApproachIn this case of Non Pre Emptive Process Scheduling, the resource cannot be withdrawn from a process before the process has finished running. When a running process finishes and transitions to the waiting state, resources are switched. Convoy Effect In First Come First Serve (FCFS )Convoy Effect is a phenomenon which occurs in the Scheduling Algorithm named First Come First Serve (FCFS). The First Come First Serve Scheduling Algorithm occurs in a way of non preemptive way. The Non preemptive way means that if a process or job is started execution, then the operating system must complete its process or job. Until, the process or job is zero the new or next process or job does not start its execution. The definition of Non Preemptive Scheduling in terms of Operating System means that the Central Processing Unit (CPU) will be completely dedicated till the end of the process or job started first and the new process or job is executed only after finishing of the older process or job. There may be a few cases, which might cause the Central Processing Unit (CPU) to allot a too much time. This is because in the First Come First Serve Scheduling Algorithm Non Preemptive Approach, the Processes or the jobs are chosen in serial order. Due, to this shorter jobs or processes behind the larger processes or jobs takes too much time to complete its execution. Due, to this the Waiting Time, Turn Around Time, Completion Time is very high. 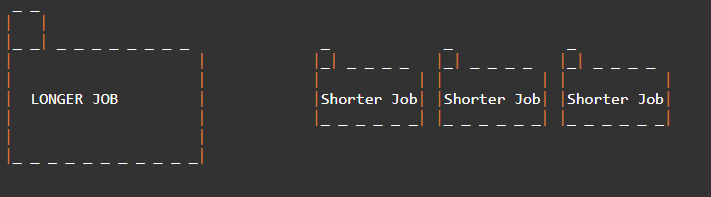
So, here as the first process is large or completion time is too high, then this Convoy effect in the First Come First Serve Algorithm is occurred. Let us assume that Longer Job takes infinite time to complete. Then, the remaining processes have to wait for the same infinite time. Due to this Convoy Effect created by the Longer Job the Starvation of the waiting processes increases very rapidly. This is the biggest disadvantage of FCFS CPU Process Scheduling. Characteristics of FCFS CPU Process SchedulingThe characteristics of FCFS CPU Process Scheduling are:
Advantages of FCFS CPU Process SchedulingThe advantages of FCFS CPU Process Scheduling are:
Disadvantages of FCFS CPU Process SchedulingThe disadvantages of FCFS CPU Process Scheduling are:
Problems in the First Come First Serve CPU Scheduling Algorithm ExampleNon Pre Emptive ApproachNow, let us solve this problem with the help of the Scheduling Algorithm named First Come First Serve in a Non Preemptive Approach. Gantt chart for the above Example 1 is: 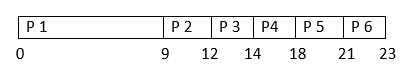
Turn Around Time = Completion Time - Arrival Time Waiting Time = Turn Around Time - Burst Time Solution to the Above Question Example 1
The Average Completion Time is: Average CT = ( 9 + 12 + 14 + 18 + 21 + 23 ) / 6 Average CT = 97 / 6 Average CT = 16.16667 The Average Waiting Time is: Average WT = ( 0 + 8 + 11 + 13 + 16 + 18 ) /6 Average WT = 66 / 6 Average WT = 11 The Average Turn Around Time is: Average TAT = ( 9 + 11 + 13 + 17 + 19 +20 ) / 6 Average TAT = 89 / 6 Average TAT = 14.83334 This is how the FCFS is solved in Non Pre Emptive Approach. Now, let us understand how they can be solved in Pre Emptive Approach Pre Emptive ApproachNow, let us solve this problem with the help of the Scheduling Algorithm named First Come First Serve in a Pre Emptive Approach. In Pre Emptive Approach we search for the best process which is available Gantt chart for the above Example 1 is: 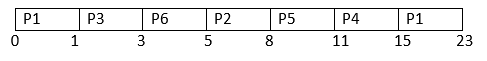
The Average Completion Time is: Average CT = ( 23 + 8 + 3 + 15 + 11 + 5 ) / 6 Average CT = 65 / 6 Average CT = 10.83333 The Average Waiting Time is: Average WT = ( 14 + 4 + 0 + 10 + 7 + 0 ) /6 Average WT = 35 / 6 Average WT = 5.83333 The Average Turn Around Time is: Average TAT = ( 23 + 7 + 2 + 14 + 9 +2 ) / 6 Average TAT = 57 / 6 Average TAT = 9.5 This is how the FCFS is solved in Pre Emptive Approach.
Next TopicConvoy Effect in FCFS
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










