Characteristics of Electronic CommerceE-commerce, often known as electronic commerce, refers to the online buying and sale of products and services. In 1994, a man sold a Spider CD to a buddy via his online presence Net Market, a platform for American retailers. This is the first instance of an end user purchasing an item from a company via the World Wide Web, which is commonly referred to as e-commerce. Following that, e-commerce developed to make it simpler to find and buy things via online retailers and marketplaces. Technical assets that include managing the supply chain, internet marketing, electronic payment processing, a system for managing information, and a system for inventory control enable e-commerce. Furthermore, online conversations, chatbots, and virtual assistants all aided e-commerce. E-commerce is described as the conduct of trade on an online platform through the use of digital devices like cell phones, laptops, tablets, and the internet. Electronic commerce is a mix of communication services, data management, and security methods that provides enterprises with a platform to communicate information about the sale of products and services: 1. Communication Services The communication services facilitate the electronic movement of information from purchaser to seller. 2. Data Management It is the sharing and storage of data in a consistent format that allows for the simple exchange of information. 3. Security Measures The following functions are provided by security mechanisms:
Electronic Commerce Characteristics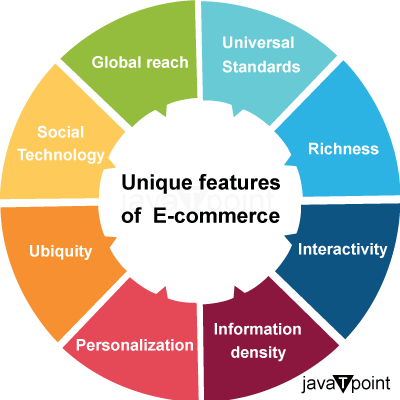
Because it is internet-based, e-business offers several effective methods to do company online. E-business is the practice of conducting business online via the World Wide Web, intranet, the extra net, and web. E-commerce is a subset of online business that is an integral component of the e-business idea. The following are the primary characteristics/features of e-business: UbiquitousOne of the primary features of e-business is its pervasiveness. Because electronic commerce depends on the internet, it can be accessible at any time and from any location. Physical space cannot stop e-business; anybody with an internet connection may simply access the company's sites and online storefronts from anywhere in the globe. 24×7 Service AvailabilityE-business/commerce services are accessible 24 hours a day, seven days a week, and never close. It is not like traditional business, when stores and shops are only open for a short period of time. Customers may use online services at any time, such as seeing goods and services, engaging with vendors, placing orders, and making payments, which are not available in conventional stores. Simple to InstallE-business is simple to get up. There is no requirement for physical location to start an e-business; all you need is a smartphone or laptop and a connection to the web. You may simply establish an electronic business from your home, workplace, or any other location, and it is also less expensive than a traditional firm. Global ImpactTechnology has no bounds and extends across national borders all around the world. Customers from the rest of the globe can readily visit a company that launches an e-commerce website. A company's clients with e-business solutions are equal to the world's whole population. WealthE-commerce has advantages over conventional trade. E-business ways to communicate are many. Customers may learn more regarding the products and services that they wish to buy by reading the content of communications offered by e-businesses such as text, video, image, communication, sounds, links, and so on. No Geographical BoundariesThe conventional business is restricted in its scope and is based in a certain place. However, because e-business having no geographic boundaries, it may readily travel throughout the world from even the most remote corner of the planet. No personalizationIn e-business and e-commerce, there is no human touch. Buyers and sellers can communicate over telecommunications networks, debate commercial transactions, and close transactions. Buyer and Seller have not MetBuyers and sellers in e-business only communicate electronically; they do not physically meet, as in traditional commerce. They communicate over the internet, place purchasing and selling purchases, and the items are delivered via various delivery routes. Density of InformationE-business and e-commerce lower information costs while improving information quality. Customers and other parties involved may quickly obtain product information from websites, blogs, publications, and reviews and compare which is superior. This does not happen in conventional commerce - if it does, it is usually an uncommon situation - merchants routinely update the data about the things they are selling based on the natures, kinds, and status of their clients, but with e-commerce, the product data remains the same. IndividualizationPersonalization is encouraged by e-business and e-commerce. They tailor marketing communications to each consumer depending on his or her previous behaviours, name, hobbies, and purchase history. Every consumer receives a tailored message from e-commerce websites that best matches their previous purchasing actions. Inventory ControlThrough inventory management, e-business boosts company productivity. When needed, the necessary information regarding sales reports, customer information, purchase data, and other reports on transactions is readily available. Payment Methods Other than CashPayments are made in e-business/commerce utilizing credit cards, debit cards, electronic wallets, and various online payment technologies. Delivery requires timeOrdered things take longer to arrive in the world of e-business/commerce. It might be a few hours, days, or minutes. It isn't like traditional commerce, where money results in quick delivery. Customers must wait until the specified time for their things to be delivered. Furthermore, the activities of electronic commerce or online commerce cannot be isolated from computing devices such as smartphones, tablets, or laptops. E-commerce, like the physical world, offers a variety of services and stores or merchants. E-commerce businesses sell everything from books to household goods to kitchen necessities to financial products and digital financial institutions. According to Investopedia, this is a time of technological disruption. E-commerce was established in numerous categories to assist small-scale enterprises such as MSMEs (Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises), or UMKM in our nation, to