Difference Between Router and SwitchRouters and switches are both networking devices that are essential components for IT infrastructure. Before we compare these two, let us first get a basic understanding of switches and routers with their benefits and drawbacks. Routers operate at the network layer and determine the shortest path for a packet from across the network. switches connect various network devices. Whereas Routers connect devices on different networks. Router
A router connects two or many packet-switched networks or channels. Its primary functions include managing traffic between networks by directing data packets to their proper IP addresses and allowing multiple devices to have access to the same Internet connection. A LAN is a geographically limited network of operational devices. A LAN typically requires a single router. There are numerous router types, but most of them transfer data among LANs (local area networks) as well as WANs (wide area networks). A wide area network (WAN) is a network which unites multiple locations. Because a WAN covers a large geographic area, it widely necessitates the use of multiple routers and switches. Large organizations and companies with multiple locations across the country will necessitate separate LANs for each position, which will be linked to form a WAN.A network switch transports data packets between divisions of devices connected to the same network, while a router transports data across networks. Features of Routers
OperationWhen multiple routers are present in a network, a routeing protocol can be used to share data about destination addresses. Each router on the network generates a routeing table, or a list of routes, between two computer systems. The router's software is composed of two concurrently running functional processing units known as planes:
A router keeps a routeing table that specifies which route and physical interface connection should be used to forwards a data packet. It accomplishes this with the help of internal pre-configured directives known as static routes, or by learning routes dynamically using a routeing protocol. The routeing table stores both static and dynamic routes. The control-plane logic then removes non-essential directives from the table and creates a forwarding information base (FIB) for use by the forwarding plane.
The forwarding plane is responsible for transporting data packets between the incoming and outgoing interface correlations. It reads the header of each arriving packet, compares the destination to entries in the control plane's FIB, and routes the packet to the FIB-specified outgoing network. Types of RoutersDepending on their intended use routers come in a variety of compositions. Routers are classified into several types which are as follows
An Ethernet cable connects a wireless router to a modem. It broadcasts data wirelessly by generating binary code packets into radio signals. Wireless routers do not build LANs instead, they build WLANs (wireless local area networks), that connect multiple devices via wireless communication.
A wired router is mostly like wireless router which uses an Ethernet cable to connect to a modem. Then using separate cables, it connects to one or more network devices, forming a LAN and engaging those devices to the Internet. In addition to both wired and wireless routers for small LANs many specialized types of routers serve specific function. A core router is used by large organizations and businesses that send large data packets over their network and router can be seen in a small business or home LAN. Core routers operate in the "core" of the network and do not communicate with other networks. A core router only handles data traffic within a large network, whereas an edge router mostly communicates with core routers and other networks.
A virtual router is a software application that performs the same functions as a physical router. If one of the virtual routers fails, the Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) can be used to create primary and backup virtual routers. Advantages of Router
Disadvantages of Routers:
Router Mode of TransmissionRouters are transferred in full-duplex mode by default. Users can, nevertheless, change this to half-duplex mode if they prefer. There are fewer collisions in routers. which degrade network performance. Switch
Switches are networking devices that operate the data link layer of the OSI model at layer two. They connect network devices by using packet switching to send, receive, and forward the data packets or data frames from across networks. A switch has multiple ports to which computers can be connected. When a data frame arrives at a network switch port the port analyses the destination address, performs the required checks and then transmits the frame to the appropriate devices. Features of Switch
How Does a Switch Function?When a device is connected to a switch, the MAC address which is a code embedded in the network interface card (NIC) is stored. An Ethernet cable connects the NIC to the switch. The switch uses the MAC address to determine how each device forwards outgoing packet data and where it should deliver packet data. The MAC address recognises the hardware device and does not include any changes whereas an IP address can be allotted to a device dynamically and over time in the network layer (Layer 3). 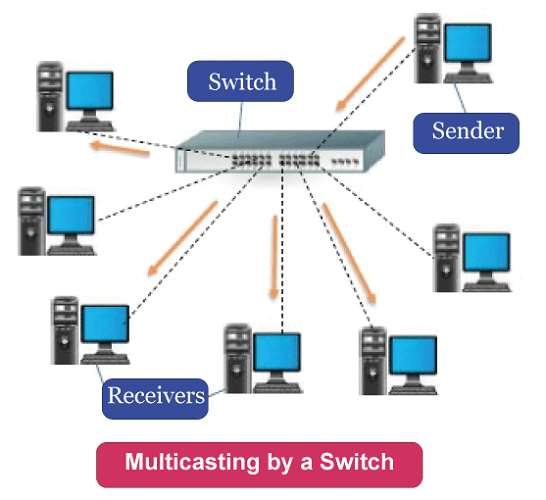
