Advantages and Disadvantages of Self PollinationThe primary method of sexual reproduction in plants is pollination. The pollen grain is also known as a microspore, and the transportation of a microspore from an anther to the stigma of a flower is known as pollination. To pollinate themselves, plants use biotic and abiotic agents. Animals like insects, birds, bees, bats, beetles, butterflies, hummingbirds, flies, moths, and natural factors like water, wind, and even plants can work as pollinating agents. 
Each living thing, including plants, strives to create offspring for the following generation. There are many methods for plants to reproduce, one of which is by producing seeds. The genetic things required to produce a new plant are present in seeds, and plants produce their seeds with the help of flowers. Types of Pollination1. Self-Pollination 
The main pollination method is self-pollination, which happens when microspores are transported from the anther into the stigma of the same flower. The genetic qualities of the species are preserved through self-pollination. Self-pollinating plants are peas, sunflowers, orchids, apricots, peas, tomatoes, potatoes, peaches, legumes, oats, peanuts, wheat, barley, and rice. 2. Cross-Pollination 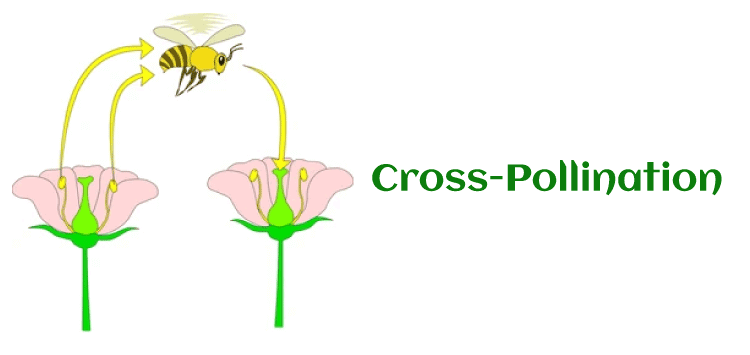
Cross-Pollination is another method of pollination, and it happens when pollen grains are transferred between flowers of different plants. Cross-pollination is beneficial because it encourages species diversity by fusing several plants' genetic components. However, cross-pollination relies on pollinators that can travel from plant to plant. Cross-pollinating plants include tulips, heather, lavender, plums, pears, blackberries, raspberries, daffodils, blackcurrants, pumpkins, strawberries, and other fruits and vegetables. Types of Self-Pollination and Cross-Pollination1. Autogamy Autogamy is a kind of self-pollination. In this, microspores move from the anther to the stigma within the same flower. Requirements for autogamy:
2. Geitonogamy Geitonogamy is a kind of self-pollination where microspores are transferred between different flowers of the same plant. 3. Xenogamy Cross-pollination is referred to as xenogamy, which happens when pollen grains are transported between flowers of different plants. Advantages and Disadvantages of Self-PollinationAdvantages of Self-Pollination
Disadvantages of Self-Pollination
Advantages and Disadvantages of Cross-PollinationAdvantages of Cross-Pollination
Disadvantages of Cross-Pollination
Self-pollinated Flowers' Characteristics
FAQ on Self Pollination1. What is homogamy? Answer: Inbreeding is also known as homogamy. When the male and female reproductive organs (of plants) mature simultaneously, this condition is called homogamy. Homogamy can be utilized to select a mate based on desired sexual partner characteristics. 2. Difference between self-pollination and cross-pollination Answer:
3. Why doesn't my self-pollinating plant produce fruit? Answer: Make sure your plant is self-pollinating first; if it is cross-pollinating, you'll need to buy at least one more plant. 4. What are the different self- and cross-pollination adaptations? Answer: Self-pollination is the transmission of pollen to the same flower's stigma. Cleistogamy, homogamy, movement of floral parts, and incomplete dichogamy are adaptations in self-pollinated plants. Cross-pollination is the transmission of pollen to the stigma of flowers of the same type of plant. Herkogamy, dichogamy, heterostyly, unisexuality, pollen prepotency, and self-sterility are the adaptations in cross-pollinated plants.
Next TopicGive Ten Advantages of Cleanliness
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









