Difference Between Hormone and EnzymeThe human body is complicated and depends on an excessive number of biological processes for it to work properly. Numerous chemicals support the biological or physical structure of our bodies and enable particular functions that are essential to life. These "chemicals" include, for instance, enzymes and hormones. To sustain, regulate, manage, and direct each and every physical or biological activity of the organism, certain molecules must operate. Enzymes and hormones are crucial for a person's daily functioning, from aiding in digestion to promoting deep sleep. We'll look at the most crucial biological elements, enzymes and hormones, with examples. 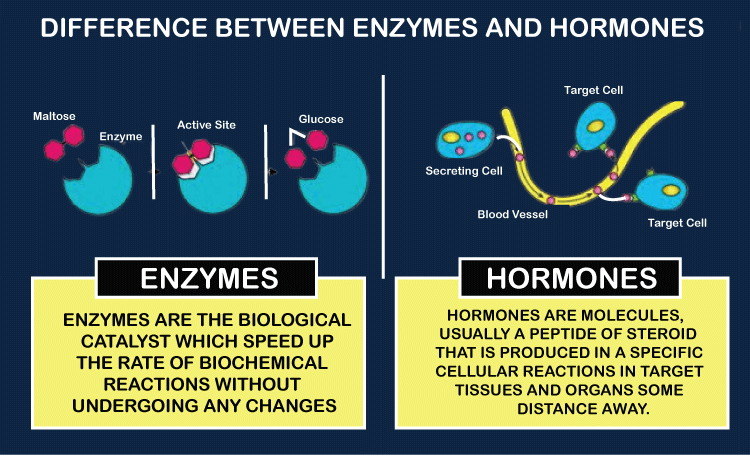
The fact that every enzyme and the majority of hormones are proteins is intriguing. All living things depend on enzymes and hormones for vital biochemical processes, although they differ greatly from one another. It's fascinating to learn about the numerous structures, chemical characteristics, and workings of these compounds. Enzymes serve as a catalyst to increase the velocity and specificity of metabolic reactions, which is the primary distinction between enzymes and hormones. Moreover enzyme is a protein having distinctive 3-dimensional structures that function as biocatalysts. On the other hand, hormones are substances that, when released by a cell or gland in one area of the body, communicate with other organs and systems to carry out specific tasks. It also goes by the term Chemical Messenger. EnzymeProteins known as enzymes have the unique ability to speed up chemical processes. Therefore, enzymes are able to catalyze chemical processes. Therefore, it might be inferred that the pace of the biochemical processes increases when enzymes are released into the bodies of animals. An enzyme can speed up processes because it lowers the activation energy required for a reaction. Enzymes often take the form of globular proteins and work on substrates. An enzyme often has a bigger size than its substrate. Enzymes break down substrates into products, which are often the little building blocks of the big substrate molecule. 
Proteins that function as biocatalysts are called enzymes and have distinctive three-dimensional structures. Enzymology, the study of enzymes, has lately come to the conclusion that some enzymes lose their capacity for biological catalysis during evolution. Through evolution, enzymes lost their capacity, and this is reflected in their amino acids. More than 5000 biochemical reactions are catalyzed by enzymes, which also function as a catalyst and aid in the regulation of biological processes in living things. Almost all metabolic activities need the catalysis of enzymes within the cell. An enzyme, for instance, could be able to split a big carbohydrate molecule into a bunch of little glucose molecules. The enzyme might be recycled after each reaction because it doesn't change. The fact that enzymes are incredibly selective to their substrates is really intriguing. This implies that there is a particular enzyme for each substrate that won't work on anything else. The lock and key mechanism describes the mechanism of enzyme substrate specificity. The temperature, pH, and enzyme and substrate concentrations are only a few examples of the variables that often affect how quickly an enzyme reacts. To regulate the speed of enzymatic processes, there exist inhibitors. UsesHumans can develop albinism and phenylketonuria, among other diseases, as a result of enzyme deficiency. Additionally, enzymes are used in the brewing of beer, the fermentation of wine, as well as the curdling of cheese. Enzymes are used in medicine for a wide range of purposes, including the treatment of wounds, the destruction of microbial diseases, and gastric juice syrups. 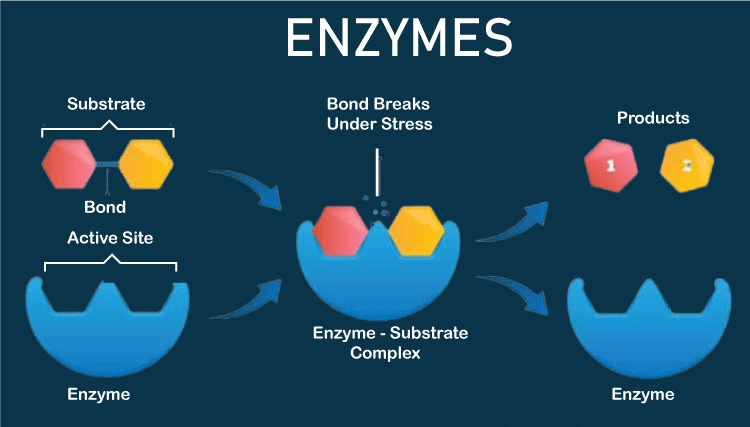
Functions of Enzymes
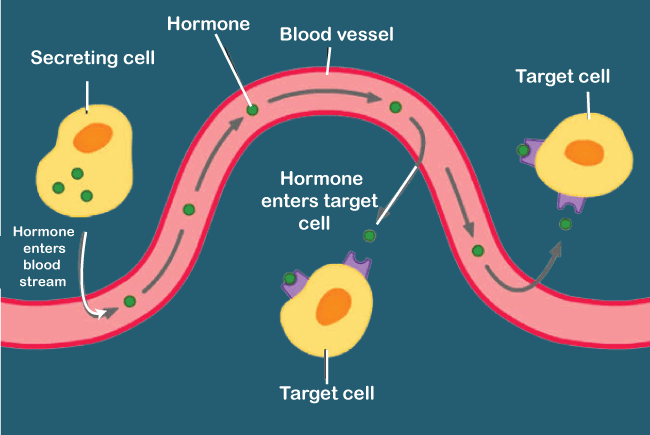
HormoneHormone is a chemical messenger that is used by all multicellular organisms to send messages from one part of the body to another. Typically, the messages are sent through the circulatory systems. The circulatory system receives hormones from glands after which they are released for action at the target place. Hormones come in two categories: endocrine and exocrine, depending on the sort of glands that create them. Exocrine hormones are released into ducts to move by diffusion or circulation, whereas endocrine hormones are delivered directly into the blood stream. It's fascinating to note that just a tiny quantity of the hormone is required to alter a tissue's overall metabolic activity. Hormones are connected to particular receptors so they won't act on cells other than their intended target. Although peptides, lipids, and polyamines are the three categories of hormones based on consistency, proteins make up the majority of them. Due to the fact that multicellular creatures' glands create them, they can be found in them. 
