Difference Between Oxidation and ReductionIntroductionThe chemical reactions that transfer electrons from one chemical substance to another. These electron-transfer reactions are known as redox reactions or oxidation-reduction reactions. These reactions are followed by energy changes such as heat, light, and electricity, among others. The oxidation and reduction reactions involve the addition of oxygen as well as hydrogen to various substances. OxidationIn chemistry, the oxidation state is also defined as the oxidation number, which is the hypothetical charge of an atom that bonds with other atoms that are completely ionic. It represents an atom's degree of oxidation (electronic loss) in a chemical compound. Positive, negative, or zero oxidation states are all possible in the oxidation state. While no bond is completely ionic, many bonds have a high ionicity where an oxidation state can be used to predict charge. An atom's oxidation state does not accurately represent its charge or any other atomic property. This is certainly relevant at high oxidation states, where the ionization energy needed to produce multiple positive ions is much superior to the energies readily available in chemical reactions. 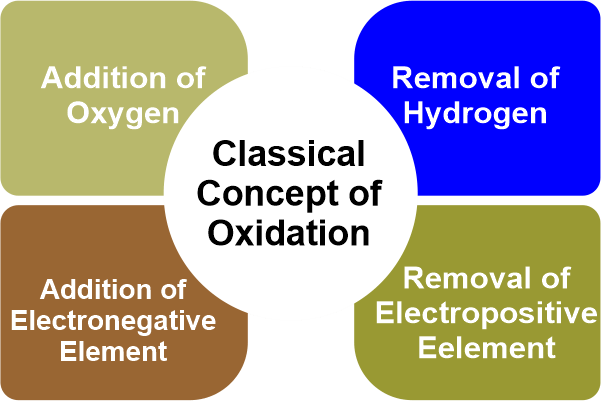
Thus, an atom's oxidation state in a compound is pure formalism. It is still useful for understanding inorganic compound nomenclature conventions. Using oxidation states, several observations regarding chemical reactions can be described at a basic level. The oxidation process at the anode either generates positive ions or eliminates negative ions from the solution (or it may transform one ion to a more positive one). Advanced OxidationAdvanced oxidation procedures are a form of chemical treatment applied to oxidize organic compounds from sewage water that are difficult for biological processes to handle and convert into simply finished goods. These are widely recognized as effective water treatment techniques which can remove a wide range of tough degradation pollutants from water. ReductionReduction is the electron transfer between species in a chemical reaction where an element gains electrons or reduces its oxidation state. During reduction, one of the atoms involved in the reaction between two chemicals gains electrons, which is also a chemical reaction. When iron reacts with oxygen, it reduces oxygen by producing iron oxides such as rust. While the oxygen is being reduced, the iron is being oxidized. This phenomenon is known as redox. A blast furnace changes that reaction by reducing the iron with carbon monoxide as a reducing agent. 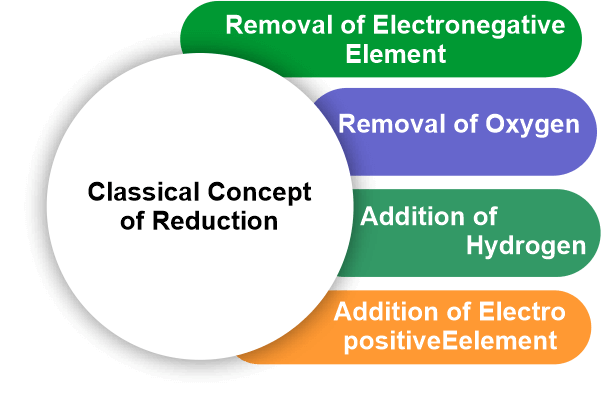
The atom that provides the electrons is thus oxidized. Reduction is a half-reaction process in which a chemical species gains electrons to reduce its oxidation number. The reaction's other half involves oxidation, which outcomes in electron loss. The term "gains" refers to the method by which something is gained. It is the process of removing oxygen from a substance. According to classical or earlier concepts, the reduction is a method that generally necessitates the removal of oxygen or another electronegative element or the addition of hydrogen or another electropositive