Difference Between Sigma and Pi BondA chemical bond is a strong force that connects two atoms. Chemical bonds can be of various shapes and sizes. The two most common chemical bonds are sigma bonds and pi bonds. The atomic orbitals of Pi and Sigma Bonds will undergo overlapping, which is the main difference between them. Sigma bonds are much stronger than pi bonds. Both sigma and pi are derived from Greek letters. Both are widely used in molecular orbital theory to predict the outcome of molecules. The shared number of bonds varies with the number of electrons. Based on the type of overlapping, covalent bonds are categorized as sigma bonds or pi bonds. About Covalent BondsIn covalent bonding, sharing electrons between the surrounding atoms results in a stable electronic structure. At least one electron from each atom will be shared by two covalently bonded atoms. When atomic orbitals overlap, covalent bonds will be formed. Electrons move among atoms in a three-dimensional structure of remarkably directed bonds. Covalent bonding can be particularly stiff, resulting in such a material with the properties listed below
Sigma BondIn chemistry, sigma bonds (σ bonds) are perhaps the most basic type of covalent chemical bond. Sigma bonding is best defined for diatomic molecules using the language as well as strategies of symmetry groups. A σ-bond is symmetrical in terms of rotation about the bond axis in this formal approach. According to this concept, the most popular sigma bonds are s+s, pz+pz, s+pz and dz2+dz2 (where z is the internuclear axis). According to quantum theory, identical symmetry molecular orbitals (MO) mix or hybridize. As a result of this diatomic molecule mixing, the wavefunctions s+s & pz+pz molecular orbitals are blended. 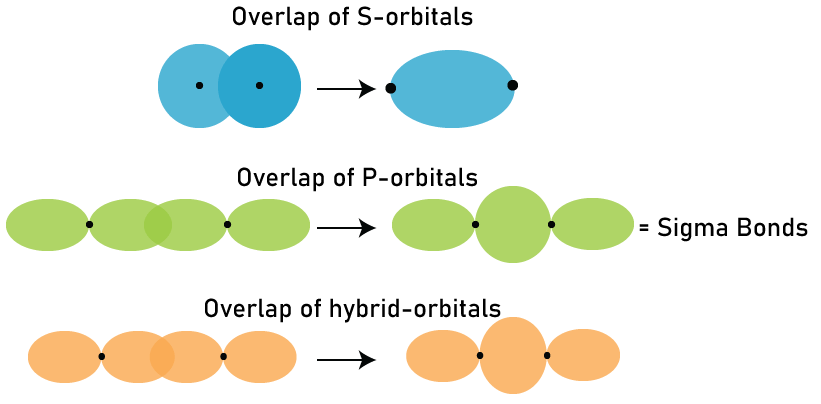
The relative energies of like-symmetry MOs determine the extent of this mixing (or hybridization or blending). Bonding σ orbitals through homo-diatomic (homonuclear diatomic molecules) molecules do not have nodal planes in which the wavefunction is zero between bonded atoms or passing through bonded atoms. The antibonding, or σ* orbital, is described by the presence of one nodal plane in the middle of two bonded atoms. Sigma bonds are most common type of covalent bond due to the direct overlap of orbitals, and the electrons in each of these bonds are described as sigma electrons. The symbol σ is the Greek letter sigma. A σ MO has circular symmetry, like a "s" atomic orbital, when viewed down the bond axis. Although multiple bonds can be formed by merging one sigma bond with pi or any other bond, a sigma bond is a single bond. A double bond is made up of one sigma as well as one pi bond, whereas the triple bond is made up of one sigma as well as two pi bonds 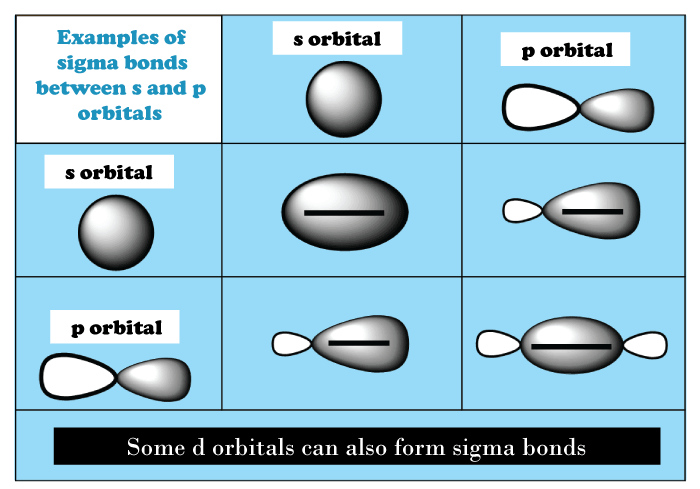
