Java NIO BuffersBuffers are defined inside java.nio package. It defines the core functionality which is common to all buffers: limit, capacity and current position. Java NIO buffers are used for interacting with NIO channels. It is the block of memory into which we can write data, which we can later be read again. The memory block is wrapped with a NIO buffer object, which provides easier methods to work with the memory block. Types of BufferFor every primitive type there is a buffer type and all buffer classes can implement the buffer interface. The mostly used buffer type is ByteBuffer. In Java NIO the core Buffer used are given below:
The above buffer's cover the basic data types that we can send via I/O: characters, double, int, long, byte, short and float. In NIO the data transfer take place by using the buffers implemented in java.nio.Buffer class. It is similar to array, and having a fixed capacity. 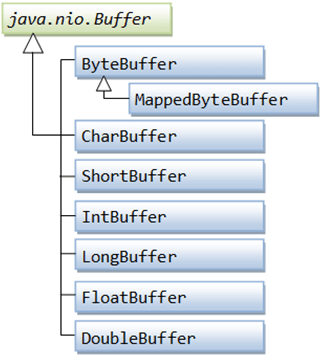
Allocating a BufferFor obtaining a buffer object we must first allocate a buffer. In every Buffer class an allocate() method is for allocating a buffer. Let's see the example showing the allocation of ByteBuffer, with capacity of 28 bytes: Let's see the example showing the allocation of CharBuffer, with space for 2048 characters: Reading Data from a BufferThere are two methods for reading the data from a Buffer:
Let's see the example that read the data from Buffer using get() method: Let's see the example that read the data from Buffer into a channel: Writing Data to a BufferThere are two methods for writing the data into a Buffer:
Basic Buffer ExampleLet's see the simple example of reading the line from testout.txt file using the BufferedReader: Output: The above program read the first line of testout.txt file and then prints the first line of file on a console.
Next TopicScatter/Gather or Vectored I/O
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










