Linux Output RedirectionOutput redirection is used to put output of one command into a file or into another command. > stdoutThe stdout is redirected with a '>' greater than sign. When shell meets the '>' sign, it will clear the file (as you already know). Example: 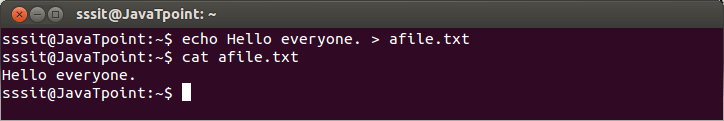
Look at the above snapshot, greater than sign '>' redirects the command 'echo' output into a file 'afile.txt'. Output File Is ErasedIn output redirection, during scanning of a command line, shell will encounter through '>' sign and will clear the file. Example: 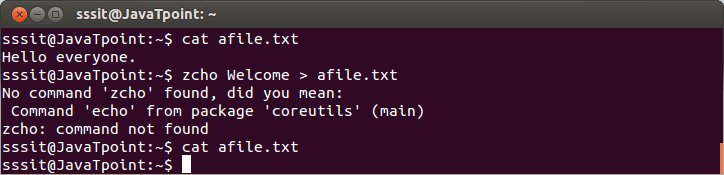
Look at the above snapshot, command "zcho Welcome > afile.txt" is wrong but still file 'afile.txt' is cleared. noclobberWe can prevent file deletion while using '>' sign with the help of noclobber option. Syntax: Example: 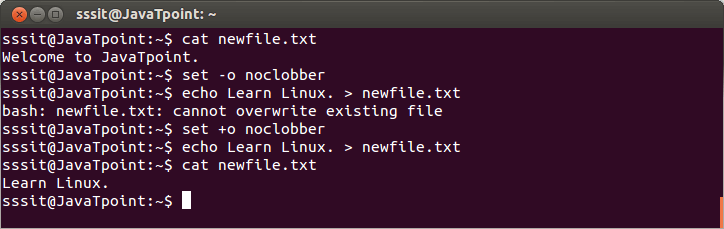
Look at the above snapshot, command "set -o noclobber" prevents file from getting overwrite. But command "set +o noclobber" allows you to overwrite the existing file. Overruling noclobberOverruling noclobber means you can overwrite an existing file while noclobber is set by using '>|' sign. Syntax: Example: 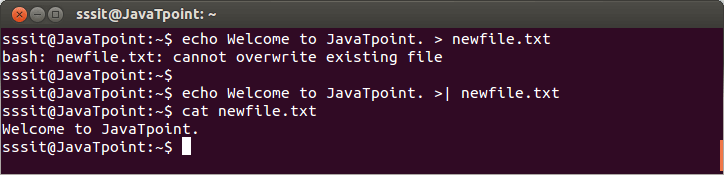
Look at the above snapshot, with greater than '>' sign, bash doesn't allow to overwrite the file 'newfile.txt'. But with '>|' sign file is overwritten. >>appendAppend '>>' sign doesn't let the file content to be overwritten and hence, displays new as well as old file content. Syntax: Example: 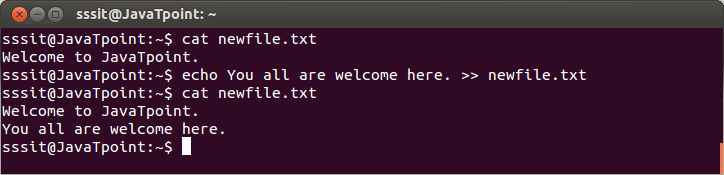
Look at the above snapshot, file 'newfile.txt' is not overwritten with append command. New content is displyed with the old one.
Next TopicLinux Error Redirection
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