The first is to alter the level of hormones being released between two endocrine glands. Release of a hormone that communicates with the target gland in this case is the endocrine gland's role. Endocrine Gland Includes
The second lies between the target organs and the endocrine gland. The endocrine gland's role in this case is to release a hormone which communicates with the target organ. For instance, the pancreas (an endocrine gland) will produce the hormone insulin to communicate with the target organ and to aid in the uptake of glucose into muscles and fat cells. 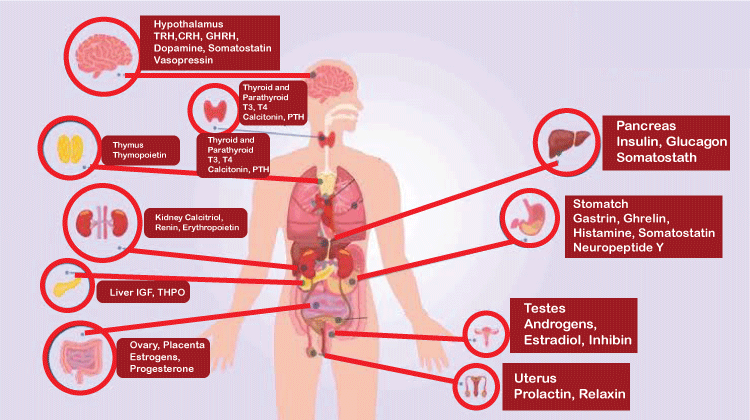
Hormones can function in an excitatory or an inhibitory manner. Hormones have a role in sexual growth and reproduction, the control of body temperature and energy, the growth and development of organs and tissues, and the internal management of water and ion concentration. It serves as a stimulant. Since the function depends on both positive and negative feedback, the primary role is to attack cells or tissues. They aid in morphogenesis control, such as the development of secondary sex traits. The brain, various bodily organs, and certain inhibitor hormones all have a role in controlling hormone levels. They have roles in the regulation of physiology, physical development, and reproduction. UsesHormones are used for a variety of bodily processes, including tissue function, digestion, sleep, metabolic process, stress indicator, respiratory process, excretion, reproductive process, growth and development, and thirst control. Due to the fact that complex creatures' glands produce them, this is found in multicellular species. Functions of Hormones
The Difference Between Hormones and EnzymesThe activity of chemicals is necessary for the human body to be able to regulate, maintain, govern, and direct almost every anatomical and physiological function within the body. Every organ needs hormones and enzymes to work properly. The numerous hormones and enzymes play a crucial role in everything from digestion to sound sleep. 
Enzymes And Hormones in Plants and AnimalsBoth plants and animals generate hormone and enzymes, which are both catalysts for chemical processes. Hormones are microscopic molecules with an additional location of action from their origin. Endocrine glands create and release them, and they travel throughout the body in fluids as blood or sap, carrying chemical messages. Hormones are therefore used by many tissues and organs to communicate. Protein molecules called enzymes catalyze biochemical processes that take place within the body. They are created where the activity takes place. When temperature and pH are unfavorable, enzymes have a tendency to change their structure. The way that each of these substances works inside the body, however, is the key distinction between a hormone and an enzyme. Enzymes are used to cure bacteria and illnesses. Enzymes are proteins in and of themselves, since one protease can be located in enzymes that degrade other proteins. High blood protease levels will help to break down the illness that activates the viruses in our systems. Enzymes aid in weight control, this is one of the most interesting and important things to know about enzymes. Although they are more than just a weight-loss aid, they certainly help with mealtime absorption and the decrease of fat conversion. ConclusionEnzymes and hormones both play important roles in how the body develops and works and are crucial to those processes. Enzymes and hormones play a crucial role in human life and survival, from initiating and digesting a chemical reaction to properly managing and delivering communications.
Next TopicDifference between
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share