What is the full form of HBsAgHBsAg: Hepatitis B Surface AntigenHBsAg stands for Hepatitis B Surface Antigen. It is a term related to health. Hepatitis B Surface Antigen is the hepatitis B virus's (HBV) surface antigen, also known as the Australian antigen. Its presence in the blood indicates the current status of hepatitis B infection in the body. In short, HBsAg is a blood test used to recognize if the patient is infected with the hepatitis B virus. In case it is found along with specific antibodies, then the patient has a hepatitis B infection. Also, it is said that if the blood is positive for HBsAg, then the body fluids or blood of the person can transfer the virus to other people. 
History of the HBsAg Hepatitis B Surface AntigenHepatitis B Surface Antigen was initially located by Baruch S. Blumberg, who is an American research physician and Nobel Prize Winner. It was taken out in one of the Australian Aboriginal person's serums. This was done by virologist Alfred Prince in the year 1968. It was in the 1980s that the first-generation hepatitis B vaccine was prepared, which was named Heptavax. It was created from the HBsAg extracted from the hepatitis patient's blood plasma. Nowadays, these vaccines are designed with the combination of the HBsAg grown in the yeast. What is the structure and function of HBsAg?It has various surface proteins, and the remaining virus acts as antigens. The antibody proteins then recognize the antigens which had explicitly bound to one of the surface proteins. What is Hepatitis B?Hepatitis B is a complex infection in the liver. It is caused by the virus named hepatitis B virus (HBV). In this disease, the risk of liver cancer or liver damage or cirrhosis is highest. Most adult patients recover entirely despite having severe signs and symptoms. A chronic hepatitis B infection is most likely to be developed in infants and children. Although there is no proven cure for this disease, a vaccine can prevent it. The dark colour of urine, fatigue, fever, loss of appetite, nausea, pain in the abdomen, pain in joints, vomiting, weakness, whitening of eyes and yellowish skin are the symptoms of this disease which are visible after 1 to 4 months after infection. 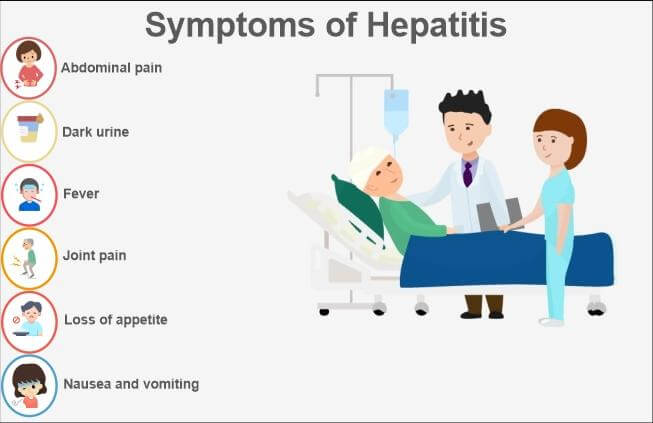
PreventionThe hepatitis B vaccine is a series of three to four injections given within six months. The vaccines are recommended for the following:-
To avoid Hepatitis B VirusCommon ways through which the Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) can spread are as below:
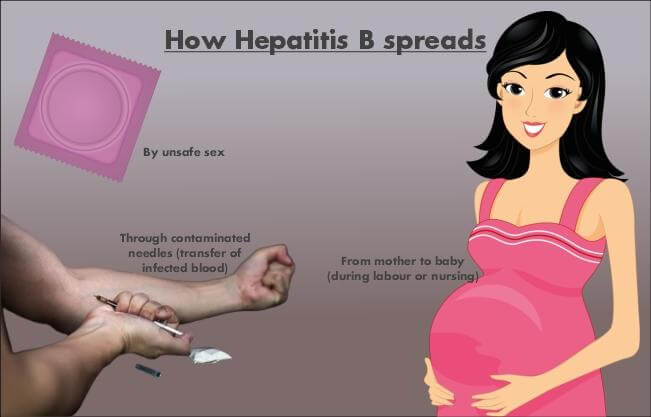
Some ways to reduce your risk of Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) include:
Types of Hepatitis BThe Hepatitis B infection is short-lived (acute), which longs for not more than six months and long-lived (chronic), which longs for a lifetime. In acute Hepatitis B, the immune system recovers and cleans the virus from the body. But if it leads to chronic infection, the immune system cannot clear it out. The risk of getting chronic hepatitis B infection is higher when young, especially for newborns and children under the age of five.
Next TopicFull Form
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










