Advantages and Disadvantages of Mean, Median, and ModeMean, median, and mode are three common measures of central tendency used in statistics. The mean is the arithmetic average of a set of numbers, calculated by adding all the values together and dividing by the number of values. The median is the middle value in a set of numbers, or the average of the two middle values if there is an even number of values. The mode is the most frequently occurring value in a set. Each of these measures has its own advantages and disadvantages, depending on the data set being analyzed. Read on to explore the advantages and disadvantages of these. But before that let's understand the fundamentals of mean, median, and mode. 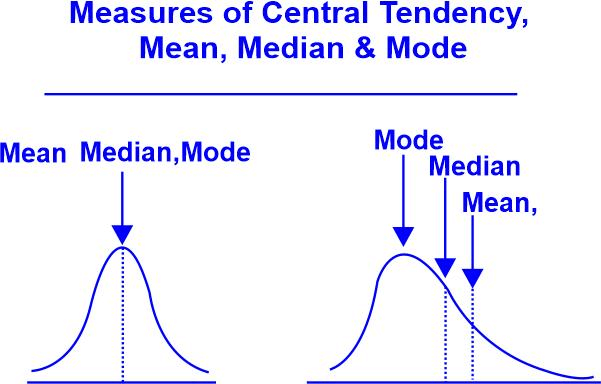
MeanMean is one of the most widely used statistical measures of central tendency. It describes the average value of a given set of numbers. It is calculated by summing up all the numbers and then dividing them by the total count of numbers in the set. Mean is an important measure in statistics because it indicates the central location of the data set. This measure is particularly useful for comparing different data sets, such as average salaries or profits over several years. Additionally, the Mean is a common basis for other measures of central tendencies, such as median, mode, and range. Mean is easy to calculate and can be easily represented in some graphs. However, it is also important to note that means is susceptible to skewness and outliers, which may not be the most reliable measure in some cases. In such scenarios, other measures, such as the median, may better represent the data set accurately. MedianThe median is the middle number in a set of numbers sorted from smallest to largest or from largest to smallest. It is the average of the two numbers in the middle if there is an even number in the set. The median is used as an alternative for the Mean (or average) when the numbers contain outliers that can significantly increase or decrease the average, skewing the results. To find the median of a set of numbers, one must first organize the data set into numerical order, meaning the numbers are in smallest to largest or largest to smallest order. Once the data is in this order, it is easy to determine the median. If the set is an odd number, then the middle number is your median. If the set is an even number, you must find the two middle numbers and average them together to get your median. ModeMode is a term used in mathematics to describe the most common value in a data set. It is one of the measures of central tendency and provides valuable information about the data. Mode is useful in many applications of mathematics, including descriptive statistics, regression analysis, and forecasting. While there may be better measures in some situations, it can give an insight into the data that may be missed when looking at the Mean or median. The mode of a data set is simply the value that appears most often. For example, if we have the following numbers: 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 5, 6, 6, 6, 7, 8. The mode would be six since it appears more times than any other value. The mode can also be found for non-numeric data, such as categories. It can provide a quick idea of data distribution or how the data are clustered around certain values. For example, the mode of a set of height measurements is 6 feet; we can infer that most of the heights are around that value. The mode can also be used to find outliers in a data set. If a value appears significantly more or less than the other values, it can be considered an outlier. This can be useful in identifying anomalies in a set that may need further investigation. Mode is a simple but powerful tool for understanding data. It can provide insights that may need to be noticed when looking at the Mean or median and can be a useful first step in data analysis. Advantages of MeanUsing the mean, or average, has many advantages. Calculating the Mean of a dataset gives an overall view of the typical values in that dataset. This makes it easier to compare data sets and analyze trends. It also minimizes the effects of outliers or unusually high or low values. 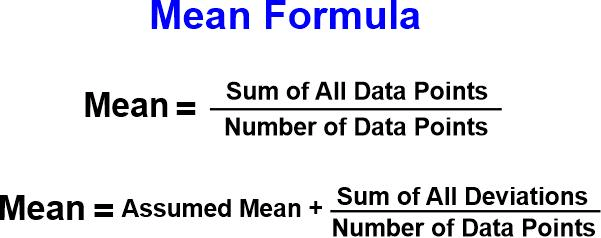
That is not representative of the population as a whole. Another advantage of using the Mean is that it is easy to compute. All you need to do is add up all the data points in your set and divide that by the number of points you have. Even for large and complex data sets, this is a relatively quick operation, making it an ideal choice for most situations. The Mean also makes it easier to compare multiple data sets with each other. For example, you could compare the mean scores of two classes to see which one is performing better. The Mean is also useful for identifying correlations between different pieces of data. 1. Reliably Represents Central TendencyMean is a measure of central tendency that reliably represents central tendency. It is one of the most popular, if not the most, central tendency measures. It is the average of a set of numbers. This measure helps to understand