When a packet reaches the switch, it reads the header and compares it to the destination or addresses and then forwards it to the appropriate devices via the appropriate ports. Most switches provide full-duplex functionality allowing packets coming from it and going to a device to use all the bandwidth of the switch connection and to reduce the possibility of colliding between network traffic flowing of a switch and a connected device simultaneously.While switches operate at Layer 2 they can also support virtual LANs (VLANs) that are logical network segments that can span subnets at Layer 3. Types of SwitchesA variety of switches can be divided into four types. 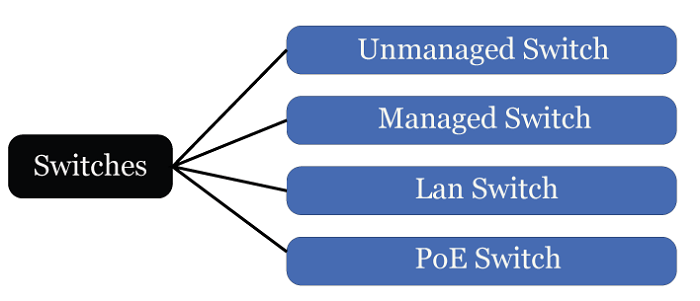
Unmanaged Switches are low-cost switches that are commonly used in home networks as well as small businesses. They can be set up by certainly making a network connection which begins to operate immediately. Additional switches are merely added using this plug- and-play method when many devices are required.
Managed switches are overpriced switches that are used by organisations with massive and complex networks because they can be personalised to perform additional functions which are not provided by a standard switch. QoS (Quality of Service) upgrades such as increased security, improved precision control, and full network management will be included.
Local Area Network (LAN) switches connect devices in an organization's internal LAN. Ethernet switches and data switches are other names for LAN. These switches are especially useful for reducing network congestion or bottlenecks.
Power over Ethernet (PoE) switches PoE Gogabit Ethernets make use of PoE switches to provide power over Ethernet. PoE technology combines power and data transfers over the same cable, permitting devices to receive both power and data. PoE switches increase flexibility and simplify cabling connections. Advantages of Switches:
Disadvantages of Switches
Switch Mode of TransmissionFull duplex as well as half-duplex transmission of data modes are used by network switches. Users can switch to auto-negotiation mode based on their preferences. Switches divide networks and smaller collision domains into larger collision domains. Each device is connected to its switch port in half-duplex mode. As a result, each port transforms into its collision domain. Which implies that in full duplex mode there is one transmitter and one receiver by removing the possibility of a collision. Similarities Between Router and Switch
Both are computer networking devices. Although they serve distinct functions, they are both used to connect devices. A network switch uses packet switching to connect peripherals on a computer by receiving and forwarding data packets to their assigned device. Similarly, a router connects different devices to a single network by routeing data packets between the networks.
Both are thought to be intelligent machines. Network switches are generally thought to be more intelligent than hubs. They are multiport devices that support virtual circuits and thus improve network efficiencies. They keep routeing tables that they can use to determine the IP address of a data packet's route. Furthermore, they can make complex routeing decisions on data packets, albeit at a slower rate than routers. Routers, too, are considered intelligent devices. They can save their routeing tables, which they use to determine the IP address of data packets' destinations. To determine the destination of these packets, they can also make complex routeing decisions faster than network switches.
They both provide modern solutions to network connectivity problems. With increased demand for Internet of Things (IoT) devices like as closed-circuit televisions (CCTV) as well as smart homes, there is a need to improve network speeds to improve user experience. Routers and network switches can both be used to increase network speeds at home, in small offices, and in businesses.
Routers and network switches both are small and have a similar appearance. This makes them portable and usable at the discretion of their owner. They can be used anywhere if they are plugged into a power source. Unlike other networking devices like modems, routers and network switches consume power to function properly.
Routers and network switches both have ports. WAN and LAN connections enable networking devices to establish them. Routers typically contain two types of ports, but users can add more if required. They have hardware ports such as LAN, WAN, USB ports, as well as software ports. Network switches have even more ports and can have up to 52 depending on their primary purpose. They are network bridges with multiple ports. Trunk ports, access ports, and hybrid ports are the three types of ports found in switches. Difference Between Router and Switch
ConclusionRouters are effective for connecting networks that are spread across the multiple locations. Routers store data and send it out via packers. on the other hand, Switches are network devices which route data from multiple input terminals to a single output port. Switches connect multiple network devices, whereas routers connect multiple networks.
Next TopicDifference Between
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










