Difference Between Reversible and Irreversible ProcessA system's behavior is described in thermodynamics using the phrases reversible and irreversible. It is possible to refer to the process that takes place in this system as either a reversible process or an irreversible process. 
Reversible processes are thermodynamic processes that can be reversed to return to the system's starting state, whereas irreversible processes are thermodynamic processes that cannot be reversed. This is the basic distinction between reversible and irreversible processes. Reversible Process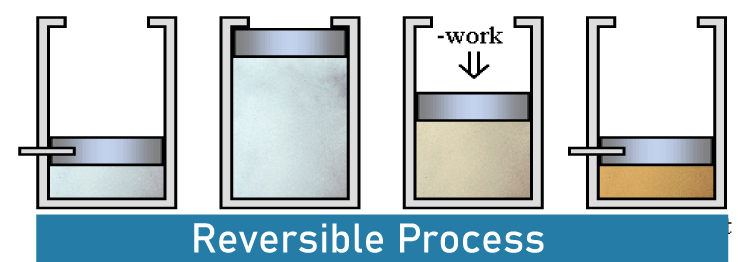
A reversible process is one that can be reversed to restore a system to its starting condition. The original state of a system changes when a certain chemical reaction (process) is finished. In other words, the system is transformed from its original condition to the final one as it goes through a certain process. Reversible processes can be reversed to return to their starting condition. Let's take a look at a system that was modified from state A to state B. A is the system's beginning state, while B is its end state. This procedure is reversible if we can reverse the process that brought about the change. Nonetheless, this process's reversal should result in state A's initial condition, and the environment's attributes should remain unchanged (no change in thermodynamic properties). A reversible process may be fully reversed to return the system to its starting state, which leaves no record that the operation ever took place. A reversible process needs two things to happen. The procedure needs to finish in the smallest amount of time possible. This means that the duration of the procedure will be unpredictable. Achieving equilibrium between the system's initial and end states should be possible. If not, the procedure cannot be reversed. Reversible Processes Examples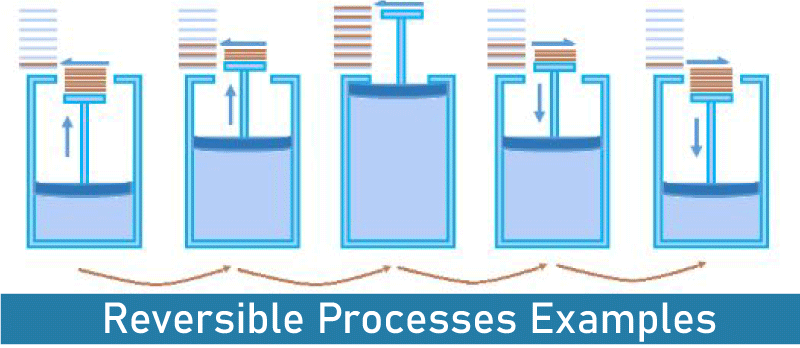
These are a few examples of reversible processes:
Irreversible Process
An irreversible thermodynamic process cannot be reversed to return a system to its starting condition. This means that if a system goes through an irreversible process, it changes to the end state, and we cannot return to the beginning state by reversing the process. As practically all processes in nature are irreversible, these kinds of processes are also known as natural processes. There are no equilibriums in a system with irreversible processes since they require a measured amount of time to complete. The irreversible process alters the system's entropy, and this alteration cannot be undone. A thermodynamic process that deviates from equilibrium is what is known as an irreversible process. Here, finite changes are performed. The movement of heat from a warmer to a colder environment, the flow of water from a high to a low level, the release of a gas into a vacuum system, etc., are some examples of irreversible processes. Irreversible Processes Examples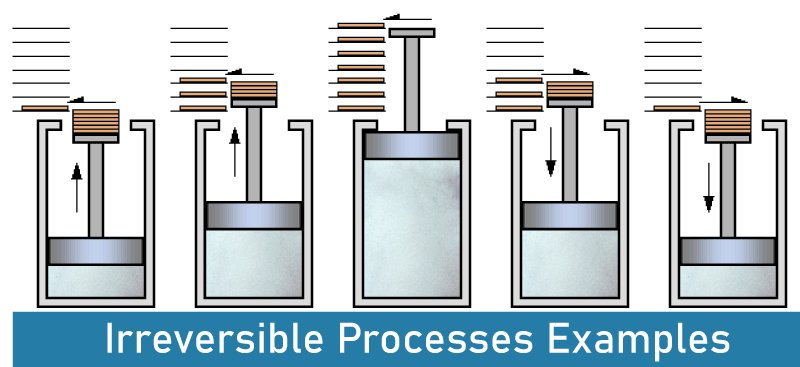
Some examples of irreversible processes include:
The Distinction Between Reversible and Irreversible Process
ConclusionProcesses that can occur in a thermodynamic system include reversible and irreversible ones. Reversible processes are thermodynamic processes that can be reversed to return to the system's starting state, whereas irreversible processes are thermodynamic processes that cannot be reversed. This is the basic distinction between reversible and irreversible processes. Reversible and Irreversible Process: Commonly Asked QuestionsQuestion 1: What are the distinctions between reversible and irreversible processes? Answer: A reversible process can be reversed to return to the system's initial state. In contrast, an irreversible process is a thermodynamic process that cannot be stopped to return to the system's starting state. Reversible processes can be reversed, but irreversible processes cannot. Question 2: Why is a reversible process more effective than an irreversible one? Answer: A reversible process often wastes less heat, which allows the energy generated to perform the most work. Irreversible processes usually produce turbulence and friction, which cause heat to escape into the environment. Question 3: Why are certain reactions reversible while others are not? Answer: Reversible reactions occur when two processes are in equilibrium, i.e., the conversion of reactants into products and the subsequent conversion of products back into reactants. Reversible reactions, on the other hand, are those in which just the reactants change into products. Question 4: Reversible processes can be quick or slow. Answer: Reversible processes move relatively slowly, making the system constantly very close to equilibrium. The system's state may then be shown on a plot of, say, pressure against volume because all its state variables are thus clearly defined and uniform. Question 5: What kinds of changes are irreversible? Answer: Irreversible changes occur when a substance cannot be changed back to its original state. For example, when a piece of wood burns and produces ash. It cannot be turned back into the wood.
Next TopicDifference Between
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










