Chromium BrowserChromium is free and open-source software developed by the Google-sponsored Chromium project. The source code can compile into a web browser. New versions of the code are published daily. Google uses the code to make its Chrome browser, which has more features than Chromium. Many other browsers are also based on Chromium code, mostly Microsoft Edge and Opera. Google and Microsoft add their proprietary code to Chromium that builds services like the browser's automated update mechanism and features such as its tab user experience (UX) to create the actual Chrome and Edge. Chromium's user interface is minimalist. Google required making the browser lightweight (cognitively and physically) and fast. Chromium is an entirely free and open-source software project. The Google-authored portion is released under the 3-clause BSD license. Other parts are subject to various licenses, including MIT, LGPL, Ms-PL, and an MPL/GPL/LGPL tri-license. A four-part version number identifies chromium releases, e.g., 47.0.2491.0 (Chromium 47 initial release 23 August 2015). The components are major.minor.build.patch.
A Major.minor branch point schedule is published. Branch points occur roughly every six to seven weeks. The published dates are the last branch date of each Chromium (Major) release and are tied to the Google Chrome development cycle. They lag the initial Chromium release by about 40 days and precede the next by about 2. How does Chromium Differ from Chrome?Here are the following differences that make Chromium differ from Chrome, such as:
How to Download Chromium?Chromium is the basis for many of today's most popular browsers, including Google Chrome, Opera, and Microsoft Edge's latest iteration. Chromium is an ongoing open-source project that can freely be used by other developers wishing to make their browsers over the top of it, and you can use the base version of Chromium yourself, too. You will not find an official Chromium browser download page. Instead, to install Chromium, visit the web page where developers post the latest hourly builds, or code updates, of Chromium for download. Chromium used to be a bit tricky to install on Windows but is now a lot simpler than it used to be. To install Chromium on Windows, follow the following steps: Step 1: Click on the following link to install the latest version of Chromium for Windows, https://commondatastorage.googleapis.com/chromium-browser-snapshots/Win_x64/871221/chrome-win.zip Step 2: After completing the downloading open the folder. Step 3: Click on the Extract all button to extract all files. 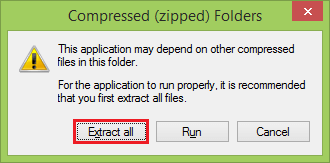
Step 4: After extracting the files, double click on the file to open it. 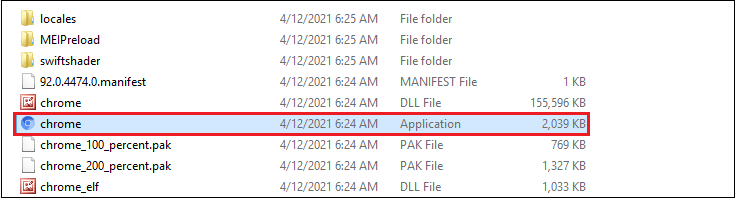
Step 5: Your computer prompts you to confirm that you would like to open a program from an unverified publisher. Step 6: Then, click on the Run button. 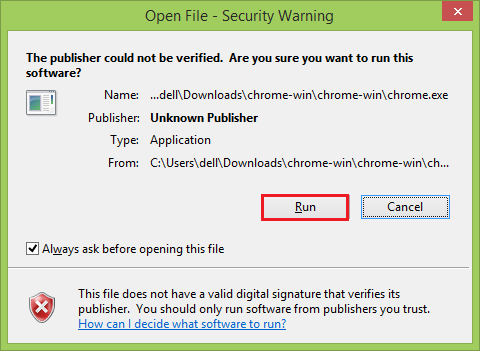
The Chromium browser should startup. You should also find shortcuts to the program on your desktop and under the Start Menu in the Windows taskbar. Chromium SnapshotsChromium snapshots are built several times a day automatically by Buildbot Buildworkers and made available as binary code releases. Once a snapshot has been built, it is placed in a directory in the chromium-browser-snapshots root directory, and it is automatically tested. If the snapshot passes the automated testing, it is placed in a directory in the chromium-browser-continuous root directory. Chromium builds can be downloaded for most Linux distributions and BSD operating systems from their respective software repositories. Chromium builds for Windows and Mac can be downloaded directly. Unlike Chrome releases, Chromium releases do not automatically update. Chromium as ToolkitChromium as a toolkit is also commonly used. Still, without Google's acceptance of a stable ABI or API upstream, every project using it as a tool maintains a fork of Chromium with an API wrapper. Many of the browsers listed previously are based on these forks rather than the upstream project directly. However, all actively maintained forks rebase frequently onto the main branch, avoiding them forking off to being completely separate projects over time. An active toolkit fork includes the following:
Next TopicWhat is ProtonVPN
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