reach a larger spectrum of consumers. Recently, e-commerce has been regarded as the most feasible centre for shortening the distribution chain. Small manufacturers may access consumers directly through e-commerce, eliminating the need for intermediaries or middlemen. Because e-commerce captures user data, retailers may approach a specific target market. The algorithm may assess the products they often browse for and then propose other goods that are relevant. ExamplesThat being said, starting a business using an e-commerce system is not as straightforward as it appears. Candidates for merchants must conduct study on the products and services that are used. This can aid in determining the target consumers, competition, and profit goals to be met. Based on the study, merchant prospects must begin creating online storefronts. It is strongly advised to set up a virtual shop on the website and to employ a paid advertising strategy as well. For example, the proprietor of a small-scale internet apparel company needs develop a website in order to promote their items online. As a result, the targeted customers are bound to be interested and will make purchases of their items. Electronic Commerce TypesToday, much of the world's commerce is conducted via online platforms that connect individuals and businesses. There are several sorts of e-commerce models in use today. The following are the biggest internet marketing domains:
Advantages of Electronic CommerceReduced Prices The prices of items accessible through websites have been reduced since the many stages of the value chain between the point of origin and destination have been reduced. The firm eliminates middlemen such as retail stores and sells its items straight to consumers rather than through intermediaries. Worldwide Marketplace E-commerce provides a worldwide marketplace where customers may buy things based on their requirements from anywhere in the globe. Anytime Access Online companies are open 24 hours a day, seven days a week, and 365 days a year and never sleep. Consumers may do transactions and inquire about any product/service supplied by the firm at any time and from any location across the world. Consumers may buy anything at any time of day or night by using the internet and a computer with a simple click of the mouse. Additional Purchase Options Online firms provide their customers additional purchase options. Before purchasing any goods, consumers may research all major brands' products and characteristics. Fast Delivery E-commerce provides consumers with more alternatives and faster delivery of items and services. Some e-commerce companies provide free home delivery to its customers. Relevant Information E-commerce offers consumers with relevant and thorough information about items and services in seconds. The consumer may easily compare items and costs. Low Entry Barriers In today's society, both small and large businesses may start and do business over the Internet. Firms' entrance costs to the Internet are miniscule (very low) since they do not require rental space. Because all Internet commerce is virtual, there is no need for a huge number of personnel to do business. Increased Potential Market Share Companies are growing their market share by making their operations internet-ready. International markets are available to online firms at any moment. Low-Cost Advertising Internet advertising is less expensive than advertising in newspapers or on television. In today's world, the Internet has become a low-cost advertising tool utilized by businesses for trade. E-mail, banners, pop-ups, streaming video and audio, and other means of advertising are available. Disadvantages of Electronic CommerceInadequate Security Consumers must have confidence and trust in e-commerce payment providers. Any type of fraud, hacking, or forgery can undermine consumer trust. Low Bandwidth In many countries, the network may cause problems due to a lack of bandwidth. Integration Difficulties It is tough to interface e-commerce software or websites with current programs and databases. In addition to network servers, vendors require customized web servers to cope with integration issues. Not All Customers Have Internet connection Because internet connection is not widely available, most of the work expended does not reach the customer. Many potential clients who live in distant communities do not have access to the Internet. Cost The initial cost of developing an e-commerce website in-house is relatively costly. Hiring trained workers to manage and update an e-commerce website may be expensive. There are additional chances for corporations to outsource online shopping to other e-commerce enterprises. However, determining where and how to outsource is a complex issue. Security and Privacy Security and privacy are key concerns in internet enterprises. Customers are cautious to divulge credit card details over the Internet due to security concerns such as credit card number theft. Consumers will refuse to buy anything over the World Wide Web if they lack trust in the online firm. Lack of Trust and User Resistance Because it is connected to trust, direct contact and written agreements are vital in commercial dealings and transactions. As a result, transferring from traditional to online retailers is challenging for any consumer. Lack of Contact and Feel Before purchasing a thing online, customers might want to have a look at it. Online retailers do not allow customers to touch and feel things such as clothing and shoes. Customer Relationship Issues Organizations require committed consumers to run their online businesses for an extended period of time. In today's competitive environment, online companies cannot survive without devoted clients. Corporate Risk Online firms have easy access to information about their products, prices, catalogs, and other offerings. This information puts websites exposed to competitive access. Online farming is the technique of gathering business intelligence from competitor's online pages. Legal Concerns There is a risk of fraud via the Internet when buyers and sellers do not know one other. As a result, there are several legal issues associated with e-commerce. ConclusionIn conclusion, with the aid of the Internet, e-commerce has created a new environment for commercial transactions and processing. Here, users may get direct information about the things they wish to buy, and the platform is set up for product marketing. It also allows for discussions, raw material orders, financial activities, and so on. |
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