or summarize a large set of numbers by representing their overall average value. Mean has many advantages, one of which is that it is easy and simple to compute. Secondly, it is resistant to extreme values or outliers and is immune to sharp peaks in the data. This makes it a robust central tendency measure. Furthermore, it applies to both qualitative and quantitative data. Mean helps analyze average group performance in the case of studies conducted for small groups. When calculating the correlation between several variables, the Mean offers more insights into the data than the alternative measures of central tendency. Additionally, mean forms the basis of numerous statistical tests and techniques, such as linear and logistic regression, t-test, ANOVA test, and std. Deviation, etc. This makes it more powerful than the other measures in uncovering patterns, trends, and relationships in data. 2. Quick to CalculateThe major advantage of the Mean is that it provides an overall measure of central tendency and spread in the data set ? it gives you an idea of what is "average" in the data and how much variation the data has. As it is based on all data points, it is seen as a more accurate figure than other measures, such as the median and mode. In addition, the Mean is useful for determining a product's or team's relative performance as it shows where the value is " on average." This measure can then be compared with other stats to answer questions such as "how is the average performance of this team compared to the other teams." Furthermore, the Mean is quickly calculated and lends itself to more complex statistical models. While other measures, such as the median, may adjust better for outliers in data, the Mean can be used in conjunction with other statistical techniques, such as regression, to provide more nuance for a data set. 3. Valuable for ComparisonFor instance, using the Mean, you can see how one value is measured against another. For example, compare the average ages of two different groups. By calculating the Mean, you can get an accurate picture of the overall difference between the two groups without getting overwhelmed by the numbers. Another great benefit of the Mean is that it measures central tendency, allowing you to identify data trends and outliers. A high mean can indicate an overall trend in your data and highlight unusually high or low numbers, enabling you to evaluate your data quickly. The Mean is a great way to identify your set's most representative data points. By quickly finding the mean and then identifying the values closest to it, you can ensure that you are dealing with the most significant data points. This can be incredibly useful in certain applications, such as working with time series data to understand long-term trends. Advantages of MedianThe median is the middle-most value in a given set of numbers, and it provides some advantages compared to the more common measures of central tendency, such as mean and mode. The median can be used to measure the central tendency of a data set when there are outliers or extremely large values. It is also useful when dealing with ordinal and discrete data, such as test scores in which the values are not continuous. One of the primary advantages of the median is that it is less affected by the presence of extreme values or outliers in a data set than the Mean. 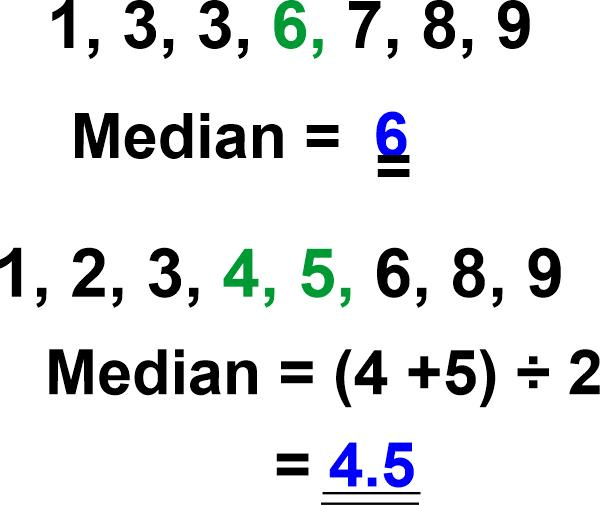
For example, if two individuals have incomes of $100,000 and $2,000,000, the mean income between the two would be $1,050,000. Such a large value doesn't accurately represent the "typical" income, so the median is a more appropriate measure. By taking the median value of two numbers, the median provides an accurate, unfluctuating representation of a data set. First, one of the primary advantages of using the median is that it is less prone to be impacted by outliers. Unlike the Mean, outliers do not heavily influence the median value of a set, which makes it favorable over the Mean when outliers are present in a data set. Second, the median can also be used when the data contains negative values or a wide range of values in the set. Since the median finds the middle number in a set, the negative and wide range of values have no impact on the median. Finally, the median is favored by some statisticians because it is resistant to skewness in the data. Skewness is the distortion of the data in one direction or another, and since the median is not affected by the values of the set, it does not produce an inaccurate result. Formula for median is: Median = {(n + 1)th term of ordered data set / 2 } where n = total number of data points in the data set. Overall, using the median when analyzing a data set is beneficial as it is more resistant to outliers, negative values, and skewness than the Mean. Furthermore, understanding the median will help make more informed decisions when analyzing data sets. Advantages of ModeThe benefits of using a mode in summarizing datasets are numerous. For one, it is a simple method that requires minimal calculation and effort; as a result, it is very efficient and straightforward. 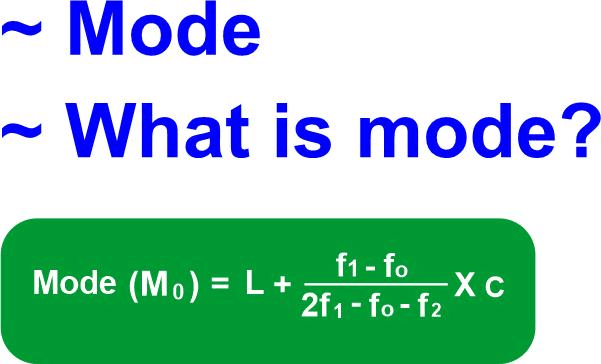