element. Whenever an atom or ion gains one or more electrons, this is referred to as reduction. Redox ReactionWhen electrons are transferred between two substances, an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction occurs. Any chemical process in which the oxidation number of a molecule, atom, or ion changes as a result of electron gain or loss is described as a redox reaction. The common and necessary redox processes include photosynthesis, respiration, combustion, and corrosion or rusting. Redox reactions are divided into two parts
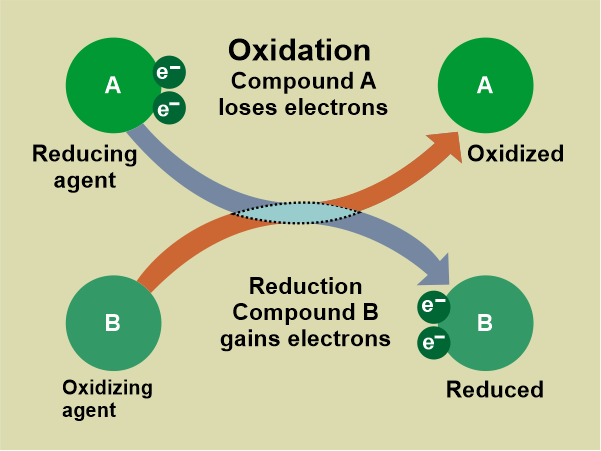
The reduced half gains electrons while the oxidized half loses electrons, causing the oxidation number to rise. The number of electrons does not change during a redox process. In the reduction half-reaction, those gained in the oxidation half-reaction are acquired by another species. The two species that transfer electrons in a redox reaction are given distinctive names
Similarities Between Oxidation and ReductionThe oxidation and reduction reactions are inextricably linked. Because electrons are neither created nor destroyed during a chemical reaction. Oxidation and reduction are mutually exclusive processes since one cannot exist in the absence of the other. Because reduction and oxidation cannot occur independently, they are known as 'Redox Reactions'. 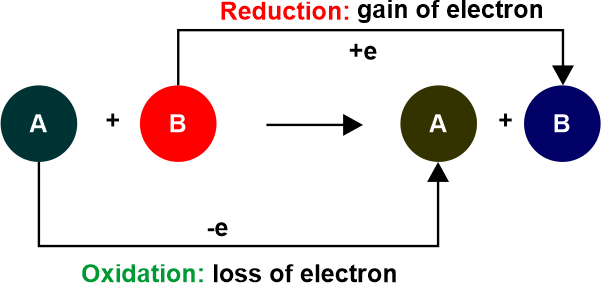
A reducing agent reduces other reactants, whereas an oxidizing agent oxidizes other reactants. This must imply that the oxidizing agent is impacting. Because oxidation is defined as the loss of electrons in difference, an oxidizing agent must gain electrons. Two chemical reactions that frequently occur together are oxidation and reduction. This reaction involves an electron exchange. Redox reactions, also known as reduction-oxidation reactions, occur when reduction and oxidation reactions occur at the same time. These are well-balanced chemical reactions. Difference Between Oxidation and ReductionThese oxidation and reduction reactions are aided by energy changes that take the form of heat, light, and electricity, among other things. The addition of oxygen or hydrogen to various compounds is implicated in both oxidation and reduction reactions. These are some key differences between reduction and oxidation.
Applications of Oxidation and Reduction Reactions
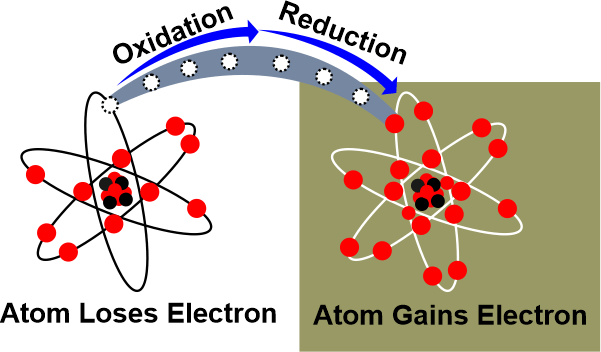
The ConclusionAn atom becomes charged and is defined as an ion when it gains or loses an electron. Because gaining an electron result in a negative charge where the atom is classified as an anion. Because losing an electron result in a positive charge in which an atom ion will be a cation. Ions are generated when atoms exchange electrons. When an atom loses or gains multiple electrons, it loses or gains multiple charges. The atom that is losing electrons is oxidized, whereas the atom that is gaining electrons is reduced. Also, because the species being oxidized can be thought of as causing the reduction, the species being oxidized is known as the reducing agent, while the species being reduced is known as the oxidizing agent.
Next TopicDifference between
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share