Bonding interactions containing overlapping a single lobe out of one orbital, including a single lobe from another which are included in the definition of sigma bonding. When atomic orbitals collide head-on, sigma bonds will be formed. For example, propane contains ten sigma bonds, one for each of the two C-C bonds and one for each of its eight C-H bonds. In complexes of transition metals to multiple bonds, such as the dihydrogen complex, sigma bonds exist around multiple bonded atoms. Other bonding interactions can be added to these sigma bonds, such as -back contribution, like in W(CO)3(PCy3)2(H2), and even δ-bonds, as in chromium (II) acetate. Organic molecules are frequently cyclic compounds with one or more rings, like benzene, and are composed of numerous sigma and pi bonds. The sigma bond rule states that the total number of atoms plus the number of rings minus one would equal the number of sigma bonds in a molecule. Nσ =Natoms + Nrings − 1 This rule is a subset of the graph's Euler characteristic representing the molecule. A molecule with no rings is represented by a tree that has the same number of bonds as atoms minus one (as in dihydrogen, H2, with only one sigma bond, NH3 or ammonia, with three sigma bonds). Only one sigma bond exists between any two atoms. Advantages of a Sigma Bond
Disadvantages of a Sigma Bond
Pi BondPi bonds (π bonds) are covalent chemical bonds that occur when two lobes of one atom's orbital overlap with all two lobes of another atom's orbital laterally. Each atomic orbital has a zero-electron density in a shared nodal plane that moves through two bonded nuclei. This plane functions as a nodal plane for the pi bond's molecular orbital. Pi bonds can combine to form double and triple bonds but rarely combine to form a single. Pi bonding is a common type of bonding in which p orbitals participate, though d orbitals also can participate. Because the pi bond has the same orbital symmetry as the p orbital when formed down the bond axis, the Greek letter π in their name referred to p orbitals. This latter mode is the foundation for metal-metal multiple bonding. The bond energy of a C-C double bond composed of one sigma and one pi bond is less than twice that of a C-C single bond, implies that the pi bond adds less strength than the sigma bond. 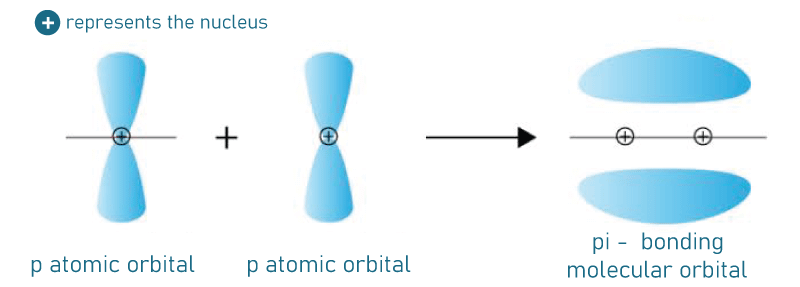
Quantum mechanics explains the bond's weakness as significantly less overlap among component p-orbitals, due to their parallel orientation. Sigma bonds, on the other hand will create bonding orbitals directly between nuclei of relevant bonding atoms ultimately results in overlap and a strong sigma bond. Pi bonds are produced by overlapping atomic orbitals that meet each other through two overlapping areas. Pi bonds are less scattering than sigma bonds. Pi electrons are electrons that can be found in pi bonds. Because rotation requires the destruction of the parallel orientation of a constituent p orbital, molecular fragments connected by a pi bond cannot spin that bond without having broken the pi bond. Bonding molecular orbitals for homonuclear diatomic molecules have only one nodal plane transferred through bonded atoms but no nodal planes among bonded atoms. A third nodal plane between these two different bonded atoms defines the molecular orbital of the antibonding, or π* ("pi-star"). 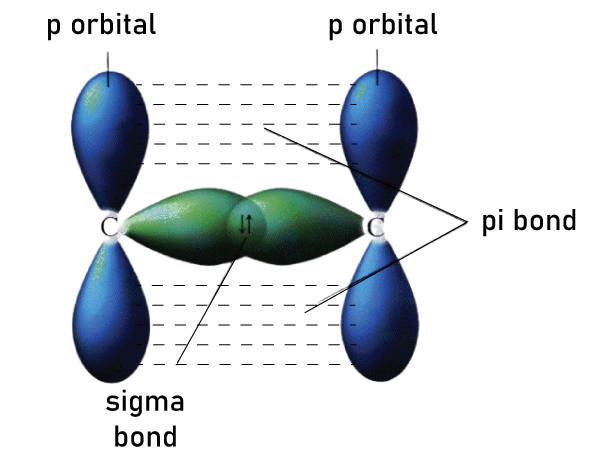