Also, it helps to identify the most frequent data element in a set, which can help to provide an overall view of the data. Additionally, it can be used to find out if there is an outlier in the dataset and help to identify underlying trends in the data. It is a useful tool for comparing two or more datasets, as it can determine if the data follows the same pattern. Overall, the mode is a great and versatile tool for summarizing datasets and should be implemented in any data analysis project. Reliability and Accuracy of ModeMode is very reliable and accurate in measuring the central tendency of variables that are categorical in nature. It is easy to interpret and it is not affected by the outliers or extreme values in the dataset. Time and Cost EfficiencyMode is the most time and cost efficient measure of central tendency. It is easy to calculate and does not require any complex calculations. Easy Interpretation Mode is the most easily interpretable measure of central tendency. It is used to measure the most frequent value in a set of data. Advantageous for Categorical DataMode is particularly useful for categorical data as it is the only measure of central tendency that can be used for such data. The other measures of central tendency such as mean and median cannot be used for categorical data. Beneficial for Skewed DataMode is also a useful measure of central tendency for data that is skewed or has outliers. The mean and median can be affected by the outliers and skewed data, but the mode is not. Disadvantages of MeanThis will explore the disadvantages of using mean headings in writing so that you can make an informed decision before including them in your work. Looking at the average or " mean" of a set of numbers is helpful in quickly discovering a great deal about the data. For instance, we can determine the most commonly occurring number and the range of values present in the data set by looking at the Mean. However, when looking at the Mean, there are some distinct drawbacks. The primary problem with the Mean is that it can be highly miscalculated by extreme values, also known as outliers. If a data set includes an outlier, depending on the size of the value, the Mean could be drastically different from the value of the rest of the data. For example, if a data set includes numbers ranging from 2 to 100, the Mean of these numbers would be 51. However, if 120 were included as an outlier, the Mean would increase to 61, which does not accurately reflect the other values within the data set. The Mean also needs to give more insight into the shape of the data set, which can be useful information. Looking at the Mean, the numbers are spread out around the same value, but the data might be spread out from small numbers too much larger ones. To determine the shape of a data set more accurately, you would need to look at other values, such as the median, range, and quartiles. The Mean is a basic statistic with potential drawbacks. Looking at other metrics alongside the Mean can provide a better understanding of the data set and avoid distortions caused by outliers. Disadvantages of MedianThe median is a statistical measure of the median value within a set of values. The value separates the higher half from the lower half when the values are arranged in numerical order. Despite its usefulness in many scenarios, the median has several disadvantages that must be considered when analyzing data. The main disadvantage of the median is that it does not indicate how varied the values are in the set. To illustrate, if a data set is comprised of five values that are all the same, the median value will still be that one value, making it look like the entire set is uniform. However, in reality, the set is not uniform at all. By considering the range of values, researchers can get the full picture of the data set. The second disadvantage of using the median is that it is sensitive to outliers. When outliers are present, they may have an exaggerated effect on the median. For example, if the set of numbers {1, 2, 3, 340, 500} is analyzed to find the median, the large and small numbers will skew the median value of the set to an unrealistic figure of 92.5, and this may not be representative of the true range of values. The median can be misleading when a data set has an odd amount of values. In such cases, the median is not necessarily the median value of the set and can often be an unrealistic representation of the data. There are certain disadvantages associated with using them. Lack of RealismOne of the foremost disadvantages of relying on the median as a measure of central tendency is the lack of realism it can exhibit. When there are outliers present in a data set?values that are significantly higher or lower than the rest of the data?the median will not necessarily reflect the true average of the data set. Difficulties with ComparisonsWhen comparing data sets, the median can make it more difficult to gain an accurate understanding of relative magnitudes. Discreet data also experience a disadvantage in this regard due to the inherent limitations of