Advantages and Disadvantages of BioremediationIntroductionWith time, things are changing rapidly, including the environment. In ancient times, the environment was pure and healthy, in which people lived healthier and happier lives compared to now. Multiplication in population has given birth to major problems like pollution (air, noise, water, and land) that contaminate the hydrosphere, biosphere, atmosphere, or lithosphere, due to which earth resides in a hazardous condition. 
Environmental pollution has contaminated our surroundings, due to which anthropogenic activities increased in the past few decades. All cancers, COVID-19, failure of organs, and other breathtaking diseases happen due to environmental pollution. We are developing a way of killing ourselves with developing diseases. We must preserve and keep our environment safe and clean. There are excellent ways humans adopt, like preventive measures for anti-pollution, use of anti-pollutant things, cleaning the environment, etc. With the motive of cleaning, the scientist does deep research and finds a way of cleaning named "bioremediation". "Bioremediation is a combination of two words "bio" and "remediate" that means "living" and "solving a problem" therefore bioremediation refers to a method of solving a problem with use of living organism (microorganism)." 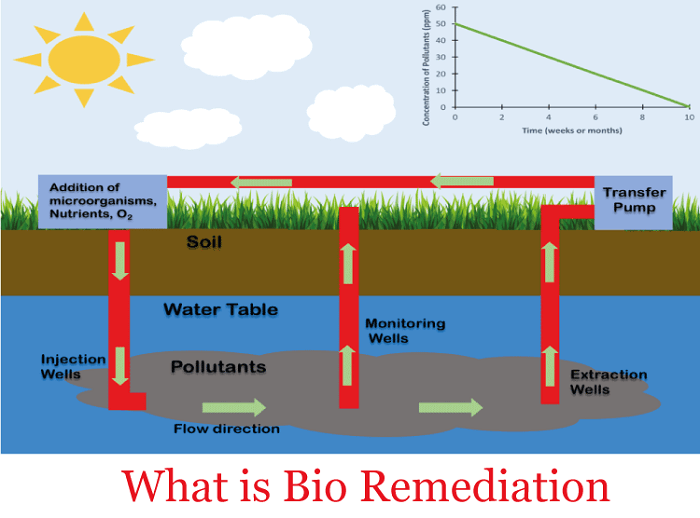
It comes under the biotechnology used to clean the soil, groundwater, and subsurface contaminations with the help of biological organisms. Bioremediation is an eco-friendly cleaning process that treats environmental pollutants like pesticides, oils, solvents, and petroleum products. It helps in the removal of
History:
Working of bioremediation 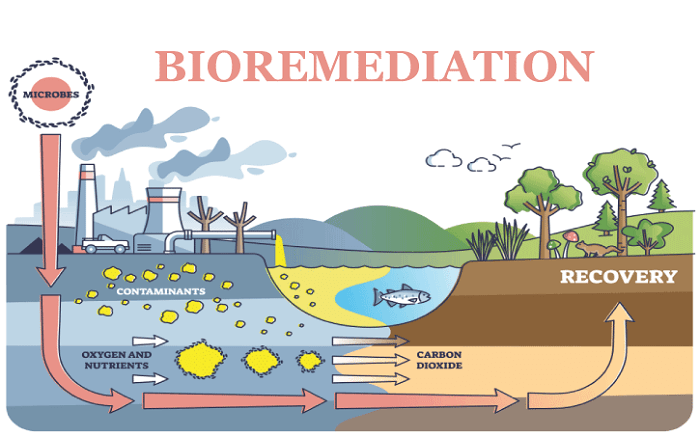
Bioremediation involves the immobilization, degradation, eradication, or detoxification of hazardous biological material and various chemical waste from the surrounding through the all-inclusive action of microorganisms. Bioremediation is of two types based on the removal and transportation of waste of treatment: 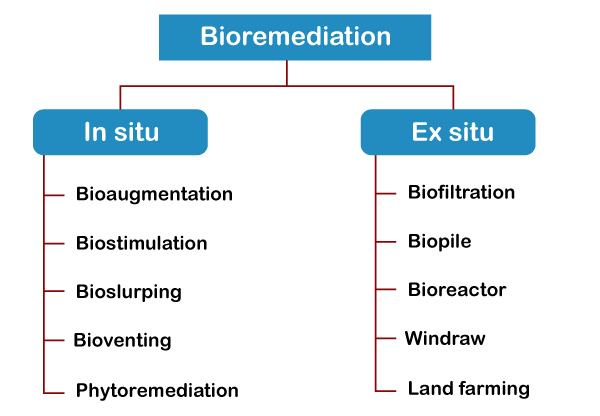
A. In Situ bioremediation (at the site of contamination)
In situ bioremediation is of two types:
Techniques of In-Situ bioremediation
B. Ex Situ bioremediation (away from the site)Ex situ bioremediation is conducted when the climate is too cold to sustain microbe activity or when nutrients are not evenly distributed in the soil due to its density. It excavates and cleans the soil above ground, adding high cost to the process. This process may take several months to several years to complete as it can take anywhere, depending on the size of the contaminated area, temperature, soil density, and concentration of contaminants. Ex situ bioremediation techniques are:
Factors affecting bioremediationThese factors affect the bioremediation process such as:
Advantages of bioremediationa. Beneficial for environment It can remove these contaminants like metals, fluoride, herbicides, insecticides, pathogens, volatile organic compounds, arsenic, nitrate, metals, saltwater intrusion, etc. these contaminants affect the land (soil) and groundwater. The residue of the bioremediation process, such as water, carbon dioxide, and cell biomass, is harmless to the environment. b. A natural process This is a natural process of cleaning nature by eliminating the pollutants and problems related to the processing and storage of pollutants. c. No threat to human The bioremediation process is conducted to eliminate the potentially harmful threat to humans and the environment due to pollutants (that contaminate everything). d. Energy efficiency This process consumes less energy than other refinement methods, including landfilling and incineration. e. Various sites can be used for bioremediation intervention This process can take on many sites to clean the environment contaminated by organic and inorganic compounds. The following are farms, industrial sites, on-site sanitation systems, petroleum