One sigma bond and one pi bond make up a typical double bond, for instance the C=C double bond in ethylene (H2C=CH2). In acetylene (HC=CH), for example, a typical triple bond contains one sigma and two pi bonds in jointly perpendicular planes that usually contain the bond axis. The number of pi bonds that can form between two atoms is limited. Quadruple bonds are exceedingly rare and can only be formed between atoms of transition metals. Each has two pi bonds, one sigma bond, and one delta bond. A pi bond is relatively weak than a sigma bond, but when they are combined, they both outperform. The stabilisation of multiple bonds over a single (sigma bond) manifest itself in a variety of ways, the most visible of which is a contraction in bond lengths. Carbon-carbon bond lengths are estimated to be 154 pm in ethane, 134 pm in ethylene, and 120 pm in acetylene. More bonds reinforce and lengthen the overall bond. 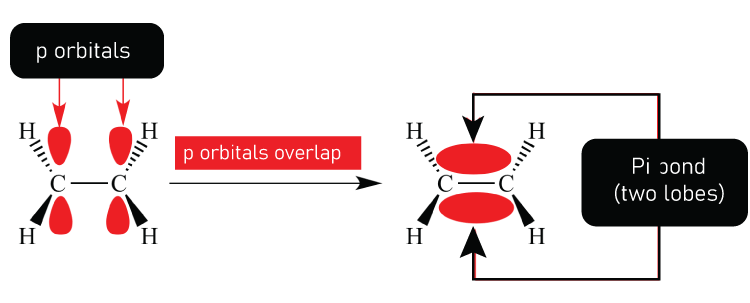
There can be a pi bond between two atoms with no net sigma-bonding consequence on each other. Pi interactions among a metal atom and alkyne and alkene pi antibonding orbitals create pi-bonds in certain metal complexes. In some cases of multiple bonds between two atoms, there is no net sigma-bonding at all, only pi bonds. Some examples include diiron hexacarbonyl (Fe2(CO)6), dicarbon (C2), and diborane (2). (B2H2). Because an anti-sigma bond accompanies the sigma bond, the central bond in such compounds is only pi bonding. These compounds served as computational models for pi bonding analysis, and the bond distances were discovered to be significantly shorter than expected to achieve the maximum orbital overlap. Advantages of the Pi Bond
Disadvantages of Pi Bond
Key Points of Sigma and Pi Bonds
Sigma and Pi Bond StrengthThe extent to which atomic orbitals overlap determines the strength of a bond. The sigma bond, which overlaps along the internuclear axis, is more powerful than the pi bond, which overlaps sideways. Pi bonds have a smaller area of overlap than sigma bonds. Therefore, the pi-bond breaks first, followed by the sigma bond. During multiple bond formation, a pi bond is formed in addition to a sigma bond. A double bond consists of one sigma bond and one pi bond, while a triple bond consists of one and two pi bonds. Sigma and pi bonds can be found in multiple bonds. In multiple bonds including boiling and melting points will influence a molecule's electrical and physical properties. Interpretation of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectra is also aided by multiple bonds. Similarities Between Sigma and Pi BondsWhen distinct molecular orbitals, like the s orbitals in sigma bonds and p orbitals in pi bonds overlap, sigma bonds and pi bonds are formed, and orbitals can be stable or unstable depending on whether electrons are all within bonding or antibonding molecular orbitals. Difference Between Sigma and Pi Bond
ConclusionWhen s orbitals overlapping along the axis that connects the coordinated nuclei form an affiliation among atoms in a molecule a sigma bond is formed. It is the first to form, and its reliability is determined by electron structure in sigma bonding and antibonding orbitals. When the p orbitals of distinctive atoms collide, a molecular connection is formed. Pi bonds have electrons distributed between and above the axis that connects the nuclei of the related atoms but not along it. The bonding and antibonding pi orbitals influence the stability of these connectivity.
Next TopicDifference Between
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