the median. Effects of Skewed DistributionsWhen data is bimodal or skewed, the median can often become a less reliable measure of central tendency. Skewed data sets have the potential to push the median far away from the true center, rendering the statistic less useful. ExpenseCalculating the median requires each value in a data set to be individually examined, processed, and then ordered. This type of information requires both an exponential amount of time and resources. As a result, the median may not be a valid option when time or financial constraints are present. Disadvantages of ModeMode is a mathematical concept used in statistics to represent numerical data's most frequently occurring value. Although this measure is widely used, it has some disadvantages. One of the disadvantages of using the mode in mathematics is that it can be misleading. It can be easily influenced by outliers, which are values much higher or lower than the rest of the data set. This means that the mode can be significantly skewed and is not necessarily representative of the data set. In addition, the mode does not tell you anything about the data distribution or the percentile ranges of the data set. While the mode does tell you the most frequent value in the data set, it does not tell you anything about where else the data values may lie. This can result in inaccurate conclusions being drawn from the data set. The mode is not useful for analyzing data sets with multiple values appearing the same number of times. This is because the mode is only designed to analyze data sets with single, non-repeated values. Therefore, if multiple values appear an equal number of times, no single mode exists. This makes the mode ineffective in such situations. Using a mode is that it is not unique. This means that multiple modes in a data set may make it difficult to interpret the data as a single value. While a single mode indicates that the most frequent value was observed multiple times, multiple modes indicate that two or more different values were observed with the same frequency. This can make it hard to communicate the overall pattern of a data set since one value cannot be determined as the most common among the group. Mode also has the disadvantage of being sensitive to outliers. Outliers are values that lie outside the broad range of a dataset and can significantly change the mode of a data set. This is because mode only considers the most frequently occurring value and can be unduly influenced by extreme values. This can mean that the mode does not accurately represent the most typical values of a dataset. Finally, the mode does not accurately measure the average of a data set, meaning that it cannot be used to identify potential meaningful trends in data. Mode represents only the most common value, meaning that it does not take account of any other values in the dataset. Therefore, there are better tools to use if you are looking to analyze, summarize, or compare data. ConclusionMean, median, and mode are the three most commonly used measures of central tendency, and each has advantages and disadvantages. The Mean, or average, is the sum of a set of values divided by the number of values. This is a useful measure for describing a large set of numbers, as it captures the entire range of values in a single number. When sorted in numerical order, the median, or middle number, is the value in the middle of a set of numbers. This is a useful measure for comparing two sets of numbers, as it captures the median value of each set in a single number. The mode, or most frequent value, is the value that appears most often in a set. This is useful for detecting patterns or trends, revealing which values are most common in a large set. The advantages of Mean, median, and mode are primarily in their simplicity. They are easy to calculate, analyze and interpret. The mean, median, and mode can provide additional insight into the data distribution. The Mean can provide a Center-Lacking Measure of Central Tendency, while the median and mode can provide Center-Consistent Measures of Central Tendency. One of the main disadvantages of Mean, median, and mode is that they could be more useful for describing certain data distributions. For example, mean, median, and mode are not useful for describing extremely skewed data. Additionally, the Mean does not capture the range of values within the data, and the median and mode do not capture the average values within the data. Finally, outlier values may affect the Mean, while the median and mode are not. Mean, median, and mode are useful tools for describing and analyzing data sets. However, they should be combined with other measures, such as the range and standard deviation, to provide a complete picture of the data. Additionally, it is important to understand the limitations of each measure's limitations and how to identify and deal with outliers and skewed data. With a proper understanding of the advantages and disadvantages of mean, median, and mode, you can use them to gain valuable insights from your data. |
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









