RAID 1
RAID 1 is an abbreviation of the Redundant Array of Independent Disk level 1.
This standard level only uses the concept of disk mirroring, without the help of parity or striping. Due to the mirroring concept, if one drive fails, the second drive is easily used for accessing data, and the drive which fails is replaced. This level requires a minimum of two disks for storing and processing.
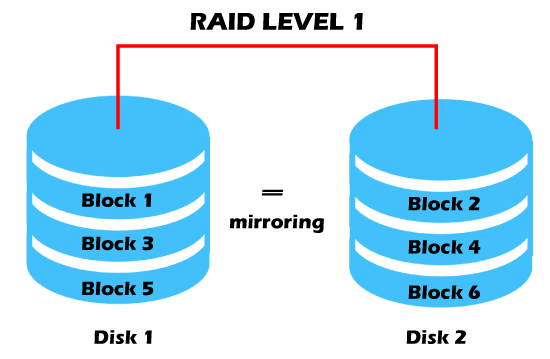
This disk level is a simple way to secure the data and to maintain the speed of 'read' and 'write' operations on drives.
It increases safety by writing the same data on the two disks but minimizes the performance. When the drive is replaced, the RAID controller creates the copy of data of the working disk onto the new disk.
As compared to RAID array 0, the performance of write operation in this RAID level is slower, but the read performance is faster.
Advantages of RAID 1
Following are the advantages or benefits of a Redundant Array of Independent Disk level 1:
- RAID 1 level is a very simple technology.
- The performance of the read operation in this RAID is excellent.
- The data redundancy is excellent at this RAID level.
- The main advantage of this RAID level is that the data can be easily recovered in case of any disk fails.
Disadvantages of RAID 1
Following are the disadvantages or limitations of Redundant Array of Independent Disk level 1:
- The performance of the write is slow.
- In this RAID level, the storage space is wasted because the same data is stored on two disks.
Differences between Raid 1 and Raid 2
Following table shows the comparisons between the RAID level 1 and RAID level 2:
| RAID 1 |
RAID 2 |
| 1. RAID 1 is an abbreviation of the Redundant Array of Independent Disk level 1. |
1. RAID 2 is an abbreviation of the Redundant Array of Independent Disk level 2. |
| 2. Disk Mirroring feature is used in this RAID level. |
2. Bit-level Striping is used in this RAID level. |
| 3. In comparison to RAID 2, this level provides good fault tolerance. |
3. In this RAID level, fault tolerance is not good. |
| 4. This RAID level does not use the Hamming codes. |
4. This level uses the Hamming codes for error correction. |
Differences between Raid 1 and Raid 0
Following table shows the comparisons between the RAID level 1 and RAID level 0:
| RAID 1 |
RAID 0 |
| 1. RAID 1 is an abbreviation of the Redundant Array of Independent Disk level 1. |
1. RAID 0 is an abbreviation of the Redundant Array of Independent Disk level 0. |
| 2. Disk Mirroring feature is used in this RAID level. |
2. Disk stripping feature is used in this RAID level. |
| 3. In this RAID technology, there exists a write penalty |
3. In this RAID technology, no write penalty exists. |
| 4. Its cost is high, i.e., this RAID level is expensive. |
4. Its cost is low. |
| 5. As compared to RAID 0, the performance of the write operation in RAID 1 is slow. |
5. As compared to RAID 1, the performance of the write operation in RAID 0 is good. |
| 6. Mirror protection is present at this RAID level. |
6. There is no protection is present at this RAID level. |
| 7. In RAID 1, storage space is 50% utilized. |
7. In RAID 0, storage space is 100% utilized. |
Differences between Raid 1 and Raid 5
Following table shows the comparisons between the RAID level 1 and RAID level 5:
| RAID 1 |
RAID 5 |
| 1. RAID 1 is an abbreviation of the Redundant Array of Independent Disk level 1. |
1. RAID 5 is an abbreviation of the Redundant Array of Independent Disk level 5. |
| 2. Data Mirroring feature is used in this RAID level. |
2. Data striping with parity feature is used in this RAID level. |
| 3. This RAID level requires a minimum of 2 physical drives. |
3. This RAID level requires a minimum of 3 physical drives. |
| 4. In this standard level, data is not divided in the disks. |
4. In this standard level, due to parity data is split in all the disks. |
| 5. The speed of writing the data in RAID 1 is slower. |
5. While the speed of writing the data in RAID 5 is good. |
| 6. This RAID level supports redundancy and mirroring concepts. |
6. Mirroring and redundancy concepts are not supported by this RAID level. |
| 7. Data security is low. |
7. Data security is very high. |
| 8. It is the best choice for the high level of applications. |
8. It is the best choice, which is used for a medium level of applications. |
| 9. This level requires large space for data mirroring. |
9. There is no need for large space. |
| 10. The rate of accessing the data is low. |
10. The rate of accessing the data is high. |
|

 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now