stations, landfills, mine site tailings, lumber processing yards, accidental chemical spills, and underground water. f. Fastest approval As bioremediation is a natural, human, and environmentally friendly process, regulatory authorities accept it and hold it in high regard. g. Cheapest way Yes, it is a cheap process as compared to other refinement technologies performed with microorganisms. It can be a small amount of investment. h. less turnaround time Other cleaning methods can take lots of time, but in the bioremediation process, the water and soil are cleaned for reuse faster. i. Minimal equipment requirement Bioremediation uses bio-organisms to eliminate harmful pollutants, requiring minimal equipment. Disadvantages of bioremediationa. Conduct under specific conditions. The bioremediation process operates under specific conditions that may or may not be present in the field where pollutants exist. b. Complete harmless compounds are absent. It is not mandatory that microorganism-treated toxins can be entirely turned into harmless compounds like bacteria that couldn't easily ingest heavy material like lead and cadmium. c. Not suitable for every pollutant It can be conducted on pollutants which can be limited as these pollutants are present in the environment in mixed form with different proportions such as solid, liquid, and gas. Therefore it needs to design specific bioremediation practices suitable for pollutant mixtures in the field. d. Difficult to evaluate The performance of the this process is difficult to evaluate against standardized criteria because this process depends on uncertain factors at the time of implementation. There is no criteria or standard of cleanliness which can guarantee 100% cleanup. Process performance is difficult to evaluate, and bioremediation treatments have no single goal. e. Biodegradable substances are treated only. Bioremediation techniques treat pollutants or contaminants like heavy metals, agrochemicals, pesticides, organic halogens, plastics, and greenhouse gases but can deal with biodegradable substances. f. Harmful new product As we know, hazardous pollutants, including petroleum products, are treated in the bioremediation process. Still, sometimes in biodegradation, a new product is released that can be more harmful to the environment compared with the original component. g. Need advancement in technology. This system is only suitable for sites with pollutants equally dispersed in the environment. Therefore, research is needed to develop and expand bioremediation systems suitable for all sites and pollutants. h. Regularity is uncertain This process is not time bounded, and we can't conclude that upto when we get the result as cleaning is uncertain. It depends on various factors, i.e., heavy metals and hazardous levels of an organic compound, environmental situation, soil nutrients, etc. i. Time-consuming Compared with other refinery methods, it is less time-consuming, but some bioremediation techniques are time-consuming as they depend on microbial action. The bioremediation ex-situ technique treats the contaminants offsite and needs large equipment with other stuff that takes time. j. Show results in a long time. Compared with other refinement methods, this process takes a long time to show results. Conclusion:It is concluded that the advantage and disadvantages of bioremediation help us in using the bioremediation process. Bioremediation helps tailor the needs of polluted sites by using specific microbes to break down the pollutant by selecting the limiting factor needed to promote their growth. This process takes more time to show results than traditional methods, but it has technical and cost advantages. In brief, the bioremediation process is designed to remove and reduce the pollution produced naturally or by humans and to produce clean water, air, a healthy environment, and soil for future generations.
Next TopicAngel Number 666
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










