Hard and Soft Real-Time Operating SystemA real-time operating system (RTOS) is intended to serve real-time applications that process data without buffer delays. A real-time system is a time-bound system with well-defined and fixed time constraints, and processing must be done within the defined constraints; otherwise, the system will fail. In a real-time operating system, processing time requirements are measured in tenths of seconds. 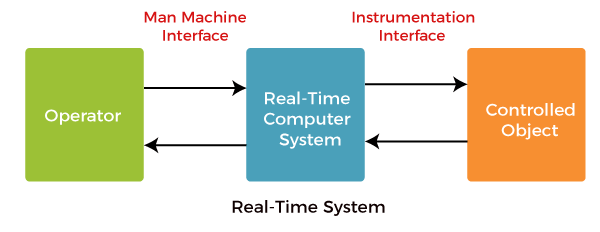
Real-Time System is used at those Places where we require higher and timely responses. Real-time operating systems involve a set of applications where the operations are performed on time to run the activities in an external system. It uses the quantitative expression of time to analyze the system's performance. The deadline in the context of a real-time system is the moment of the time by which the job's execution is needed to be accomplished. Most real-time operating systems use a pre-emptive scheduling algorithm. Examples of Real-Time Operating SystemsBelow are some examples of the real-time operating system, such as:
The quick response of the process is a must in real-time operating systems. There is no chance of any delay in completing any process because a little delay can cause several dangerous issues. Advantages of Real-Time Operating SystemsThe real-time operating system has the following advantages, such as: 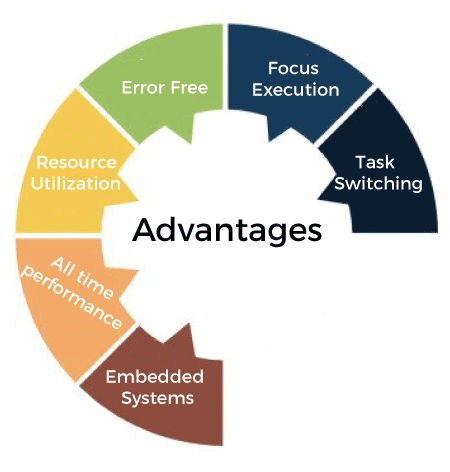
Types of Real-Time SystemA real-time operating system is divided into two systems, such as:
Hard and Soft real-time systems are the variants of real-time systems where the hard real-time system is more restrictive than the soft real-time system. The hard real-time system must assure to finish the real-time task within the specified deadline. While this is not the case in the soft real-time system, it assigns superior scheduling priority to real-time tasks. Hard Real-Time SystemA hard real-time system considers timelines as a deadline, and it should not be omitted in any circumstances. Hard real-time Systems do not use any permanent memory, so their processes must be complete properly in the first time itself. 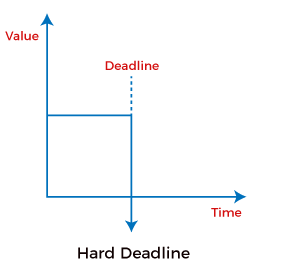
Hard Real-Time System must generate accurate responses to the events within the specified time. A hard real-time system is a purely deterministic and time constraint system. For example, users expected the output for the given input in 5 sec then the system should process the input data and give the output exactly by the 5th second. It should not give the output by the 6th second or by the 4th second. Here above 5 seconds is the deadline to complete the process for given data. In the hard real-time system, meeting the deadline is very important if the deadline is not met, the system performance will fail. Examples of Hard Real-Time SystemsBelow are some examples of the hard real-time operating system, such as:
Soft Real-Time SystemA soft real-time system is a system whose operation is degraded if results are not produced according to the specified timing requirement. In a soft real-time system, the meeting of deadline is not compulsory for every task, but the process should get processed and give the result. Even the soft real-time systems cannot miss the deadline for every task or process according to the priority it should meet the deadline or miss the deadline. 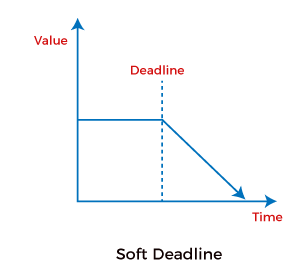
If a system is missing the deadline every time, the system's performance will be worse and cannot be used by the users. The best example for the soft real-time system is a personal computer, audio and video systems, etc. Soft real-time systems consider the processes as the main task and control the entire task. Examples of Soft Real-Time SystemsHere are some common examples of soft real-time operating systems, such as:
Difference between Hard and Soft Real-Time SystemAn operating system is system software that manages the computer hardware according to the instructions provided by the software. An operating system provides various tasks. File management, memory management, controlling peripheral devices and process scheduling are some of them. One type of operating system is a real-time operating system, and it is further divided into hard real-time systems and soft real-time systems. 
The key difference between hard and soft real-time systems is that a hard-real time system is a system in which a single failure to meet the deadline may lead to a complete system failure. In contrast, a soft real-time system is a system in which one or more failures to meet the deadline are not considered complete system failure, but its performance is considered degraded.
Next TopicConcurrency in Operating System
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










