Cloud MigrationCloud migration is the procedure of transferring applications, data, and other types of business components to any cloud computing platform. There are several parts of cloud migration an organization can perform. The most used model is the applications and data transfer through an on-premises and local data center to any public cloud. But, a cloud migration can also entail transferring applications and data from a single cloud environment or facilitate them to another- a model called cloud-to-cloud migration. The other type of cloud migration is reverse cloud migration, cloud exit, and cloud repatriation where applications or data are transferred and back to the local data center. Pros of Cloud MigrationOrganizations migrate to a cloud for various reasons, but, normally when faced with many challenges of developing IT infrastructure within the most secure and cost-effective way possible. Some of the advantages of migrating to a cloud are as follows: 
Cloud Migration Strategies TypesMigrating to a cloud can be a good investment for our business. We might be admiring where to start like several companies. 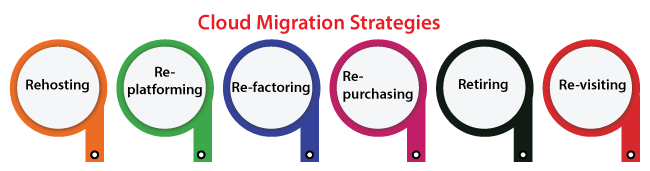
1. Rehosting (lift-and-shift)The most general path is rehosting (or lift-and-shift), which implements as it sounds. It holds our application and then drops it into our new hosting platform without changing the architecture and code of the app. Also, it is a general way for enterprises unfamiliar with cloud computing, who profit from the deployment speed without having to waste money or time on planning for enlargement. Besides, by migrating our existing infrastructure, we are applying a cloud just like other data centers. It pays for making good use of various cloud services present for a few enterprises. For example, adding scalable functions to our application to develop the experience for an improving segment of many users. 2. Re-platformingRe-platforming is called "lift-tinker-and-shift". It includes making some cloud optimizations without modifying our app's core architecture. It is the better strategy for enterprises that are not ready for configuration and expansion, or those enterprises that wish to improve trust inside the cloud. 3. Re-factoringIt means to rebuild our applications from leverage to scratch cloud-native abilities. We could not perform serverless computing or auto-scaling. A potential disadvantage is vendor lock-in as we are re-creating on the cloud infrastructure. It is the most expensive and time-consuming route as we may expect. But, it is also future-proof for enterprises that wish to take benefit from more standard cloud features. 4. Re-purchasingIt means replacing our existing applications along with a new SaaS-based and cloud-native platform (such as a homegrown CRM using Salesforce). The complexity is losing the existing training and code's familiarity with our team over a new platform. However, the profit is ignoring the cost of the development. Re-purchasing is the most cost-effective process if moving through a highly personalized legacy landscape and minimizing the apps and service number we have to handle. Once we have accessed the nature and size of our application portfolio, we may detect cloud migration is not correct for us. 5. RetiringWhen we don't find an application useful and then simply turn off these applications. The consequencing savings may boost our business situation for application migration if we are accessible for making the move. 6. Re-visitingRe-visiting may be all or some of our applications must reside in the house. For example, applications that have unique sensitivity or handle internal processes to an enterprise. Don't be scared for revisiting cloud computing at any later date. We must migrate only what makes effects to the business. Process of Cloud MigrationThe way we consider the strategies of cloud migration as mentioned above depends on migration goals, the complexity, size of our current environment, and our business model. At this time, we will want to trust our IT team's expertise to understand the various outs and in of our environment. 1. Plan our migrationCloud migration needs a solid planning strategy to be successful. Get clear over our reasons for the transfer and which of the migration strategy best helps them before getting begun. Here is where we might apply cloud migration resources and tools for supporting our migration plan by:
2. Select our cloud environmentWe are ready to select any cloud provider that matches our requirements after evaluating our latest application resource needs. 3. Migrate our data and appsWe have three options for moving a local data center to a public cloud such as online transfer with either private network or public internet, or an offline transfer (offline). Here, we upload data on an appliance for shipping to any cloud provider. One of the best approaches relies on the type and amount of data we are speed and moving on which to implement it. 4. Certify post-move successOur work is not complete until we can show any return over investment in our migration. Cloud Migration ToolsThird-party vendors and cloud providers facilitate a lot of automated, cloud-based, and open-source services and tools designed to:
Let's discuss some essentials. 1. APM (Application Performance Management)Bear in mind that during cloud vendors offer access to the metric's rich set for acknowledging modifications in our cloud environment. Usually, these metrics aren't in the overall application context. We will need an isolated monitoring solution for the visibility level. We can create real-time correlations among end-user experience, application performance, and cloud service utilization with a solution that includes AppDynamics APM. 2. Unified MonitoringIt is an emerging ability that gives full visibility into our whole application supporting components, infrastructure, database, application, end-user, and ecosystem. These are running in the cloud and on-premises. We can easily find the issues of cloud migration that will usually cause war-room calls. We have to be ensured for selecting tools that incorporate our platforms and operating systems. The capabilities of cloud migration we require down the line may even resolve which cloud provider we opt for today. 3. Business Intelligence MonitoringIt is a kind of tool we will need to verify cloud migration profits. Check for a tool same as AppDynamics Business iQ, that can compare post and pre-move performance baselines through a business and technical perspective. Accordingly, optimize enterprise performance simulates the experience of the user during all the phases of our migration project, and track enterprise transactions for revealing the true effect on our bottom line. Cloud Migration ChallengesWe can't use the strategies of the cloud without accurate planning. Some of the common pitfalls are discussed below: 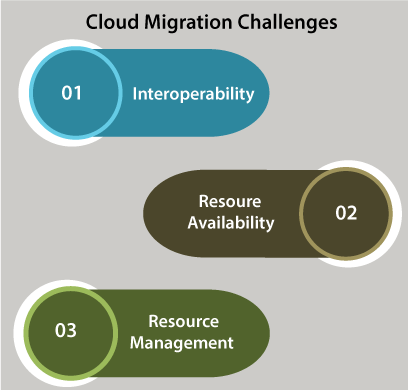
The more complex or larger our latest infrastructure, the stronger these challenges are for overcoming. That is why out IT team must hold on to this appealing transformation armed using services of cloud migration that could mitigate these issues including openness to modification, room for development, and a sound strategy.
Next TopicTypes of Bank Accounts
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










